A new view of galaxy evolution
... at near the speed of light, such as a neutrino, A primary method is through examining then the first structures in the universe would the structures of galaxies and how they have be large. These large structures would then con- evolved through time. As mentioned above, dense to form smaller systems ...
... at near the speed of light, such as a neutrino, A primary method is through examining then the first structures in the universe would the structures of galaxies and how they have be large. These large structures would then con- evolved through time. As mentioned above, dense to form smaller systems ...
The size of AB Doradus A from VLTI/AMBER interferometry⋆
... contains 5 exposures of the target (AB Dor A) or calibrator (see below) and two additional exposures for dark and flat correction, each exposure having 200 frames, each recorded with a DIT of 50 milliseconds. Target and calibrator were observed alternatively. To ensure a proper amplitude calibration ...
... contains 5 exposures of the target (AB Dor A) or calibrator (see below) and two additional exposures for dark and flat correction, each exposure having 200 frames, each recorded with a DIT of 50 milliseconds. Target and calibrator were observed alternatively. To ensure a proper amplitude calibration ...
Silicon isotopic abundance toward evolved stars and its application
... stars were born and the different ratios are the results of different ages, which mainly depend on their masses and metallicities. The other possibility is that the stellar evolution can significantly change the silicon isotope ratios. The first possibility implies that the 29 Si/30 Si ratio in the IS ...
... stars were born and the different ratios are the results of different ages, which mainly depend on their masses and metallicities. The other possibility is that the stellar evolution can significantly change the silicon isotope ratios. The first possibility implies that the 29 Si/30 Si ratio in the IS ...
Astronomy Astrophysics Gaia-ESO Survey: The analysis of high-resolution The
... 2006) photometry (point sources with quality flags “AAA”). A box is defined in a color-magnitude diagram with limits 12 < J < 14 and 0.23 < (J − K) < 0.45 + 0.5 × E(B − V). The Schlegel et al. (1998) maps are used to determine the extinction E(B − V). The targets selected before April 2012 had a bri ...
... 2006) photometry (point sources with quality flags “AAA”). A box is defined in a color-magnitude diagram with limits 12 < J < 14 and 0.23 < (J − K) < 0.45 + 0.5 × E(B − V). The Schlegel et al. (1998) maps are used to determine the extinction E(B − V). The targets selected before April 2012 had a bri ...
IRAM Annual Report 2014
... of the COMs along the jet, and hence that COM emission is not arising from shocked envelope material at the base of the jet. Down to similar sizes, the dust emission is well reproduced with a single power-law envelope model, and thus does not favor the hypothesis that COM emission arises from the th ...
... of the COMs along the jet, and hence that COM emission is not arising from shocked envelope material at the base of the jet. Down to similar sizes, the dust emission is well reproduced with a single power-law envelope model, and thus does not favor the hypothesis that COM emission arises from the th ...
Star Formation in the Milky Way and Nearby Galaxies Further
... star formation on all scales, thanks in no small part to new facilities such as the Galaxy Evolution Explorer (GALEX), the Spitzer Space Telescope, and the Herschel Space Observatory; the introduction of powerful new instruments on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST); and a host of ground-based optical ...
... star formation on all scales, thanks in no small part to new facilities such as the Galaxy Evolution Explorer (GALEX), the Spitzer Space Telescope, and the Herschel Space Observatory; the introduction of powerful new instruments on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST); and a host of ground-based optical ...
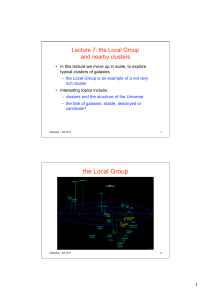
the Local Group - Simon P Driver
... – for example, the Sagittarius dSph is only 15 kpc from the centre of the Milky Way – the MW rotation curve shows that ~1011 Msolar lies within this radius – the Sgr galaxy would need 1010 Msolar to retain its own stars, but has a luminosity of only 107 Lsolar – this means it will lose its stars ...
... – for example, the Sagittarius dSph is only 15 kpc from the centre of the Milky Way – the MW rotation curve shows that ~1011 Msolar lies within this radius – the Sgr galaxy would need 1010 Msolar to retain its own stars, but has a luminosity of only 107 Lsolar – this means it will lose its stars ...
The Star of Bethlehem
... The philologist would surely notice that the majority of attempts at an astronomical explanation do not take statements in Matthew into account. Some even contradict them blatantly. Some are no more than speculations and, at best, the text is only considered when it serves their particular point of ...
... The philologist would surely notice that the majority of attempts at an astronomical explanation do not take statements in Matthew into account. Some even contradict them blatantly. Some are no more than speculations and, at best, the text is only considered when it serves their particular point of ...
Formation of Molecular Clouds and Global Conditions for Star
... 2009; Juneau et al. 2009; Garcı́a-Burillo et al. 2012) also show power-law correlations but with smaller indices; the index appears to depend mostly on the line critical density, a result that can be explained through models (Krumholz and Thompson 2007; Narayanan et al. 2008b,a). Within galaxies the ...
... 2009; Juneau et al. 2009; Garcı́a-Burillo et al. 2012) also show power-law correlations but with smaller indices; the index appears to depend mostly on the line critical density, a result that can be explained through models (Krumholz and Thompson 2007; Narayanan et al. 2008b,a). Within galaxies the ...
GEK 1506 Heavenly Mathematics: Cultural Astronomy
... the direction of the sun by the shadow cast by the sunset. gnomon on the sundial. Sundials were made not only for timekeeping also as votive offerings placed in temples. The sundial separates the day-night period into 24 equal hours. However, the length of each day actually varies due to the seasona ...
... the direction of the sun by the shadow cast by the sunset. gnomon on the sundial. Sundials were made not only for timekeeping also as votive offerings placed in temples. The sundial separates the day-night period into 24 equal hours. However, the length of each day actually varies due to the seasona ...
Clusters as laboratories for the study of galaxy evolution
... merging, it took place at higher redshifts (z >> 1 ) than is predicted by current semianalytical models.” p.s. van Dokkum and Stanford, 2003 ApJ, 585, 78, have measured velocity “…bright endfor of the was already in dispersions 3 ofLF the bright galaxies in this cluster, which confirm the large mass ...
... merging, it took place at higher redshifts (z >> 1 ) than is predicted by current semianalytical models.” p.s. van Dokkum and Stanford, 2003 ApJ, 585, 78, have measured velocity “…bright endfor of the was already in dispersions 3 ofLF the bright galaxies in this cluster, which confirm the large mass ...
Local Group Encyclopedia of Astronomy & Astrophysics eaa.iop.org Mario L Mateo
... Local Group remain particularly important to astronomers because their proximity allows us to obtain our most detailed views of the properties of normal galaxies beyond our own. These nearby systems also provide our clearest views of how galaxies interact with one another in the relatively small vol ...
... Local Group remain particularly important to astronomers because their proximity allows us to obtain our most detailed views of the properties of normal galaxies beyond our own. These nearby systems also provide our clearest views of how galaxies interact with one another in the relatively small vol ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.