A Detailed Derivation of the Radial Velocity Equation
... Of the over 300 extrasolar planets discovered to date, the vast majority have been found using the RADIAL VELOCITY METHOD (also known as DOPPLER SPECTROSCOPY or the DOPPLER METHOD). The purpose of this paper is to derive the theoretical equation that is asso ...
... Of the over 300 extrasolar planets discovered to date, the vast majority have been found using the RADIAL VELOCITY METHOD (also known as DOPPLER SPECTROSCOPY or the DOPPLER METHOD). The purpose of this paper is to derive the theoretical equation that is asso ...
EXPLORING FUNDAMENTAL PHYSICS WITH NEUTRON STARS
... visible range, except for a large transparency window in the radio frequency range, a fact which made the early discovery of (radio-)pulsars possible. Nowadays, thanks to the existing fleet of space telescopes, pulsars are observed in all the different bands of the electromagnetic spectrum and their ...
... visible range, except for a large transparency window in the radio frequency range, a fact which made the early discovery of (radio-)pulsars possible. Nowadays, thanks to the existing fleet of space telescopes, pulsars are observed in all the different bands of the electromagnetic spectrum and their ...
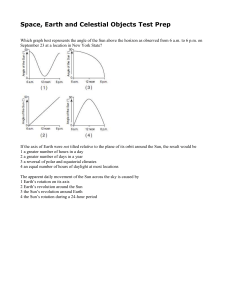
Space, Earth and Celestial Objects Test Prep
... and Jupiter, in a vast ring known as the Asteroid Belt. Occasionally, though, an asteroid leaves this orbit belt and moves into a more eccentric orbit that brings it into the inner solar system. This sudden change may be caused by an impact with another asteroid or by the gravitational pull of Jupit ...
... and Jupiter, in a vast ring known as the Asteroid Belt. Occasionally, though, an asteroid leaves this orbit belt and moves into a more eccentric orbit that brings it into the inner solar system. This sudden change may be caused by an impact with another asteroid or by the gravitational pull of Jupit ...
Cygnus X-2, super-Eddington mass transfer, and pulsar binaries
... We consider the unusual evolutionary state of the secondary star in Cygnus X-2. Spectroscopic data give a low mass (M 2 . 0:5 2 0:7 M( ) and yet a large radius (R2 . 7 R( ) and high luminosity (L2 . 150 L( ). We show that this star closely resembles a remnant of early massive Case B evolution, durin ...
... We consider the unusual evolutionary state of the secondary star in Cygnus X-2. Spectroscopic data give a low mass (M 2 . 0:5 2 0:7 M( ) and yet a large radius (R2 . 7 R( ) and high luminosity (L2 . 150 L( ). We show that this star closely resembles a remnant of early massive Case B evolution, durin ...
Survey of Astrophysics A110 The Milky Way Galaxy
... where new stars will form. The rotation of the galaxy, which can be observed by studying stellar proper motions and Doppler shifts, then orders these concentrations of stars into a spiral-like pattern. – 2. The density wave theory of spiral structure predicts that the rotation and gravity of the mas ...
... where new stars will form. The rotation of the galaxy, which can be observed by studying stellar proper motions and Doppler shifts, then orders these concentrations of stars into a spiral-like pattern. – 2. The density wave theory of spiral structure predicts that the rotation and gravity of the mas ...
MASTER PRACTITIONER`S COURSE IN FENG SHUI
... From the preceding story, anyone reading this must realize that updating your feng shui each year using the annual chart is not only important, it is a crucial part of practicing feng shui successfully, especially to protect your home against the annual afflictions and to overcome them with feng shu ...
... From the preceding story, anyone reading this must realize that updating your feng shui each year using the annual chart is not only important, it is a crucial part of practicing feng shui successfully, especially to protect your home against the annual afflictions and to overcome them with feng shu ...
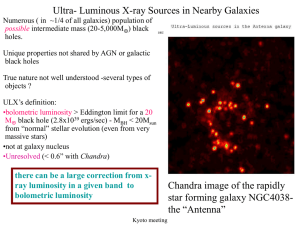
ULXs: General Properties and Variability - X
... •X-ray time variability on long (years) to short (seconds) time scales •Luminosity functions •Correlations with galaxy properties ...
... •X-ray time variability on long (years) to short (seconds) time scales •Luminosity functions •Correlations with galaxy properties ...
{2.} and {4.}
... through the slot place a grease mark at the DEC. and the body name. Planets wander among the stars, but this position can be used for about one week. Stars can be permanently added in the same manner using SHA as GHA and DEC. Greater than 30 degrees (out side of the slot) use the other side DEC 180 ...
... through the slot place a grease mark at the DEC. and the body name. Planets wander among the stars, but this position can be used for about one week. Stars can be permanently added in the same manner using SHA as GHA and DEC. Greater than 30 degrees (out side of the slot) use the other side DEC 180 ...
Night Sky II - Cornell Astronomy
... Each night a given object will pass over the meridian 4 minutes earlier. This corresponds to 2 hours earlier each month, or 24 hours in one year. Objects rise and set earlier each day. At a given time, the RA crossing the meridian increases by 4 min. per day. ...
... Each night a given object will pass over the meridian 4 minutes earlier. This corresponds to 2 hours earlier each month, or 24 hours in one year. Objects rise and set earlier each day. At a given time, the RA crossing the meridian increases by 4 min. per day. ...
Kidd_Thesis_2015April14_Final.
... Henrietta Leavitt who, while plotting and examining the stars’ light curves, discovered there is a relationship between their period and luminosity. Brighter mean magnitude stars have longer periods. A little later, Harlow Shapley used what she had discovered in addition to the absolute magnitude of ...
... Henrietta Leavitt who, while plotting and examining the stars’ light curves, discovered there is a relationship between their period and luminosity. Brighter mean magnitude stars have longer periods. A little later, Harlow Shapley used what she had discovered in addition to the absolute magnitude of ...
Kidd_Thesis_2015April15_Final.
... Henrietta Leavitt who, while plotting and examining the stars’ light curves, discovered there is a relationship between their period and luminosity. Brighter mean magnitude stars have longer periods. A little later, Harlow Shapley used what she had discovered in addition to the absolute magnitude of ...
... Henrietta Leavitt who, while plotting and examining the stars’ light curves, discovered there is a relationship between their period and luminosity. Brighter mean magnitude stars have longer periods. A little later, Harlow Shapley used what she had discovered in addition to the absolute magnitude of ...
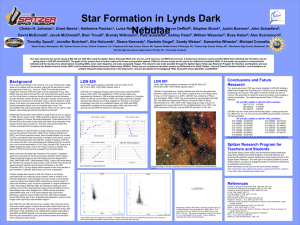
SciPoster_Jan2009
... associated with any molecular cloud complex, there is mention of an extended distribution of dust between the main clouds in Chamaeleon, Lupus and Ophiuchus (Sartori 2000). Ophiuchus is another region of active star formation, much of which is localized in a region centered on r Oph. According to Wi ...
... associated with any molecular cloud complex, there is mention of an extended distribution of dust between the main clouds in Chamaeleon, Lupus and Ophiuchus (Sartori 2000). Ophiuchus is another region of active star formation, much of which is localized in a region centered on r Oph. According to Wi ...
WILLIAM HERSCHEL AND THE `GARNET` STARS: μ CEPHEI AND
... this remark, Argelander—who was very interested in variable stars—watched this star from 1848 to 1864 (Argelander, 1869: 371– 372), and it became clear to him that the red colour created difficulties when it came to making magnitude comparisons with nearby stars. During the early years that he monit ...
... this remark, Argelander—who was very interested in variable stars—watched this star from 1848 to 1864 (Argelander, 1869: 371– 372), and it became clear to him that the red colour created difficulties when it came to making magnitude comparisons with nearby stars. During the early years that he monit ...
Chapter15- Our Galaxy-pptx - SFA Physics and Astronomy
... If we could view the Milky Way from above the disk, we would see its spiral arms. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... If we could view the Milky Way from above the disk, we would see its spiral arms. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Learn to write, compare, and order decimals using place value and
... Additional Example 1A & B: Reading and Writing Decimals Write each decimal in standard form, expanded form, and words. ...
... Additional Example 1A & B: Reading and Writing Decimals Write each decimal in standard form, expanded form, and words. ...
5 Report of the Panel on Stars and Stellar Evolution
... stellar phenomena, leading to a number of breakthrough discoveries. Newly discovered radio pulsars in binaries, including the unique double pulsar system, provide some of the most stringent tests of general relativity. Advances in X-ray astronomy have led to new discoveries related to accreting neut ...
... stellar phenomena, leading to a number of breakthrough discoveries. Newly discovered radio pulsars in binaries, including the unique double pulsar system, provide some of the most stringent tests of general relativity. Advances in X-ray astronomy have led to new discoveries related to accreting neut ...
No. 6
... may see a celestial body passing in front of another celestial body and preventing its light to reach to the Earth. This is called occultation. In occultation observations you see one body in the sky is getting dark, disappear or blinks when another body moves in front of it. Based on the bodies cre ...
... may see a celestial body passing in front of another celestial body and preventing its light to reach to the Earth. This is called occultation. In occultation observations you see one body in the sky is getting dark, disappear or blinks when another body moves in front of it. Based on the bodies cre ...
Testing
... • What does our galaxy look like? – Our galaxy consists of a disk of stars and gas, with a bulge of stars at the center of the disk, surrounded by a large spherical halo. ...
... • What does our galaxy look like? – Our galaxy consists of a disk of stars and gas, with a bulge of stars at the center of the disk, surrounded by a large spherical halo. ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.