Presentation available here - Lunar and Planetary Institute
... All core collapse explosions are asymmetric, maybe produced by magnetic jets. How can this be proved? Gamma-ray bursts are caused by jets of material moving at nearly the speed of light. Do they mark the birth of black holes? At least some gamma-ray bursts (and maybe all) arise in supernova ex ...
... All core collapse explosions are asymmetric, maybe produced by magnetic jets. How can this be proved? Gamma-ray bursts are caused by jets of material moving at nearly the speed of light. Do they mark the birth of black holes? At least some gamma-ray bursts (and maybe all) arise in supernova ex ...
Today`s Objectives - RanelaghALevelPhysics
... curves change as temperature is increased. Use Wien’s displacement law to estimate blackbody temperature of sources. Use Stefan’s law to estimate area needed for sources to have same power output as the sun. Recap inverse square law, state assumptions in ...
... curves change as temperature is increased. Use Wien’s displacement law to estimate blackbody temperature of sources. Use Stefan’s law to estimate area needed for sources to have same power output as the sun. Recap inverse square law, state assumptions in ...
2-star-life-cycle-and-star-classification
... A) in the Sun by fusion B) when water condenses in Earth's atmosphere C) from the movement of crustal plates D) during nuclear decay 23. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows an inferred sequence in which our solar system formed from a giant interstellar cloud ...
... A) in the Sun by fusion B) when water condenses in Earth's atmosphere C) from the movement of crustal plates D) during nuclear decay 23. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows an inferred sequence in which our solar system formed from a giant interstellar cloud ...
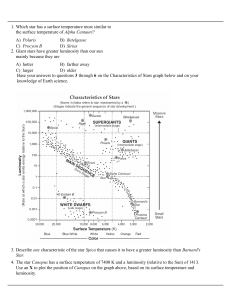
Spica The Star - Emmi
... Spica in an HR Diagram This is Spica in an HR Diagram. As you can see Spica is located three places from the middle for the brightness and its surface temperature 25,000 fahrenhieght. ...
... Spica in an HR Diagram This is Spica in an HR Diagram. As you can see Spica is located three places from the middle for the brightness and its surface temperature 25,000 fahrenhieght. ...
The Science of Life in the Universe (Chap 2
... Why are some elements (like gold) quite rare, while others (like carbon) are more common? Are there other solar systems? What evidence is there for other solar systems? (to be discussed later in semester) ...
... Why are some elements (like gold) quite rare, while others (like carbon) are more common? Are there other solar systems? What evidence is there for other solar systems? (to be discussed later in semester) ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... Why are some elements (like gold) quite rare, while others (like carbon) are more common? Are there other solar systems? What evidence is there for other solar systems? (to be discussed later in semester) ...
... Why are some elements (like gold) quite rare, while others (like carbon) are more common? Are there other solar systems? What evidence is there for other solar systems? (to be discussed later in semester) ...
January 2015 - Newbury Astronomical Society
... about 21:00 on 15th January. West is to the right and east to the left. The curved line across the sky is the ecliptic. This is the imaginary line along which the Sun, Moon and planets appear to move across the sky. The constellations through which the ecliptic passes are known as the constellations ...
... about 21:00 on 15th January. West is to the right and east to the left. The curved line across the sky is the ecliptic. This is the imaginary line along which the Sun, Moon and planets appear to move across the sky. The constellations through which the ecliptic passes are known as the constellations ...
Gravitation
... At the surface, or photosphere, of the red super giant star Betelgeuse, the gravitational force between the star and a 1.00 kg mass of hot gas is only 2.19 × 10 -3 N. This is because the mean radius of Betelgeuse is so large. Given that the mass of Betelgeuse is 20 times that of the sun, or 3.98 × 1 ...
... At the surface, or photosphere, of the red super giant star Betelgeuse, the gravitational force between the star and a 1.00 kg mass of hot gas is only 2.19 × 10 -3 N. This is because the mean radius of Betelgeuse is so large. Given that the mass of Betelgeuse is 20 times that of the sun, or 3.98 × 1 ...
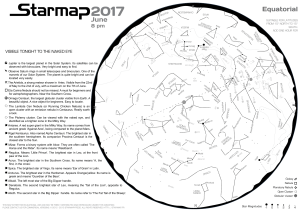
20 pm - Starmap
... The most informative and interactive handheld planetarium App ! Starmap is available on the iPhone™, iPad™, and iTouch™. When your device has a compass, Starmap displays exactly the portion of the sky you are pointing at. Hold the device parallel to your line of vision and discover the map smoothly ...
... The most informative and interactive handheld planetarium App ! Starmap is available on the iPhone™, iPad™, and iTouch™. When your device has a compass, Starmap displays exactly the portion of the sky you are pointing at. Hold the device parallel to your line of vision and discover the map smoothly ...
tut35 Magnitudes
... of asteroids, comets, and meteors. Factors such as color, albedo, and phase angles must, at times, be considered in their evaluation. The article will cover this topic with example calculations that can provide a firmer understanding of astronomical magnitudes. 1. SOME HISTORY Greek astronomers were ...
... of asteroids, comets, and meteors. Factors such as color, albedo, and phase angles must, at times, be considered in their evaluation. The article will cover this topic with example calculations that can provide a firmer understanding of astronomical magnitudes. 1. SOME HISTORY Greek astronomers were ...
Surveying the Stars
... • What is the significance of the main sequence? — Normal stars that fuse H to He in their cores fall on the main sequence of an H-R diagram. — A star’s mass determines its position along the main sequence (high mass: luminous and blue; low mass: faint and red). ...
... • What is the significance of the main sequence? — Normal stars that fuse H to He in their cores fall on the main sequence of an H-R diagram. — A star’s mass determines its position along the main sequence (high mass: luminous and blue; low mass: faint and red). ...
visual photometry - El Camino College
... professional astronomers.) The standard stars that are closest in brightness to the unknown star will determine an upper and lower limits for the unknown’s visual magnitude. In other words, if the unknown is fainter than standard 1, but is brighter than standard 2, the visual magnitude should lie be ...
... professional astronomers.) The standard stars that are closest in brightness to the unknown star will determine an upper and lower limits for the unknown’s visual magnitude. In other words, if the unknown is fainter than standard 1, but is brighter than standard 2, the visual magnitude should lie be ...
Galaxy
... star it is called an eclipsing star Astronomers know there are actually 2 stars by looking at the effects of gravity Our solar system is not the only solar system with planets revolving around a star In 2000, astronomers discovered a solar system about 10.5 light-years away with planets simila ...
... star it is called an eclipsing star Astronomers know there are actually 2 stars by looking at the effects of gravity Our solar system is not the only solar system with planets revolving around a star In 2000, astronomers discovered a solar system about 10.5 light-years away with planets simila ...
Lecture 3
... small and have the property that they scatter blue light more efficiently than red light. This is called `interstellar reddening’. – Most stars appear to be REDDER than they really are (cooler) – Stars of a given luminosity appear FAINTER than you would calculate given their distance and the inverse ...
... small and have the property that they scatter blue light more efficiently than red light. This is called `interstellar reddening’. – Most stars appear to be REDDER than they really are (cooler) – Stars of a given luminosity appear FAINTER than you would calculate given their distance and the inverse ...
Outline - March 16, 2010 Interstellar Medium (ISM) Why should you
... Most common “tracer” molecule is CO (carbon monoxide) ...
... Most common “tracer” molecule is CO (carbon monoxide) ...
Word
... Sword are distinctive patterns to look for; the shoulder star Betelgeuse is a very bright red star while the bright blue star Rigel is in the hunter’s knee. (We’ll talk about the colors of stars later.) Also, take a look nearly overhead and you should be able to see the Pleiades star cluster. (You m ...
... Sword are distinctive patterns to look for; the shoulder star Betelgeuse is a very bright red star while the bright blue star Rigel is in the hunter’s knee. (We’ll talk about the colors of stars later.) Also, take a look nearly overhead and you should be able to see the Pleiades star cluster. (You m ...
Project 3. Colour in Astronomy
... The first step is to obtain instrumental and absolute BVR magnitudes. This is accomplished by observing at least one standard star with known magnitudes on the standard system along with your night’s data and using it to determine the transformation equations. Often the st ...
... The first step is to obtain instrumental and absolute BVR magnitudes. This is accomplished by observing at least one standard star with known magnitudes on the standard system along with your night’s data and using it to determine the transformation equations. Often the st ...
Lecture082802
... which is swinging along the east-west line This pendulum will not rotate At latitudes in the middle, the pendulum will rotate with a period more than 24 hours ...
... which is swinging along the east-west line This pendulum will not rotate At latitudes in the middle, the pendulum will rotate with a period more than 24 hours ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.