QUESTION
... • ANSWER: The fuel that maintains the burning of the sun. As it is used, it decreases and helium increases. • QUESTION: What is hydrogen? ...
... • ANSWER: The fuel that maintains the burning of the sun. As it is used, it decreases and helium increases. • QUESTION: What is hydrogen? ...
PDF
... What can have happened to these star-forming peculiars so that they were so numerous 5 billion years ago but virtually absent by the present epoch? Two hypotheses are popular. The first suggests that the peculiars are transformed via mergers or by other means into regular ellipticals and spirals. Th ...
... What can have happened to these star-forming peculiars so that they were so numerous 5 billion years ago but virtually absent by the present epoch? Two hypotheses are popular. The first suggests that the peculiars are transformed via mergers or by other means into regular ellipticals and spirals. Th ...
Summary of Talks at Growing Black Holes 2004 in Garching
... -> High resolution CO observations of the object resolve it spatially into two peaks. It also resolved in velocity space, with a CO line width of 280 km/s and a bulge mass estimate of 1e10 solar masses within 2kpc, which is lower than expected from M sigma relation. Is this object not fully assemble ...
... -> High resolution CO observations of the object resolve it spatially into two peaks. It also resolved in velocity space, with a CO line width of 280 km/s and a bulge mass estimate of 1e10 solar masses within 2kpc, which is lower than expected from M sigma relation. Is this object not fully assemble ...
Edwin Hubble (1889
... bright blue stars near the Sun, they must be about 50,000 light years away to explain why they looked so faint. He pushed ahead to establish distances more conclusively using a new and ingenious method of measuring the universe. M22, a globular cluster of many thousands of stars. By assuming that ce ...
... bright blue stars near the Sun, they must be about 50,000 light years away to explain why they looked so faint. He pushed ahead to establish distances more conclusively using a new and ingenious method of measuring the universe. M22, a globular cluster of many thousands of stars. By assuming that ce ...
Masses of Dwarf Satellites of the Milky Way
... Here, Lgal and LMW are the individual probability distributions of Segue 1 and the Milky Way galaxies parameterized by the set Mgal,MW . The metallicity distribution of the member and nonmember stars are each modeled by Gaussians with mean metallicities w̄gal , w̄MW and widths σw,gal , σw,MW respect ...
... Here, Lgal and LMW are the individual probability distributions of Segue 1 and the Milky Way galaxies parameterized by the set Mgal,MW . The metallicity distribution of the member and nonmember stars are each modeled by Gaussians with mean metallicities w̄gal , w̄MW and widths σw,gal , σw,MW respect ...
X-ray emission from supernova shock waves Tanja Kramer Nymark Department of Astronomy
... The field of supernova research is a quite new one, compared with astronomy in general – it is only about eighty years since astronomers first became aware that some of the “new stars” which occasionally appeared were far too energetic to be understood in the context of what was at the time known ab ...
... The field of supernova research is a quite new one, compared with astronomy in general – it is only about eighty years since astronomers first became aware that some of the “new stars” which occasionally appeared were far too energetic to be understood in the context of what was at the time known ab ...
Planet Hunters Education Guide
... classrooms to participate in this type of activity. Citizen science projects can make it easier for teachers to incorporate real science in classroom science investigations. Citizen science is when crowd sourcing is used to solve a big data problem by asking the general public to assist scientists i ...
... classrooms to participate in this type of activity. Citizen science projects can make it easier for teachers to incorporate real science in classroom science investigations. Citizen science is when crowd sourcing is used to solve a big data problem by asking the general public to assist scientists i ...
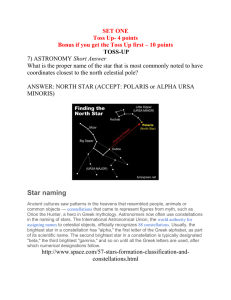
TOSS-UP 7) ASTRONOMY Short Answer
... Constellations are patterns of stars visible to the unaided eye, or regions of space seen from Earth that are bounded by borders designated by the International Astronomical Union. Asterisms are also naked-eye star patterns, but they do not form constellations on their own. An example is the Big Dip ...
... Constellations are patterns of stars visible to the unaided eye, or regions of space seen from Earth that are bounded by borders designated by the International Astronomical Union. Asterisms are also naked-eye star patterns, but they do not form constellations on their own. An example is the Big Dip ...
Article PDF - IOPscience
... detections of extrasolar meteors. When a meteoroid enters Earth’s atmosphere, air molecules ablate and ionize material from the meteoroid. The free electrons created by this ablation reflect radio waves, a fact exploited by radar aficionados. The size of individual meteoroids detected by radar syste ...
... detections of extrasolar meteors. When a meteoroid enters Earth’s atmosphere, air molecules ablate and ionize material from the meteoroid. The free electrons created by this ablation reflect radio waves, a fact exploited by radar aficionados. The size of individual meteoroids detected by radar syste ...
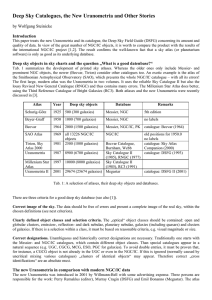
Deep Sky Catalogues, the New Uranometria and Other Stories
... Tab. 1 summarizes the development of printed sky atlases. Whereas the older ones only include Messier- and prominent NGC objects, the newer (Becvar, Tirion) consider other catalogues too. An exotic example is the atlas of the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO), which presents the whole NGC/ ...
... Tab. 1 summarizes the development of printed sky atlases. Whereas the older ones only include Messier- and prominent NGC objects, the newer (Becvar, Tirion) consider other catalogues too. An exotic example is the atlas of the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO), which presents the whole NGC/ ...
Radiative winds, accretion disks and massive stars physics using
... drive the wind? If the force from electron scattering were to exceed gravity (known as the Eddington limit) the surface of a star could not remain bound and the star would blow itself apart. • Instead, stellar winds are rather stable, using electrons bound in atoms to absorb the radiation: Radiation ...
... drive the wind? If the force from electron scattering were to exceed gravity (known as the Eddington limit) the surface of a star could not remain bound and the star would blow itself apart. • Instead, stellar winds are rather stable, using electrons bound in atoms to absorb the radiation: Radiation ...
Galileo`s Observation of Neptune 1612-1613
... “Most Serene Prince. Galileo Galilei most humbly prostrates himself before Your Highness, watching carefully, and with all spirit of willingness, not only to satisfy what concerns the reading of mathematics in the study of Padua, but to write of having decided to present to Your Highness a telescope ...
... “Most Serene Prince. Galileo Galilei most humbly prostrates himself before Your Highness, watching carefully, and with all spirit of willingness, not only to satisfy what concerns the reading of mathematics in the study of Padua, but to write of having decided to present to Your Highness a telescope ...
New INTEGRAL High Mass X
... XTE/PCA pointings performed during the 4th outburst in 2006 showed variability which suggested a pulsation period of approximately 195 +/- 10 s (Smith et al. 2006). The pulsations have been confirmed during the 5 th outburst in Feb 2007 (Swank et al. ATel # 999): Pspin=186.78 +/- 0.3 s This would im ...
... XTE/PCA pointings performed during the 4th outburst in 2006 showed variability which suggested a pulsation period of approximately 195 +/- 10 s (Smith et al. 2006). The pulsations have been confirmed during the 5 th outburst in Feb 2007 (Swank et al. ATel # 999): Pspin=186.78 +/- 0.3 s This would im ...
Chapter 2 CELESTIAL COORDINATE SYSTEMS
... That is, if one faces south, stars would appear to move from the east towards the west, which would be from your left to your right and is referred to as the apparent diurnal rotation of the celestial sphere. The rate of this motion is 15 degrees per hour. This number comes from the fact that Earth, ...
... That is, if one faces south, stars would appear to move from the east towards the west, which would be from your left to your right and is referred to as the apparent diurnal rotation of the celestial sphere. The rate of this motion is 15 degrees per hour. This number comes from the fact that Earth, ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.