galaxy - 106Thursday130-430
... because of its spiral arms, which contain many hot young stars and therefore is luminous. ...
... because of its spiral arms, which contain many hot young stars and therefore is luminous. ...
Lecture 1
... • 15 multiple planetary systems Pulsar planets • 6 planets Free-floating planets • 1 planet New planets are being found at a rate of around 1 per month ...
... • 15 multiple planetary systems Pulsar planets • 6 planets Free-floating planets • 1 planet New planets are being found at a rate of around 1 per month ...
Quiz # 5 – 11/15/2011
... A. the 50-watt light bulb is located 125 times further away than the 2-watt light bulb B. the 50-watt light bulb is located 25 times further away than the 2-watt light bulb C. the 50-watt light bulb is located 5 times further away than the 2-watt light bulb D. the 2-watt light bulb is located 5 time ...
... A. the 50-watt light bulb is located 125 times further away than the 2-watt light bulb B. the 50-watt light bulb is located 25 times further away than the 2-watt light bulb C. the 50-watt light bulb is located 5 times further away than the 2-watt light bulb D. the 2-watt light bulb is located 5 time ...
society journal - Auckland Astronomical Society
... was shown. The first part was about large raging storms in the atmospheres of the gas giant planets. Some of these storms are the size of our planet Earth, with winds blowing at many hundreds of kilometers per hour. It also showed an interview with the Australian amateur astronomer who discovered an ...
... was shown. The first part was about large raging storms in the atmospheres of the gas giant planets. Some of these storms are the size of our planet Earth, with winds blowing at many hundreds of kilometers per hour. It also showed an interview with the Australian amateur astronomer who discovered an ...
A Collection of Curricula for the STARLAB Deep Sky Objects
... Nebulae are very important in astronomy because they are the key to understanding the birth of stars. All stars, including the sun, formed from nebulae like the Orion Nebula. Astronomers have also found, however, that certain types of nebulae mark the death of stars (see slides #62 and 63). In old a ...
... Nebulae are very important in astronomy because they are the key to understanding the birth of stars. All stars, including the sun, formed from nebulae like the Orion Nebula. Astronomers have also found, however, that certain types of nebulae mark the death of stars (see slides #62 and 63). In old a ...
Kerboodle Gravity Questions673 KB
... The article below has been adapted from www.space.com. Surprising observations of a star swiftly orbiting the cloudy heart of the Milky Way Galaxy have verified with near certainty the existence of a central black hole, a theoretical object that still eludes direct detection. Astronomers watched the ...
... The article below has been adapted from www.space.com. Surprising observations of a star swiftly orbiting the cloudy heart of the Milky Way Galaxy have verified with near certainty the existence of a central black hole, a theoretical object that still eludes direct detection. Astronomers watched the ...
PPT - El Camino College
... No more electron degeneracy pressure support. Rapidly shrinks: Earth-size shrinks to town-size in 1 second! Lots of energy released. Turn on neutron degeneracy pressure. ...
... No more electron degeneracy pressure support. Rapidly shrinks: Earth-size shrinks to town-size in 1 second! Lots of energy released. Turn on neutron degeneracy pressure. ...
Astronomy 21 – Test 2 – Answers
... emission (explain the astrophysical mechanism)? You have to look through dust so you have to use longer wavelength observations. The 21cm line is useful for that (it is radiation emitted during the spin flip of the electron of atomic hydrogen). Redshifts of that line can be measured and velocities c ...
... emission (explain the astrophysical mechanism)? You have to look through dust so you have to use longer wavelength observations. The 21cm line is useful for that (it is radiation emitted during the spin flip of the electron of atomic hydrogen). Redshifts of that line can be measured and velocities c ...
H Exhaustion - University of Arizona
... produce enough L in shell to support envelope move to RGB on H burning timescales • Sun will spend ~4 Gyr moving from core H exhaustion to RGB - 40% of total H consumption and lifetime ...
... produce enough L in shell to support envelope move to RGB on H burning timescales • Sun will spend ~4 Gyr moving from core H exhaustion to RGB - 40% of total H consumption and lifetime ...
apparent magnitude
... the brightness that a star would have at a distance of 32.6 light-years from Earth • light-year the distance that light travels in one year; about 9.46 trillion kilometers ...
... the brightness that a star would have at a distance of 32.6 light-years from Earth • light-year the distance that light travels in one year; about 9.46 trillion kilometers ...
Document
... • RR Lyrae variables used like this to find our place in the Galaxy. • Distances that can be reached depend on the intrinsic brightness of the standard candle – and the limiting magnitude of your telescope ...
... • RR Lyrae variables used like this to find our place in the Galaxy. • Distances that can be reached depend on the intrinsic brightness of the standard candle – and the limiting magnitude of your telescope ...
Neutron Stars and Black Holes
... is about 0.877 X 10-13 cm (according to the Wikipedia). The volume of the proton is 4/3 π r3 = 2.82 X 10-39 cm3. The density = mass/volume = 5.9 X 1014 g/cm3. The Sun’s mass is 2 X 1030 kg = 2 X 1033 g. A one solar mass black hole has radius r ~ 3 km = 3 X 105 cm. The average mass within the Schwarz ...
... is about 0.877 X 10-13 cm (according to the Wikipedia). The volume of the proton is 4/3 π r3 = 2.82 X 10-39 cm3. The density = mass/volume = 5.9 X 1014 g/cm3. The Sun’s mass is 2 X 1030 kg = 2 X 1033 g. A one solar mass black hole has radius r ~ 3 km = 3 X 105 cm. The average mass within the Schwarz ...
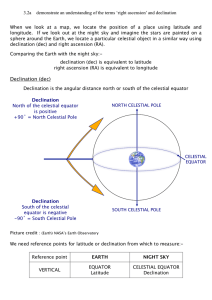
3.2a Right Ascension and Declination
... If a person was able to see the night sky shown above for a full day, the full band of stars would pass in front of them, moving steadily towards the right. The longitude reference point was more difficult. Many countries have laid claim to the Prime Meridian – the Chinese once used a gate from the ...
... If a person was able to see the night sky shown above for a full day, the full band of stars would pass in front of them, moving steadily towards the right. The longitude reference point was more difficult. Many countries have laid claim to the Prime Meridian – the Chinese once used a gate from the ...
Photometry – I. “All sky”
... years, you might not even be able to get the same glass that was used previously. Detectors are also not really uniform; CCDs are much more red-sensitive than photomultipliers and different types (of either) might have significantly different responses as a function of wavelength. At the same time, ...
... years, you might not even be able to get the same glass that was used previously. Detectors are also not really uniform; CCDs are much more red-sensitive than photomultipliers and different types (of either) might have significantly different responses as a function of wavelength. At the same time, ...
stars & galaxies
... Our galaxy is a spiral galaxy, in which the sun is one in a billion stars that are found inside. All the stars in the Milky Way have their own motion, some are moving towards the sun while others are moving away from our sun. Our sun is located on one of the spiral arms. It is rotating around the nu ...
... Our galaxy is a spiral galaxy, in which the sun is one in a billion stars that are found inside. All the stars in the Milky Way have their own motion, some are moving towards the sun while others are moving away from our sun. Our sun is located on one of the spiral arms. It is rotating around the nu ...
Recipe for a Star
... draws these elements toward the core of the star. Lighter elements move outward to form a layer. The heaviest elements in the core then undergo more nuclear fusion, making heavier and heavier elements. Heavier elements displace lighter elements, forcing them outward from the core. The star has a lay ...
... draws these elements toward the core of the star. Lighter elements move outward to form a layer. The heaviest elements in the core then undergo more nuclear fusion, making heavier and heavier elements. Heavier elements displace lighter elements, forcing them outward from the core. The star has a lay ...
Test 3 Version 3 1. Milky Way halo stars follow: (a) differential
... 3. Which one of the following statements is true? (a) stars in the halo are deficient in heavy elements, (b) stars in the galactic disk are deficient in heavy elements, (c) stars in the nucleus have the largest amounts of heavy elements, (d) all chemical elements are distributed more or less uniform ...
... 3. Which one of the following statements is true? (a) stars in the halo are deficient in heavy elements, (b) stars in the galactic disk are deficient in heavy elements, (c) stars in the nucleus have the largest amounts of heavy elements, (d) all chemical elements are distributed more or less uniform ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.