McDonald Observatory Planet Search - tls
... • Long period variations are most likely due to giant planets around stars with Mstar > 1 Mסּ • Short period variations are due to radial pulsations in the fundamental and overtone modes • Pulsations can be used to get funamental parameters of ...
... • Long period variations are most likely due to giant planets around stars with Mstar > 1 Mסּ • Short period variations are due to radial pulsations in the fundamental and overtone modes • Pulsations can be used to get funamental parameters of ...
Powerpoint for today
... A: Evaporated by the Sun when it becomes a Red Giant in 5 billion years. B: Blown to bits by a nearby supernova. C: Stripped away from the Sun by an encounter with another star in 1015 years. D: Blown to bits by silly humans with atomic bombs. ...
... A: Evaporated by the Sun when it becomes a Red Giant in 5 billion years. B: Blown to bits by a nearby supernova. C: Stripped away from the Sun by an encounter with another star in 1015 years. D: Blown to bits by silly humans with atomic bombs. ...
Astronomy - Career Account Web Pages
... The Universe's Most Ancient Object The farthest and one of the very earliest galaxies ever seen in the universe appears as a faint red blob in this ultra-deep–field exposure taken with NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. This is the deepest infrared image taken of the universe. Based on the object's colo ...
... The Universe's Most Ancient Object The farthest and one of the very earliest galaxies ever seen in the universe appears as a faint red blob in this ultra-deep–field exposure taken with NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. This is the deepest infrared image taken of the universe. Based on the object's colo ...
Word doc - UC-HiPACC - University of California, Santa Cruz
... 847 and counting: that’s the number of planets confirmed as existing around 642 stars within several hundred light-years of our Sun. And more than 2,000 additional detections are awaiting confirmation by follow-up observations. By far, the most potential exoplanets have been found by the NASA spacec ...
... 847 and counting: that’s the number of planets confirmed as existing around 642 stars within several hundred light-years of our Sun. And more than 2,000 additional detections are awaiting confirmation by follow-up observations. By far, the most potential exoplanets have been found by the NASA spacec ...
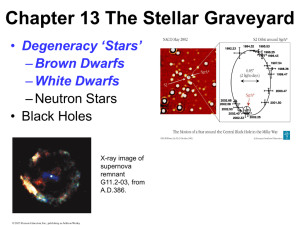
Ch 20 Stellar Evolution
... • In Sun-like stars, the helium burning starts with a helium flash before the star is once again in equilibrium. • The star develops a nonburning carbon core, surrounded by shells burning helium and hydrogen. • The shell expands into a planetary nebula, and the core is visible as a white dwarf. • ...
... • In Sun-like stars, the helium burning starts with a helium flash before the star is once again in equilibrium. • The star develops a nonburning carbon core, surrounded by shells burning helium and hydrogen. • The shell expands into a planetary nebula, and the core is visible as a white dwarf. • ...
I Cloudy with a Chance of Making a star is no easy thing
... suggesting that the balance recently tilted in favor of collapse. Other studies find evidence for external triggering. Thomas Preibisch of the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy in Bonn and his collaborators have showed that widely distributed stars in the Upper Scorpius region all formed near ...
... suggesting that the balance recently tilted in favor of collapse. Other studies find evidence for external triggering. Thomas Preibisch of the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy in Bonn and his collaborators have showed that widely distributed stars in the Upper Scorpius region all formed near ...
Summary: Nuclear burning in stars
... • Spiral arms have higher density than space between arms • Excess gravitational attraction slows down gas, stars when they pass through spiral arm in course of their orbits. • Î spiral arms are a traffic jam ...
... • Spiral arms have higher density than space between arms • Excess gravitational attraction slows down gas, stars when they pass through spiral arm in course of their orbits. • Î spiral arms are a traffic jam ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Center for Gravitational Wave Physics
... Helium novae (Eddington-limited) every ~250 years, one large He explosion every ~5,000 years, and WD-WD mergers every 200 years ...
... Helium novae (Eddington-limited) every ~250 years, one large He explosion every ~5,000 years, and WD-WD mergers every 200 years ...
phys-1600 - Dave Heppenstall
... The Moon and Mercury: The Moon • Even when Galileo looked at the moon, he didn't think of it as a place, but as an object. • 15% of the moon's surface are dark surfaces thousands of miles across which are now understood to be frozen lava flows. • The intense cratering on the moon can be traced back ...
... The Moon and Mercury: The Moon • Even when Galileo looked at the moon, he didn't think of it as a place, but as an object. • 15% of the moon's surface are dark surfaces thousands of miles across which are now understood to be frozen lava flows. • The intense cratering on the moon can be traced back ...
Where Are They?
... Why should there be anything special about our civilization? Our Sun is an apparently normal, middle-aged star, of average mass, in an average galaxy. Earth may be in just the right place, but the sheer numbers mean even with a low probability of success then earth-like planets should exist elsewher ...
... Why should there be anything special about our civilization? Our Sun is an apparently normal, middle-aged star, of average mass, in an average galaxy. Earth may be in just the right place, but the sheer numbers mean even with a low probability of success then earth-like planets should exist elsewher ...
PPT - Yale University
... Most disks probably do not last this long before being disrupted by violent interactions in a realistic system of forming stars because . . . ...
... Most disks probably do not last this long before being disrupted by violent interactions in a realistic system of forming stars because . . . ...
Birth - Wayne State University Physics and Astronomy
... Each second in the Sun, about 600 million tons of hydrogen undergo fusion into helium, with about 4 million tons turning to energy in the process This rate of hydrogen use means that eventually the Sun (and all other stars) will run out of central fuel ...
... Each second in the Sun, about 600 million tons of hydrogen undergo fusion into helium, with about 4 million tons turning to energy in the process This rate of hydrogen use means that eventually the Sun (and all other stars) will run out of central fuel ...
“Astronomy Picture of the Day” Leads to a Research Breakthrough
... information about the targets and the instruments we wanted to use. One step we had not yet gotten to was checking the public archives to see what was already available. On the morning of January 25, 2011, during the usual morning survey of arXiv, science blogs, etc., we pulled up the Astronomy Pict ...
... information about the targets and the instruments we wanted to use. One step we had not yet gotten to was checking the public archives to see what was already available. On the morning of January 25, 2011, during the usual morning survey of arXiv, science blogs, etc., we pulled up the Astronomy Pict ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... Probably new molecular clouds form continually out of less dense gas. Some collapse under their own gravity. Others may be more stable. Magnetic fields and rotation also have some influence. Gravity makes cloud want to ...
... Probably new molecular clouds form continually out of less dense gas. Some collapse under their own gravity. Others may be more stable. Magnetic fields and rotation also have some influence. Gravity makes cloud want to ...
Stellar Populations of Galaxies- 2 Lectures H
... by mass (Z) in sun is ~0.013 to zeroth order (more later) there are 4 sources of metals BBN- Li Be Atomic Number Type I SN -Fe, Ni etc Type II SN - O, Ne, etc Other (stellar winds, planetary nebulae •in nearby stars, 40-80% of the carbon is due to lowand intermediate-mass stars. etc) - N, C - still ...
... by mass (Z) in sun is ~0.013 to zeroth order (more later) there are 4 sources of metals BBN- Li Be Atomic Number Type I SN -Fe, Ni etc Type II SN - O, Ne, etc Other (stellar winds, planetary nebulae •in nearby stars, 40-80% of the carbon is due to lowand intermediate-mass stars. etc) - N, C - still ...
slides - Indico
... Why the Fascination with Metal-Poor Stars ? • Extremely metal-poor (MP) stars have recorded the heavy element abundances produced in the first generations of stars in the Universe • The shape of the low-metallicity tail of the Metallicity Distribution Function will (eventually) show structure that ...
... Why the Fascination with Metal-Poor Stars ? • Extremely metal-poor (MP) stars have recorded the heavy element abundances produced in the first generations of stars in the Universe • The shape of the low-metallicity tail of the Metallicity Distribution Function will (eventually) show structure that ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... Composition unknown. Probably mostly exotic particles that don't interact with ordinary matter at all (except gravity). Some may be brown dwarfs, dead white dwarfs … Most likely it's a dark halo surrounding the Milky Way. ...
... Composition unknown. Probably mostly exotic particles that don't interact with ordinary matter at all (except gravity). Some may be brown dwarfs, dead white dwarfs … Most likely it's a dark halo surrounding the Milky Way. ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.