slooh celebrates dwarf planet night with ceres dancing with asteroid
... starting at 5:00 pm PDT / 8:00 pm EDT / 00:00 UTC (7/4), live from Slooh observatories located in the northern and southern hemispheres. The northern hemisphere observatory is located off the west coast of Africa, at the Institute of Astrophysics of the Canary Islands, and the southern hemisphere ...
... starting at 5:00 pm PDT / 8:00 pm EDT / 00:00 UTC (7/4), live from Slooh observatories located in the northern and southern hemispheres. The northern hemisphere observatory is located off the west coast of Africa, at the Institute of Astrophysics of the Canary Islands, and the southern hemisphere ...
File - Science Website
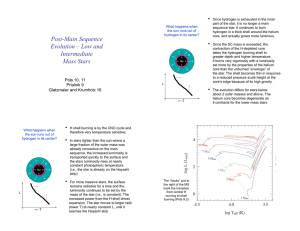
... Describe, in as much detail as you can, how our star (the Sun) formed from the time when there was just dust and gas (mostly hydrogen) up to now when it is in its main stable period. To gain full marks in this question you should write your ideas in good English. Put them into a sensible order and u ...
... Describe, in as much detail as you can, how our star (the Sun) formed from the time when there was just dust and gas (mostly hydrogen) up to now when it is in its main stable period. To gain full marks in this question you should write your ideas in good English. Put them into a sensible order and u ...
Day-26
... newly forming star that was much hotter than the protoSun. What would we expect about its planets? A. The planets orbit at random angles around the star. B. Rocky planets might be formed over a wider range of distances than in our Solar System. C. The star would be “naked,” without a surrounding dis ...
... newly forming star that was much hotter than the protoSun. What would we expect about its planets? A. The planets orbit at random angles around the star. B. Rocky planets might be formed over a wider range of distances than in our Solar System. C. The star would be “naked,” without a surrounding dis ...
Stellar aberration
... Apparent displacements of celestial objects about their locations are referred to as stellar aberration (astronomical aberration or aberration of light). All contemporary explanations of this phenomenon are based on the assumption that earth moves around (static) sun, in elliptical orbital path. In ...
... Apparent displacements of celestial objects about their locations are referred to as stellar aberration (astronomical aberration or aberration of light). All contemporary explanations of this phenomenon are based on the assumption that earth moves around (static) sun, in elliptical orbital path. In ...
THE INNER CORE OF A NEUTRON STAR Part 1
... fewer quantum states than electrons, neutron degeneracy pressure is stronger than electron degeneracy pressure. The tremendous nuclear forces between the densely packed neutrons cause quantum waves, forcing the neutrons to flow along lines of minimized repulsive nuclear forces [8]. The tremendous nu ...
... fewer quantum states than electrons, neutron degeneracy pressure is stronger than electron degeneracy pressure. The tremendous nuclear forces between the densely packed neutrons cause quantum waves, forcing the neutrons to flow along lines of minimized repulsive nuclear forces [8]. The tremendous nu ...
How we found about BLACK HOLES
... Even using a telescope won’t help much. Only the nearest stars show visible changes in position. The dim, distant stars are so far away that they don’t seem to move at all. One of the stars nearest to us is Sirius. It is about 80 million millions of kilometers away, but that is close for a star. It ...
... Even using a telescope won’t help much. Only the nearest stars show visible changes in position. The dim, distant stars are so far away that they don’t seem to move at all. One of the stars nearest to us is Sirius. It is about 80 million millions of kilometers away, but that is close for a star. It ...
ASTR 101 Scale of the Universe: an Overview
... What is the shape of the milky way? Where is the Sun’s location in it? What is the estimated number of stars in the Milky way, what is its diameter? Can we see all of the Milky way galaxy from Earth? What is the reason we see Milky way as a luminous cloud? What is most distant object in the universe ...
... What is the shape of the milky way? Where is the Sun’s location in it? What is the estimated number of stars in the Milky way, what is its diameter? Can we see all of the Milky way galaxy from Earth? What is the reason we see Milky way as a luminous cloud? What is most distant object in the universe ...
The Solar System Interplanetary Matter and the Birth of the Planets
... The idea that the solar system was born from the collapse of a cloud of dust and gas for proposed by Immanuel Kant (1755) and by Pierre Simon Laplace (40 years later). During the first part of the 20th century, some proposed that the solar system was the result of a near collision of the Sun with an ...
... The idea that the solar system was born from the collapse of a cloud of dust and gas for proposed by Immanuel Kant (1755) and by Pierre Simon Laplace (40 years later). During the first part of the 20th century, some proposed that the solar system was the result of a near collision of the Sun with an ...
Animated Planets PowerPoint Presentation
... The next visible comet is Comet Faye. Comet Faye's last perihelion was on November 15, 2006. It reached an apparent magnitude of 9.5 during that orbit. The orbital period of Comet Faye is 7.55 years Its next perihelion will occur on May 29, 2014. During this next appearance, its apparent magnitude i ...
... The next visible comet is Comet Faye. Comet Faye's last perihelion was on November 15, 2006. It reached an apparent magnitude of 9.5 during that orbit. The orbital period of Comet Faye is 7.55 years Its next perihelion will occur on May 29, 2014. During this next appearance, its apparent magnitude i ...
Leo Powerpoint
... death and using one of his claws tore away his skin, which he later used as an impermeable armor on his body for the remaining 11 tasks that he had to complete. As Hercules came out successful in his first labor, his step mother was furious but she couldn't have undone what Hercules had done. She st ...
... death and using one of his claws tore away his skin, which he later used as an impermeable armor on his body for the remaining 11 tasks that he had to complete. As Hercules came out successful in his first labor, his step mother was furious but she couldn't have undone what Hercules had done. She st ...
The Bible and big bang cosmology
... “A nebula is a large amount of gas and dust spread out in an immense volume. All stars begin their lives as parts of nebula. Gravity can pull some of the gas and dust in a nebula together. The interacting cloud is then called a protostar. … A star is born when the contracting gas and dust become so ...
... “A nebula is a large amount of gas and dust spread out in an immense volume. All stars begin their lives as parts of nebula. Gravity can pull some of the gas and dust in a nebula together. The interacting cloud is then called a protostar. … A star is born when the contracting gas and dust become so ...
PowerPoint
... 1. angle. 2. the time between successive orbital positions. 3. length along a circle 4. the time between oscillations of a standard clock. ...
... 1. angle. 2. the time between successive orbital positions. 3. length along a circle 4. the time between oscillations of a standard clock. ...
Perseids meteor showers are looking good
... bright meteoroid. A fireball's brightness is measured just as star brightness is measured ... by apparent magnitude (m). What’s weird is that the smaller the magnitude the brighter the star or fireball. For instance: • The planet Venus is brighter than any star in our night sky. It’s magnitude range ...
... bright meteoroid. A fireball's brightness is measured just as star brightness is measured ... by apparent magnitude (m). What’s weird is that the smaller the magnitude the brighter the star or fireball. For instance: • The planet Venus is brighter than any star in our night sky. It’s magnitude range ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.