Astronomy Review - Cockeysville Middle
... because it travels so quickly, all light takes time to go any distance. Light travels at 3 x 108 m/s. To the right, are some light travel times. Even when I look at you, I see what was! The further away we look, the further back in time we see. ...
... because it travels so quickly, all light takes time to go any distance. Light travels at 3 x 108 m/s. To the right, are some light travel times. Even when I look at you, I see what was! The further away we look, the further back in time we see. ...
Homework, November 16, 2006 AST110-6
... how many stars have Earth-like planets, nor do we know the likelihood that such planets might harbor advanced civilizations like our own. However, some stars can probably be ruled out as candidates for advanced civilizations. For example, given that it took a few billion years for humans to evolve o ...
... how many stars have Earth-like planets, nor do we know the likelihood that such planets might harbor advanced civilizations like our own. However, some stars can probably be ruled out as candidates for advanced civilizations. For example, given that it took a few billion years for humans to evolve o ...
Stellar Magnitude, Distance, and Motion
... Proper motion - the apparent change of position of a star on the celestial sphere o Denoted by the Greek symbol "mu" o Is a velocity in units of seconds of arc per year o Proper motion is not large. The star with the largest proper motion is called Barnard's Star. It moves 10.3 seconds of ar ...
... Proper motion - the apparent change of position of a star on the celestial sphere o Denoted by the Greek symbol "mu" o Is a velocity in units of seconds of arc per year o Proper motion is not large. The star with the largest proper motion is called Barnard's Star. It moves 10.3 seconds of ar ...
stars and galaxies – study guide
... 21. Hydrogen is the “fuel” of the sun. 22. By using a tool called a spectroscope astronomers can identify the elements in a star. 23. On an H-R Diagram, stars are classified by temperature and absolute magnitude. 24. What is the next stage of the sun? Red Giant 25. An example of a winter constellat ...
... 21. Hydrogen is the “fuel” of the sun. 22. By using a tool called a spectroscope astronomers can identify the elements in a star. 23. On an H-R Diagram, stars are classified by temperature and absolute magnitude. 24. What is the next stage of the sun? Red Giant 25. An example of a winter constellat ...
An Introduction to the Night Sky Stars and Constellations
... An Introduction to the Night Sky Stars and Constellations 1. What is the Latin root word of star? 2. Why do stars “twinkle”? 3. Why do planets “shine”? ...
... An Introduction to the Night Sky Stars and Constellations 1. What is the Latin root word of star? 2. Why do stars “twinkle”? 3. Why do planets “shine”? ...
Other Objects in Space
... Some stars may actually be brighter than the sun, but the sun is closer to Earth so it appears brighter ...
... Some stars may actually be brighter than the sun, but the sun is closer to Earth so it appears brighter ...
Space Science Distance Definitions
... one tenth up to about 50 solar masses. High mass stars are extremely rare and most stars contain one solar mass or less ...
... one tenth up to about 50 solar masses. High mass stars are extremely rare and most stars contain one solar mass or less ...
8th Grade Midterm Test Review
... 13. Red and yellow stars have a relatively (hot or cool) temperature while blue and white stars have a relatively (hot or cool) temperature. • Red & Yellow Stars= Cool • Blue & White Stars= Hot ...
... 13. Red and yellow stars have a relatively (hot or cool) temperature while blue and white stars have a relatively (hot or cool) temperature. • Red & Yellow Stars= Cool • Blue & White Stars= Hot ...
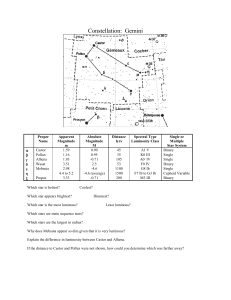
Gemini
... edition of Uranometria 2000.0 gives 434, while Cudworth (1971) counted 513 probable member stars. At its distance of 2,700 (WEBDA) or 2,800 light years (Sky Catalogue 2000.0), this corresponds to a linear diameter of about 24 light years; its central density is about 6.21 stars per cubic parsec. Som ...
... edition of Uranometria 2000.0 gives 434, while Cudworth (1971) counted 513 probable member stars. At its distance of 2,700 (WEBDA) or 2,800 light years (Sky Catalogue 2000.0), this corresponds to a linear diameter of about 24 light years; its central density is about 6.21 stars per cubic parsec. Som ...
1. Compute the deflection angle of a star whose light... limb of the Sun. Also compute the deflection angle of...
... 1. Compute the deflection angle of a star whose light just grazes the limb of the Sun. Also compute the deflection angle of a star whose light just grazes the limb of a 1.4M neutron star, if the neutron star was at the same distance from the Earth as the Sun. State assumptions. 2. Use the Plummer p ...
... 1. Compute the deflection angle of a star whose light just grazes the limb of the Sun. Also compute the deflection angle of a star whose light just grazes the limb of a 1.4M neutron star, if the neutron star was at the same distance from the Earth as the Sun. State assumptions. 2. Use the Plummer p ...
stars and constellations
... the axis will only point at Polaris for a few hundred years, then, another star will be “North”. The ancient Egyptians could not have used Polaris as a compass. Why stars “move” ...
... the axis will only point at Polaris for a few hundred years, then, another star will be “North”. The ancient Egyptians could not have used Polaris as a compass. Why stars “move” ...
ASTRONOMY 313
... 6. When the Sun has swollen to full red-giant size (R 0.5 A.U. = 107.5 R), its luminosity will be about 2000 times greater than it is now (i.e. L/L = 2000). Assume that the size of the Earth’s orbit remains unchanged. a. Calculate the Sun’s angular diameter at that time as seen from the Earth. ...
... 6. When the Sun has swollen to full red-giant size (R 0.5 A.U. = 107.5 R), its luminosity will be about 2000 times greater than it is now (i.e. L/L = 2000). Assume that the size of the Earth’s orbit remains unchanged. a. Calculate the Sun’s angular diameter at that time as seen from the Earth. ...
Space
... Earth is a home of many species Earth has beautiful seas and waters Earth is a home for you and me ...
... Earth is a home of many species Earth has beautiful seas and waters Earth is a home for you and me ...
Surface Environments of the Planets o+ our Solar System
... In this exercise, you will also become more familiar with the various naming systems for stars. Remember, only the brightest stars which form our constellations have been given proper names. There are thousands of stars that have either Bayer Greek letter names, and even more that have Flamsteed num ...
... In this exercise, you will also become more familiar with the various naming systems for stars. Remember, only the brightest stars which form our constellations have been given proper names. There are thousands of stars that have either Bayer Greek letter names, and even more that have Flamsteed num ...
Slide 1
... • Size can be small, medium or massive • Binary Stars: when two stars orbit around each other • Stars of equal mass have their center of mass in the middle ...
... • Size can be small, medium or massive • Binary Stars: when two stars orbit around each other • Stars of equal mass have their center of mass in the middle ...
Stellar Evolution and the HR Diagram Study Guide
... Which star will appear brighter in the night sky, a star with an apparent magnitude of 0 or a star with an apparent magnitude of +1? Star with apparent magnitude of 0 ...
... Which star will appear brighter in the night sky, a star with an apparent magnitude of 0 or a star with an apparent magnitude of +1? Star with apparent magnitude of 0 ...
File
... Back to Distance • Suppose we take the spectrum of a star and find it is a K5 II. We then know it – is a red giant with a surface temperature of 4000º K – has a luminosity about 1100x that of the Sun or an absolute magnitude of about -2.0 ...
... Back to Distance • Suppose we take the spectrum of a star and find it is a K5 II. We then know it – is a red giant with a surface temperature of 4000º K – has a luminosity about 1100x that of the Sun or an absolute magnitude of about -2.0 ...
February - Bristol Astronomical Society
... Batista Hodierna around 1654, it was probably quite well known to ancient astronomers. Charles Messier, was one of many people who later rediscovered the cluster. He added it to his famous catalogue on January 16, 1765 ...
... Batista Hodierna around 1654, it was probably quite well known to ancient astronomers. Charles Messier, was one of many people who later rediscovered the cluster. He added it to his famous catalogue on January 16, 1765 ...
HR-diagram - Bakersfield College
... • two stars with the same absolute magnitude would not be the same apparent magnitude WHY? • To compare absolute brightness • use a standard distance of 32.6 light-years away from earth ...
... • two stars with the same absolute magnitude would not be the same apparent magnitude WHY? • To compare absolute brightness • use a standard distance of 32.6 light-years away from earth ...
What do we see in the night sky - Laureate International College
... If you watch the stars for a whole night they appear to move from ______________ (as sun does during day). But the stars are not actually moving across the celestial sphere – Earth’s ____________ causes the illusion of movement. ...
... If you watch the stars for a whole night they appear to move from ______________ (as sun does during day). But the stars are not actually moving across the celestial sphere – Earth’s ____________ causes the illusion of movement. ...
Aquarius (constellation)
Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for ""water-carrier"" or ""cup-carrier"", and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♒), a representation of water.Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac (the sun's apparent path). It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Eridanus the river.