Origin and Age of the Universe
... 3. Approximately when did the Big Bang occur? 4. What is some recent evidence that supports the Big Bang Theory? ...
... 3. Approximately when did the Big Bang occur? 4. What is some recent evidence that supports the Big Bang Theory? ...
Lecture 23 - Empyrean Quest Publishers
... How far? 1 AU = 1.5x108 km = 8.3 light mins (Pluto-5.5 lt hrs) How bright? Power output at source = Luminosity, L = 4 x 1026 watts. Enough power to cover surface with 100 watt tiny Christmas tree lights. ...
... How far? 1 AU = 1.5x108 km = 8.3 light mins (Pluto-5.5 lt hrs) How bright? Power output at source = Luminosity, L = 4 x 1026 watts. Enough power to cover surface with 100 watt tiny Christmas tree lights. ...
Brighter than the average star?
... discovered M class star SO25300.5+165258 (red sphere on left) and the Sun. The radius of the red dwarf star is just 1/7 that of the Sun. Small and dim M type stars seem to be the most common stars in space, at least in our part of the Milky Way. Of the 100 closest stars to the Sun, 80 are red dwarfs ...
... discovered M class star SO25300.5+165258 (red sphere on left) and the Sun. The radius of the red dwarf star is just 1/7 that of the Sun. Small and dim M type stars seem to be the most common stars in space, at least in our part of the Milky Way. Of the 100 closest stars to the Sun, 80 are red dwarfs ...
Gr9_unit1_ch10_notes-2015
... built observatories to track the motions of the heavens and developed theories and models to explain the motions they saw. Examples of this include Stonehenge, in England, and the Pyramids of Giza, in Egypt. Contributions to our knowledge and understanding of celestial bodies and their motions have ...
... built observatories to track the motions of the heavens and developed theories and models to explain the motions they saw. Examples of this include Stonehenge, in England, and the Pyramids of Giza, in Egypt. Contributions to our knowledge and understanding of celestial bodies and their motions have ...
22 October: The Formation of Stars
... • When we see massive main sequence stars (spectral class O), we know they are young. • With fairly simple observations, we can find groups of O and B stars (OB associations) ...
... • When we see massive main sequence stars (spectral class O), we know they are young. • With fairly simple observations, we can find groups of O and B stars (OB associations) ...
Science 9: Unit 4 Review
... 23. Astronomers believe that the universe is expanding. What does this ...
... 23. Astronomers believe that the universe is expanding. What does this ...
The Universe - Lancaster High School
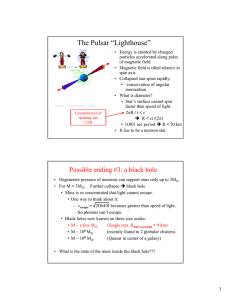
... -stars the size of Sun or smaller 2. Neutron star – collapses under gravity – all particles are neutrons – extremely dense -stars 5-20 times mass of Sun -Pulsar – spinning Neutron star 3. Black Hole – gravity so immense that nothing can escape – not even light -stars 20 times or more massive than Su ...
... -stars the size of Sun or smaller 2. Neutron star – collapses under gravity – all particles are neutrons – extremely dense -stars 5-20 times mass of Sun -Pulsar – spinning Neutron star 3. Black Hole – gravity so immense that nothing can escape – not even light -stars 20 times or more massive than Su ...
Thought Question
... How would the absolute magnitude of Alpha Centauri change if it were three times farther away? A. It would be +3 magnitudes fainter B. It would be -3 magnitudes brighter C. It would stay the same (its absolute magnitude is an intrinsic property of a star) ...
... How would the absolute magnitude of Alpha Centauri change if it were three times farther away? A. It would be +3 magnitudes fainter B. It would be -3 magnitudes brighter C. It would stay the same (its absolute magnitude is an intrinsic property of a star) ...
Which has a hotter temperature, a red star or a blue star? How do
... radiated by a small piece of a black body. Both are energy, but they are not the same thing. ...
... radiated by a small piece of a black body. Both are energy, but they are not the same thing. ...
here
... • ‘Head’ is made up of billions of particles of dust and rock and it shines by reflected light. • ‘Tail’ is made up of gas and gives off its own light and it points away from the sun due to the pressure of solar winds. • The most famous comet is Haley's Comet. In 1705 Edmund Haley predicted that a ...
... • ‘Head’ is made up of billions of particles of dust and rock and it shines by reflected light. • ‘Tail’ is made up of gas and gives off its own light and it points away from the sun due to the pressure of solar winds. • The most famous comet is Haley's Comet. In 1705 Edmund Haley predicted that a ...
24exoplanets8s
... Recently hundreds of planets around other stars have been found The planets are detected by: measuring the motions they induce in the central star measuring the dimming of the central star when the planet passes in front of it ...
... Recently hundreds of planets around other stars have been found The planets are detected by: measuring the motions they induce in the central star measuring the dimming of the central star when the planet passes in front of it ...
Astronomy
... Something that is achieved when the inward force of gravity is balanced by the outward pressure from fusion and radiation inside a star ...
... Something that is achieved when the inward force of gravity is balanced by the outward pressure from fusion and radiation inside a star ...
bYTEBoss lesson 3 life of star
... The end of the life cycle of really massive stars is different to that of massive stars. After a really massive red giant collapses in a supernova explosion, it leaves a star so dense that not even light can escape its gravitational pull. This is called a black hole! Some scientists believe that the ...
... The end of the life cycle of really massive stars is different to that of massive stars. After a really massive red giant collapses in a supernova explosion, it leaves a star so dense that not even light can escape its gravitational pull. This is called a black hole! Some scientists believe that the ...
Solution Key
... This is just like calculating the distance to the Pleiades, which we did in studio, but in globular clusters, only the low mass stub of the main sequence is visible. You can use any point on that stub to get the distance. For example, at B-V=0.5, the apparent visual magnitude V ≈ 18. The absolute vi ...
... This is just like calculating the distance to the Pleiades, which we did in studio, but in globular clusters, only the low mass stub of the main sequence is visible. You can use any point on that stub to get the distance. For example, at B-V=0.5, the apparent visual magnitude V ≈ 18. The absolute vi ...
HR Diagram
... 8. Compare your results for NGC with data given at end of writeup. If way off check for errors. 9. Go through the step 6 procedure again using M45 (younger cluster) 10. Go thought step 7 procedure again using M45. 11. Go through procedure again using M67 (older cluster). 12. Compute the distances in ...
... 8. Compare your results for NGC with data given at end of writeup. If way off check for errors. 9. Go through the step 6 procedure again using M45 (younger cluster) 10. Go thought step 7 procedure again using M45. 11. Go through procedure again using M67 (older cluster). 12. Compute the distances in ...
ASTR 553/554 (1) : Questions
... if the object is 10 pc distant. From these definitions, show that the distance modulus, m - M, is given by: m - M = -5 + 5 log10 dpc b. If IV is the V band surface brightness measured in LV, pc-2 and µV is the corresponding V band surface brightness measured in V mag arcsec-2 (mag/ss), show that µV ...
... if the object is 10 pc distant. From these definitions, show that the distance modulus, m - M, is given by: m - M = -5 + 5 log10 dpc b. If IV is the V band surface brightness measured in LV, pc-2 and µV is the corresponding V band surface brightness measured in V mag arcsec-2 (mag/ss), show that µV ...
AnwerkeyTypes-of-stars-and-HR-diagram
... 2. How does surface temperature of White dwarf compares to red giants? __________________Higher______ 3. What is color of stars with highest Surface Temperature? ____________blue____________ 4. What is color of stars with lowest Surface Temperature? _______________Red_________ 5. List the colors fro ...
... 2. How does surface temperature of White dwarf compares to red giants? __________________Higher______ 3. What is color of stars with highest Surface Temperature? ____________blue____________ 4. What is color of stars with lowest Surface Temperature? _______________Red_________ 5. List the colors fro ...
Seasonal Motion
... How do we “see” that the earth is moving around the sun or v.v.? • Small discrepancy between sun’s motion and motion of stars • Sidereal vs solar day • At noon, say, the sun is not exactly in front of the same stars on the next day. – It is exactly in the south – The stars are faster, so a little w ...
... How do we “see” that the earth is moving around the sun or v.v.? • Small discrepancy between sun’s motion and motion of stars • Sidereal vs solar day • At noon, say, the sun is not exactly in front of the same stars on the next day. – It is exactly in the south – The stars are faster, so a little w ...
Chapter 23
... Jupiter has been visited by 8 spacecraft. These were Pioneer 10, Pioneer 11, Voyager 1 and 2, Galileo, Ulysses, Cassini and New Horizons. The very first mission to explore Jupiter was Pioneer 10, an American spacecraft launched in 1972. This was a true pioneering mission in that, before it left Eart ...
... Jupiter has been visited by 8 spacecraft. These were Pioneer 10, Pioneer 11, Voyager 1 and 2, Galileo, Ulysses, Cassini and New Horizons. The very first mission to explore Jupiter was Pioneer 10, an American spacecraft launched in 1972. This was a true pioneering mission in that, before it left Eart ...
Aquarius (constellation)
Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for ""water-carrier"" or ""cup-carrier"", and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♒), a representation of water.Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac (the sun's apparent path). It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Eridanus the river.