Star Classification Lab
... In bold letters, label the following regions of your Hertzsprung-Russell diagram: White Dwarfs, Red Dwarfs, Red Giants, Main Sequence Stars, and Blue Supergiants. ...
... In bold letters, label the following regions of your Hertzsprung-Russell diagram: White Dwarfs, Red Dwarfs, Red Giants, Main Sequence Stars, and Blue Supergiants. ...
WORD - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... a. They change from one day to the next due to the Earth's rotation. b. They are measured with respect to the observer's local zenith and horizon. c. They are fixed in space with respect to Earth's axis and the Sun's direction at the vernal equinox. d. They were used by the ancient Greeks to determi ...
... a. They change from one day to the next due to the Earth's rotation. b. They are measured with respect to the observer's local zenith and horizon. c. They are fixed in space with respect to Earth's axis and the Sun's direction at the vernal equinox. d. They were used by the ancient Greeks to determi ...
PISGAH Text by Dr. Bob Hayward ASTRONOMICAL Astronomer
... the southeast as the sky darkens. On the evening of June 16 the moon will lie just above Mars. Two nights later the moon will have moved on eastward to lie near Saturn. The ringed planet is not as bright as either Jupiter or Mars but should be visible even close to an almost full moon. Saturn is put ...
... the southeast as the sky darkens. On the evening of June 16 the moon will lie just above Mars. Two nights later the moon will have moved on eastward to lie near Saturn. The ringed planet is not as bright as either Jupiter or Mars but should be visible even close to an almost full moon. Saturn is put ...
Universal Gravitation
... gravitational field inside solid massive spheres. For any bound system, the total energy is negative. This can be seen from the second total energy equation above. ...
... gravitational field inside solid massive spheres. For any bound system, the total energy is negative. This can be seen from the second total energy equation above. ...
Star project
... have their own gravity and have a fixed position in space. • They are extremely burning hot. • The nearest star to us is the sun. • They are made up of mainly hydrogen and helium, but have a little bit of other elements like oxygen and carbon as well. ...
... have their own gravity and have a fixed position in space. • They are extremely burning hot. • The nearest star to us is the sun. • They are made up of mainly hydrogen and helium, but have a little bit of other elements like oxygen and carbon as well. ...
exoplanets
... •Planets as small as Earth and smaller •Observational bias favors finding large planets •Often find planets very close to star •Observational bias •Gas giants can live very near their stars •Orbits often highly eccentric ...
... •Planets as small as Earth and smaller •Observational bias favors finding large planets •Often find planets very close to star •Observational bias •Gas giants can live very near their stars •Orbits often highly eccentric ...
Module 6: “The Message of Starlight Assignment 9: Parallax, stellar
... At this point there is no way to avoid the units that astronomers use: we have mentioned magnitude already, which is a brightness scale in which very bright stars are roughly magnitude 0, faint stars are magnitude 5, and really faint stars have larger and larger magnitudes. These are further divide ...
... At this point there is no way to avoid the units that astronomers use: we have mentioned magnitude already, which is a brightness scale in which very bright stars are roughly magnitude 0, faint stars are magnitude 5, and really faint stars have larger and larger magnitudes. These are further divide ...
Star- large ball of gas held together by large ball of gas held
... Stars originate from clouds of gas and dust molecules that clump up due to gravity. When the clump reaches the size of Jupiter, it creates enough energy by nuclear fusion to shine – becoming a star. For stars that are about the size of our sun, after main sequence they become giants, white dwarfs, a ...
... Stars originate from clouds of gas and dust molecules that clump up due to gravity. When the clump reaches the size of Jupiter, it creates enough energy by nuclear fusion to shine – becoming a star. For stars that are about the size of our sun, after main sequence they become giants, white dwarfs, a ...
AST101_lect_13
... T increases to compensate Nuclear reaction rate increases L increases Tph increases Stars evolve up and to left in MS (but not much) Solar luminosity has increased by 30% in 4.6 Gyr ...
... T increases to compensate Nuclear reaction rate increases L increases Tph increases Stars evolve up and to left in MS (but not much) Solar luminosity has increased by 30% in 4.6 Gyr ...
AST101 Lecture 13 The Lives of the Stars
... T increases to compensate Nuclear reaction rate increases L increases Tph increases Stars evolve up and to left in MS (but not much) Solar luminosity has increased by 30% in 4.6 Gyr ...
... T increases to compensate Nuclear reaction rate increases L increases Tph increases Stars evolve up and to left in MS (but not much) Solar luminosity has increased by 30% in 4.6 Gyr ...
HR Diagram of a Star Cluster
... A true Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is an XY plot of absolute magnitude vs. temperature (or equivalently, color or spectral class). We will assume that every one of the stars on this photograph is a member of the cluster NGC 6819 and so we will assume that they all lie at about the same distance from ...
... A true Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is an XY plot of absolute magnitude vs. temperature (or equivalently, color or spectral class). We will assume that every one of the stars on this photograph is a member of the cluster NGC 6819 and so we will assume that they all lie at about the same distance from ...
5th Grade Astronomy Test Study Guide
... Phases: the shape of the moon that is lit up and can be seen from Earth Stars: a body in outer space made of hot gases that shines in the night sky Constellations: group of stars with a recognizable shape Lunar: having to do with the moon Solar having to do with the sun Eclipse: the blocking of ligh ...
... Phases: the shape of the moon that is lit up and can be seen from Earth Stars: a body in outer space made of hot gases that shines in the night sky Constellations: group of stars with a recognizable shape Lunar: having to do with the moon Solar having to do with the sun Eclipse: the blocking of ligh ...
Stars and Galaxies Misconceptions
... Students who confuse terms like “Galaxy” with “Solar System” or who have no conception of the scale of the Milky Way may think that the stars in the night sky are from other galaxies. All the stars we see with our “naked eyes” are in the Milky Way Galaxy –we cannot see individual stars in other gala ...
... Students who confuse terms like “Galaxy” with “Solar System” or who have no conception of the scale of the Milky Way may think that the stars in the night sky are from other galaxies. All the stars we see with our “naked eyes” are in the Milky Way Galaxy –we cannot see individual stars in other gala ...
Observing the Sky - University of Northern Iowa
... distance to the Sun. The Sun will be directly over your head at noon during the summer. The Sun will always rise/set due east/west as seen from Iowa. ...
... distance to the Sun. The Sun will be directly over your head at noon during the summer. The Sun will always rise/set due east/west as seen from Iowa. ...
characteristics of stars
... Our galaxy is called the Milky Way because when we view it, it looks like __________ __________. There are at least _____ billion stars in our galaxy. The Milky Way is _________ - shaped. The sun is located near the ______ of the disk. In the central bulge, the stars are so numerous that they appear ...
... Our galaxy is called the Milky Way because when we view it, it looks like __________ __________. There are at least _____ billion stars in our galaxy. The Milky Way is _________ - shaped. The sun is located near the ______ of the disk. In the central bulge, the stars are so numerous that they appear ...
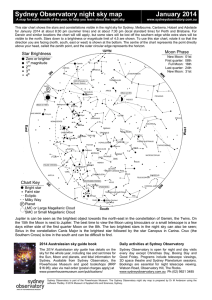
Sydney Observatory night sky map January 2014
... the 15th the Moon is next to Jupiter. The best time to view the Moon using binoculars or a small telescope is a few days either side of the first quarter Moon on the 8th. The two brightest stars in the night sky can also be seen; Sirius in the constellation Canis Major is the brightest star followed ...
... the 15th the Moon is next to Jupiter. The best time to view the Moon using binoculars or a small telescope is a few days either side of the first quarter Moon on the 8th. The two brightest stars in the night sky can also be seen; Sirius in the constellation Canis Major is the brightest star followed ...
Stellar Classification Worksheet 2
... Explain how each of the 5 characteristics in the boxes below is used to classify stars. In each box, give 2 examples of stars and their specific characteristics. Use pages 127-129 in the textbook and the examples below to complete the worksheet. ...
... Explain how each of the 5 characteristics in the boxes below is used to classify stars. In each box, give 2 examples of stars and their specific characteristics. Use pages 127-129 in the textbook and the examples below to complete the worksheet. ...
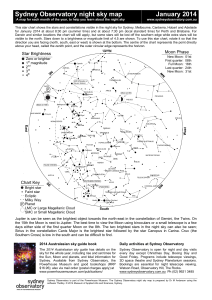
your star chart here - Australasian Science Magazine
... the 15th the Moon is next to Jupiter. The best time to view the Moon using binoculars or a small telescope is a few days either side of the first quarter Moon on the 8th. The two brightest stars in the night sky can also be seen; Sirius in the constellation Canis Major is the brightest star followed ...
... the 15th the Moon is next to Jupiter. The best time to view the Moon using binoculars or a small telescope is a few days either side of the first quarter Moon on the 8th. The two brightest stars in the night sky can also be seen; Sirius in the constellation Canis Major is the brightest star followed ...
star
... large that the unit used to measure distance is a light-year Light-year – the distance light will travel in a vacuum in one year 1light-year = 9,460,730,472,580.8 km (9.5x1012km) or 5,878,625,373,183.608 miles ...
... large that the unit used to measure distance is a light-year Light-year – the distance light will travel in a vacuum in one year 1light-year = 9,460,730,472,580.8 km (9.5x1012km) or 5,878,625,373,183.608 miles ...
Aquarius (constellation)
Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for ""water-carrier"" or ""cup-carrier"", and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♒), a representation of water.Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac (the sun's apparent path). It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Eridanus the river.