Document
... The multi-colored area shows a dust disk surrounding a newborn star. The red-orange area at the center represents the brightest region, which contains the young star. It is surrounded by the cooler, dusty disk, which appears as yellow, green and blue. The diameter of the disk is about 20 times large ...
... The multi-colored area shows a dust disk surrounding a newborn star. The red-orange area at the center represents the brightest region, which contains the young star. It is surrounded by the cooler, dusty disk, which appears as yellow, green and blue. The diameter of the disk is about 20 times large ...
Ourdraft
... Presenting the Research Process to High School Students Young Stars in IC 2118 We are studying a nebula (cloud of gas and dust) called Interstellar Cloud 2118, or the Witch Head Nebula, that is being excited by a young, very hot star called Rigel. Because Rigel is so energetic, it sends off shock wa ...
... Presenting the Research Process to High School Students Young Stars in IC 2118 We are studying a nebula (cloud of gas and dust) called Interstellar Cloud 2118, or the Witch Head Nebula, that is being excited by a young, very hot star called Rigel. Because Rigel is so energetic, it sends off shock wa ...
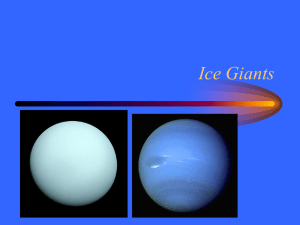
Ice Giants
... Eighth planet 30 AU from Sun 3.8 times Earth size 17 times Earth mass 165 year revolution 16 hour day Water and iron core Temperature -200 °C ...
... Eighth planet 30 AU from Sun 3.8 times Earth size 17 times Earth mass 165 year revolution 16 hour day Water and iron core Temperature -200 °C ...
SNC 1D1 Space Unit Review Answers How long does it take the
... Chromosphere: A thin red layer that is only seen during a solar eclipse Photosphere: The yellow part of the Sun with temperatures of about 5500°C Corona: The hot outer layer of the Sun Solar Flare: Large bright streams of particles going out from the photosphere Solar Prominences: Explosions at the ...
... Chromosphere: A thin red layer that is only seen during a solar eclipse Photosphere: The yellow part of the Sun with temperatures of about 5500°C Corona: The hot outer layer of the Sun Solar Flare: Large bright streams of particles going out from the photosphere Solar Prominences: Explosions at the ...
ISP 205: Visions of the Universe Fall 2001 Professor: ER Capriotti
... 10. Galileo's studies of moving objects led to the idea that a moving object A. comes to rest only if a force stops it. B. is subject to the Universal Law of Gravity. C. will go faster the heavier it is. D. will seek its natural state of rest. E. requires a force to keep it moving. 11. Galileo demon ...
... 10. Galileo's studies of moving objects led to the idea that a moving object A. comes to rest only if a force stops it. B. is subject to the Universal Law of Gravity. C. will go faster the heavier it is. D. will seek its natural state of rest. E. requires a force to keep it moving. 11. Galileo demon ...
Solution - Caltech Astronomy
... m A = 4.13 MŸ , mB = 0.998 MŸ . (d) Assuming the orbital separation is much larger than the stellar radii, and that the orbits are circular, we can treat the velocity of the stars during eclipse as completely in the plane of the sky. For circular orbits, the maximum radial velocities given are the c ...
... m A = 4.13 MŸ , mB = 0.998 MŸ . (d) Assuming the orbital separation is much larger than the stellar radii, and that the orbits are circular, we can treat the velocity of the stars during eclipse as completely in the plane of the sky. For circular orbits, the maximum radial velocities given are the c ...
ď - Google Sites
... d. The hottest stars emit shorter wavelengths of light and appear bluer, while cooler stars appear more red. ...
... d. The hottest stars emit shorter wavelengths of light and appear bluer, while cooler stars appear more red. ...
File
... Answer the following questions in your notebook. Write the complete question and write your answer in complete sentences. 4. Explain how astronomers measure the distance to nearby stars. 5. What are the main characteristics used to classify stars? 6. How would you classify the sun based on each of t ...
... Answer the following questions in your notebook. Write the complete question and write your answer in complete sentences. 4. Explain how astronomers measure the distance to nearby stars. 5. What are the main characteristics used to classify stars? 6. How would you classify the sun based on each of t ...
Mountain Skies - Pisgah Astronomical Research Institute
... the earth. As such, they always appear close to the sun in the evening twilight as later this month or close to the sun in the morning twilight as back in January. Venus was in conjunction behind the sun on June 6 and Mercury follows suit this coming Wednesday. Since Mercury moves much faster, it wi ...
... the earth. As such, they always appear close to the sun in the evening twilight as later this month or close to the sun in the morning twilight as back in January. Venus was in conjunction behind the sun on June 6 and Mercury follows suit this coming Wednesday. Since Mercury moves much faster, it wi ...
Astronomy 82 - Problem Set #1
... angular diameter of the wobble be? If Jupiter was only 1 AU from the Sun, what would the angular wobble be? From the definition of Center of Mass, the separation d of two objects from their common center of mass is given by: m* d *=m J d J . For Jupiter, the sum of these distances is approximately i ...
... angular diameter of the wobble be? If Jupiter was only 1 AU from the Sun, what would the angular wobble be? From the definition of Center of Mass, the separation d of two objects from their common center of mass is given by: m* d *=m J d J . For Jupiter, the sum of these distances is approximately i ...
where it is, how big it
... Jupiter along with other gas planets has high velocity winds (about 400mph) which are confined in wide bands of latitude. Slight chemical and temperature differences between these bands are responsible for the distinct alternating colors. The light colored bands are called zones; the dark ones belts ...
... Jupiter along with other gas planets has high velocity winds (about 400mph) which are confined in wide bands of latitude. Slight chemical and temperature differences between these bands are responsible for the distinct alternating colors. The light colored bands are called zones; the dark ones belts ...
Life on Other Planets
... • So far, all known Life on Earth is based on amino-acid molecules (proteins and DNA) – Based on 6 fundamental elements: hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus; • Considered irreplaceable until the recent experiment of replacing phosphorus with arsenic in bacteria dredged from ...
... • So far, all known Life on Earth is based on amino-acid molecules (proteins and DNA) – Based on 6 fundamental elements: hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus; • Considered irreplaceable until the recent experiment of replacing phosphorus with arsenic in bacteria dredged from ...
GIZMO H-RDiagramSE
... Gizmo Warm-up In the early 1900s, astronomers were able to identify many star characteristics such as color, size, temperature, and luminosity—or how bright a star is. However, astronomers did not yet understand exactly how these characteristics were related. Using the H-R Diagram Gizmo™, you will d ...
... Gizmo Warm-up In the early 1900s, astronomers were able to identify many star characteristics such as color, size, temperature, and luminosity—or how bright a star is. However, astronomers did not yet understand exactly how these characteristics were related. Using the H-R Diagram Gizmo™, you will d ...
PowerPoint-presentatie
... A shooting star is a common name for the visible path of a meteorite as it starts to burn when it enters the atmosphere. Question 3 (GG 55) A star/ sun is a ball of burning gas in the middle of a solar system. A sun sends out light and heat. Planets orbit a sun. They don’t send out light, but the ge ...
... A shooting star is a common name for the visible path of a meteorite as it starts to burn when it enters the atmosphere. Question 3 (GG 55) A star/ sun is a ball of burning gas in the middle of a solar system. A sun sends out light and heat. Planets orbit a sun. They don’t send out light, but the ge ...
Sun, Moon and Stars - Mona Shores Public Schools
... The Earth rotates once every 24 hours. Each time the Earth rotates we have one day and one night. When we are on the sun side of the earth, we have daylight. When we rotate away from the sun, we have night. ...
... The Earth rotates once every 24 hours. Each time the Earth rotates we have one day and one night. When we are on the sun side of the earth, we have daylight. When we rotate away from the sun, we have night. ...
Solar Nebula Theory
... Large (106 km), hot (106 K) region of diffuse gas surrounding Sun • Heated to such high temperatures by the Sun’s magnetic field • Visible during a total solar eclipse or with use of coronagraph ...
... Large (106 km), hot (106 K) region of diffuse gas surrounding Sun • Heated to such high temperatures by the Sun’s magnetic field • Visible during a total solar eclipse or with use of coronagraph ...
©M. Rieke 1 Correct responses in BOLDFACE. 1. Why did
... c. it appears to have many of the conditions needed for life in its early history, so we might find signs that life formed. d. the face on Mars suggests there is a dead civilization we might discover. e. its huge mountains and canyons would be highly scenic. 12. The only body other than Earth to sho ...
... c. it appears to have many of the conditions needed for life in its early history, so we might find signs that life formed. d. the face on Mars suggests there is a dead civilization we might discover. e. its huge mountains and canyons would be highly scenic. 12. The only body other than Earth to sho ...
1 Correct responses in BOLDFACE. 1. Henrietta Leavitt`s period
... a. at the end the electrons in the atoms have gone to lower energy levels and given off the energy they lost b. the atoms join together into bigger molecules, and the molecular binding energy is released c. the fusion products weigh a little less than the input materials, and the mass that is lost a ...
... a. at the end the electrons in the atoms have gone to lower energy levels and given off the energy they lost b. the atoms join together into bigger molecules, and the molecular binding energy is released c. the fusion products weigh a little less than the input materials, and the mass that is lost a ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • Stars below the Main Sequence are called White Dwarfs ...
... • Stars below the Main Sequence are called White Dwarfs ...
Aquarius (constellation)
Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for ""water-carrier"" or ""cup-carrier"", and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♒), a representation of water.Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac (the sun's apparent path). It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Eridanus the river.