The Copernican Model (1543)
... The Sun and Celestial Sphere are fixed. The Earth, Moon, and Planets all move. ...
... The Sun and Celestial Sphere are fixed. The Earth, Moon, and Planets all move. ...
Chapter20
... For stars less than 8 solar masses, a strong stellar wind develops and the outer layers of the star are removed to expose the hot degenerate core As the gas is expelled and the core is visible, the color of the star becomes much bluer and moves to the left in the HR diagram The star begins to emit l ...
... For stars less than 8 solar masses, a strong stellar wind develops and the outer layers of the star are removed to expose the hot degenerate core As the gas is expelled and the core is visible, the color of the star becomes much bluer and moves to the left in the HR diagram The star begins to emit l ...
NOVAE and SUPERNOVAE
... Chandrasekhar limit. The entire star collapses, the interior temperature rises to hundreds of millions of degrees, fusion reactions are ignited everywhere within the star. Fusion occurs through all stages right up to the production of iron. Nothing remains behind. The remnants of the star are bl ...
... Chandrasekhar limit. The entire star collapses, the interior temperature rises to hundreds of millions of degrees, fusion reactions are ignited everywhere within the star. Fusion occurs through all stages right up to the production of iron. Nothing remains behind. The remnants of the star are bl ...
PDF version
... Remember how we talked about how stars have things revolving around them? Planets are one good example. Earth is a planet, and there are seven other planets in our solar system that all revolve around the sun. Mercury is the closest planet to the sun, and it's the smallest of the eight. Venus is the ...
... Remember how we talked about how stars have things revolving around them? Planets are one good example. Earth is a planet, and there are seven other planets in our solar system that all revolve around the sun. Mercury is the closest planet to the sun, and it's the smallest of the eight. Venus is the ...
File
... crust, about a kilometer thick. This crust is very hard and very smooth. Gravity would probably prevent any irregularities larger than half a centimeter. ...
... crust, about a kilometer thick. This crust is very hard and very smooth. Gravity would probably prevent any irregularities larger than half a centimeter. ...
keplers laws and newton - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... • Angular momentum is related to the amount of energy stored in an object due to its rotation and revolution • Angular momentum is also related to the sideways or tangential velocity of an orbiting object • Angular momentum is conserved--as the spread of mass decreases, the rotation rate must increa ...
... • Angular momentum is related to the amount of energy stored in an object due to its rotation and revolution • Angular momentum is also related to the sideways or tangential velocity of an orbiting object • Angular momentum is conserved--as the spread of mass decreases, the rotation rate must increa ...
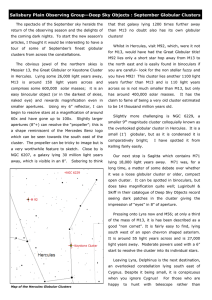
September Globular Clusters - Salisbury Plain Observing Group
... seek some of these celestial long term denizens this autumn, and get out under the night sky. ...
... seek some of these celestial long term denizens this autumn, and get out under the night sky. ...
TABLE OF CONTENTS Page Title Date 1
... 1. Mars has the largest volcano in the entire Solar System called Olympus Mons. 340 miles wide and 16.7 miles high!! 2. Mars is also home to the largest canyon in the Solar System, more than 10x larger than our Grand Canyon! 3. In Mars temperatures reach a comfy 600 F in the summer but in the winter ...
... 1. Mars has the largest volcano in the entire Solar System called Olympus Mons. 340 miles wide and 16.7 miles high!! 2. Mars is also home to the largest canyon in the Solar System, more than 10x larger than our Grand Canyon! 3. In Mars temperatures reach a comfy 600 F in the summer but in the winter ...
Life Cycle Of A Star
... that produces heat and light. There are many stars in our galaxy, and many more in others, but the star that is the most important and the one that we orbit around is called the Sun. The Sun produces heat and light for us and is also keeping all the planets in orbit. Stars aren’t just beautiful thin ...
... that produces heat and light. There are many stars in our galaxy, and many more in others, but the star that is the most important and the one that we orbit around is called the Sun. The Sun produces heat and light for us and is also keeping all the planets in orbit. Stars aren’t just beautiful thin ...
Star Life Study Guide
... 4. _____The most terrifying concept of astrophysics lies in the bottom of a black hole called the a. event horizon b. accretion disk c. singularity 5. _____ Nearly 90% of all stars are in the mid-life point of their life cycle and are called a. red giants b. main sequence c. planetary nebulas 6. ___ ...
... 4. _____The most terrifying concept of astrophysics lies in the bottom of a black hole called the a. event horizon b. accretion disk c. singularity 5. _____ Nearly 90% of all stars are in the mid-life point of their life cycle and are called a. red giants b. main sequence c. planetary nebulas 6. ___ ...
STAAR Review – Week Ten
... b. a medium-sized star. c. an extremely small star. d. an extremely large star. 16. Which statement about the universe is correct? a. It is known as the Milky Way. b. It is made up mostly of empty space. c. It is gradually getting smaller. d. It consists of one Sun, nine planets, and satellites. ...
... b. a medium-sized star. c. an extremely small star. d. an extremely large star. 16. Which statement about the universe is correct? a. It is known as the Milky Way. b. It is made up mostly of empty space. c. It is gradually getting smaller. d. It consists of one Sun, nine planets, and satellites. ...
Midterm Study Guide
... 67. What is the color of a mineral in its powdered form called? (we rubbed it on a piece of tile) 68. What is it called when a mineral breaks in even planes? 69. What do we call a minerals resistance to scratch? 70. What type of rock forms when magma or lava cools and hardens? 71. What type of rock ...
... 67. What is the color of a mineral in its powdered form called? (we rubbed it on a piece of tile) 68. What is it called when a mineral breaks in even planes? 69. What do we call a minerals resistance to scratch? 70. What type of rock forms when magma or lava cools and hardens? 71. What type of rock ...
History of astronomy
... When did we prove that Copernicus was right, that the Earth really does orbit the Sun? A.1543, when his book was published B.1610, when Galileo first observed with a telescope C.1687, when Newton published the Law of Gravity D.1830’s, when astronomers measured the first trigonometric parallaxes ...
... When did we prove that Copernicus was right, that the Earth really does orbit the Sun? A.1543, when his book was published B.1610, when Galileo first observed with a telescope C.1687, when Newton published the Law of Gravity D.1830’s, when astronomers measured the first trigonometric parallaxes ...
A105 Stars and Galaxies
... Image from the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory's 0.9meter telescope ...
... Image from the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory's 0.9meter telescope ...
Stellar Evolution (Powerpoint) 17
... fusion at once. What a star normally takes billions of years to burn, this star burns all at once. BIG explosion! ...
... fusion at once. What a star normally takes billions of years to burn, this star burns all at once. BIG explosion! ...
HR Diagram and Life of a star
... temp This means that they are very large and can range in size from 100-1000 times the size of the sun GIANTS- large bright stars a bit smaller and fainter than Super giants Super giants in the Red temp range tend to be in their last stages of life. They are out of hydrogen and are now fusing Helium ...
... temp This means that they are very large and can range in size from 100-1000 times the size of the sun GIANTS- large bright stars a bit smaller and fainter than Super giants Super giants in the Red temp range tend to be in their last stages of life. They are out of hydrogen and are now fusing Helium ...
Astronomy PowerPoint - Petal School District
... (no man has ever been farther than the moon) One way: space telescopes! the Hubble Space Telescope (looks at distant galaxies & at planets in our solar system) ...
... (no man has ever been farther than the moon) One way: space telescopes! the Hubble Space Telescope (looks at distant galaxies & at planets in our solar system) ...
(HR) Diagrams
... a. For instance, in the range of A type stars, how many A sub-types are there and what are their names? b. Write down the spectral class of the sub-type halfway between K and M. 6. Which is the hottest type of star, O, B, A, F, G, K or M? Circle the hottest type. 7. Which is the coldest type of star ...
... a. For instance, in the range of A type stars, how many A sub-types are there and what are their names? b. Write down the spectral class of the sub-type halfway between K and M. 6. Which is the hottest type of star, O, B, A, F, G, K or M? Circle the hottest type. 7. Which is the coldest type of star ...
kolynos - Look and Learn
... needs within a limit of ten miles ; these Aunt Sallys every few yards are silly. Country Planning should be put in the hands of an elected District Committee with one member from each parish, the members becoming part of the District Council for Country PlanHow to find the Pole Star ning only. This ...
... needs within a limit of ten miles ; these Aunt Sallys every few yards are silly. Country Planning should be put in the hands of an elected District Committee with one member from each parish, the members becoming part of the District Council for Country PlanHow to find the Pole Star ning only. This ...
Chapter 16 - "The Universe"
... – The classification is based on apparent magnitude scale – The first magnitude is defined as 100 times brighter than a sixth magnitude star. – There are then 5 equal divisions between these two. – Each magnitude is approximately 2.51 times fainter than the next higher magnitude number. – The absolu ...
... – The classification is based on apparent magnitude scale – The first magnitude is defined as 100 times brighter than a sixth magnitude star. – There are then 5 equal divisions between these two. – Each magnitude is approximately 2.51 times fainter than the next higher magnitude number. – The absolu ...
a2Lec115
... Use mks system: length=meter, mass =kgm, time=sec Astronomical Unit (AU): Distance from the earth to the sun = semi-major axis of the orbit of Earth around Sun 1 AU = d(sun) = 1.5 x 1011 m Parsec (PC): Distance at which 1 AU subtends Angle of 1 second 1 pc (parsec) = 206625 AU = 3.086 x 1016 m = 3.2 ...
... Use mks system: length=meter, mass =kgm, time=sec Astronomical Unit (AU): Distance from the earth to the sun = semi-major axis of the orbit of Earth around Sun 1 AU = d(sun) = 1.5 x 1011 m Parsec (PC): Distance at which 1 AU subtends Angle of 1 second 1 pc (parsec) = 206625 AU = 3.086 x 1016 m = 3.2 ...
Aquarius (constellation)
Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for ""water-carrier"" or ""cup-carrier"", and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♒), a representation of water.Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac (the sun's apparent path). It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Eridanus the river.