DTU 8e Chap 11 Characterizing Stars
... alternately toward and away from Earth. An eclipsing binary is a system whose orbits are viewed nearly edge on from Earth, so that one star periodically eclipses the other. Detailed information about the stars in an eclipsing binary can be obtained by studying the binary’s light curve. ...
... alternately toward and away from Earth. An eclipsing binary is a system whose orbits are viewed nearly edge on from Earth, so that one star periodically eclipses the other. Detailed information about the stars in an eclipsing binary can be obtained by studying the binary’s light curve. ...
STAR TYPES
... their existence; this stage generally lasts for about 5 billion years. As stars begin to die, they become giants and supergiants (above the main sequence). These stars have depleted their hydrogen supply and are very old. The core contracts as the outer layers expand. These stars will eventually exp ...
... their existence; this stage generally lasts for about 5 billion years. As stars begin to die, they become giants and supergiants (above the main sequence). These stars have depleted their hydrogen supply and are very old. The core contracts as the outer layers expand. These stars will eventually exp ...
Neutron Stars
... Clicker Question: Which of the following is true about a binary pulsar system? A: It will last forever. B: They can only be found in star forming regions C: The total mass of the two pulsars must be more than 10 solar masses. D: Each of the pulsars was produced by a massive star that exploded in a ...
... Clicker Question: Which of the following is true about a binary pulsar system? A: It will last forever. B: They can only be found in star forming regions C: The total mass of the two pulsars must be more than 10 solar masses. D: Each of the pulsars was produced by a massive star that exploded in a ...
The extragalactic universe and distance measurements
... – Tried to determine distribution of stars in Milky Way – described Milky Way as “detached nebula”, with Sun near center. – Thought that the nebulae could be similar systems – Turns out that his conclusions were heavily effected by dust in the Milky Way – Milky Way is much bigger and better ordered ...
... – Tried to determine distribution of stars in Milky Way – described Milky Way as “detached nebula”, with Sun near center. – Thought that the nebulae could be similar systems – Turns out that his conclusions were heavily effected by dust in the Milky Way – Milky Way is much bigger and better ordered ...
ASTR 300 Stars and Stellar Systems Fall 2011
... the luminosity over the distance squared. For the earth d = 1AU, while for Mercury d = 0.39AU. The sun’s luminosity is the same for both, so the flux at Mercury’s distance is 1/0.392 = 1/0.1521 = 6.57 times greater than the flux at the earth. 6. In class we derived a formula for the radius of a star ...
... the luminosity over the distance squared. For the earth d = 1AU, while for Mercury d = 0.39AU. The sun’s luminosity is the same for both, so the flux at Mercury’s distance is 1/0.392 = 1/0.1521 = 6.57 times greater than the flux at the earth. 6. In class we derived a formula for the radius of a star ...
The Gravitational Assist
... flyby design put Voyager close by Neptune’s moon Triton rather than attained more speed—see Figure 4. Such layout of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune occurs about every 175 years. Voyager 2 is still the only spacecraft which has visited Uranus and Neptune [7]. For both Voyagers more than 10 000 t ...
... flyby design put Voyager close by Neptune’s moon Triton rather than attained more speed—see Figure 4. Such layout of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune occurs about every 175 years. Voyager 2 is still the only spacecraft which has visited Uranus and Neptune [7]. For both Voyagers more than 10 000 t ...
Star Formation
... gas is blown away, but its thermal energy comes from gravitational contraction, not fusion 4) The collapsing gas becomes a young stellar object with an accretion disk and jets 4) When the young stellar object begins fusing hydrogen into helium it becomes a true star ...
... gas is blown away, but its thermal energy comes from gravitational contraction, not fusion 4) The collapsing gas becomes a young stellar object with an accretion disk and jets 4) When the young stellar object begins fusing hydrogen into helium it becomes a true star ...
Station 1 - Fall River Public Schools
... extremely far apart. The next nearest star to Earth, besides the sun, is Proxima Centauri. Light travels 9,460,000,000,000 kilometers in one year, or 300,000 kilometers per second. Even if you traveled at the speed of light, it would take you 4.3 years to reach Proxima Centauri. What Makes Up the Un ...
... extremely far apart. The next nearest star to Earth, besides the sun, is Proxima Centauri. Light travels 9,460,000,000,000 kilometers in one year, or 300,000 kilometers per second. Even if you traveled at the speed of light, it would take you 4.3 years to reach Proxima Centauri. What Makes Up the Un ...
Introducing Astronomy
... “Latitude” is measured as Declination, a positive (above) or negative (below) degree from the Celestial Equator ...
... “Latitude” is measured as Declination, a positive (above) or negative (below) degree from the Celestial Equator ...
Measuring the Properties of Stars (ch. 17)
... masses of stars is from binary stars, using Newton’s form of Kepler’s 3rd law. There are three types of binary stars, which depend on how close they are to each other, their relative brightnesses, the distance of the binary, and other factors: a.Visual binaries—can see both stars, and so monitor orb ...
... masses of stars is from binary stars, using Newton’s form of Kepler’s 3rd law. There are three types of binary stars, which depend on how close they are to each other, their relative brightnesses, the distance of the binary, and other factors: a.Visual binaries—can see both stars, and so monitor orb ...
Artifact # 2, The Solar System
... These are the kind of instruments used to discover our galaxy before satellite imaging was available. The first telescope capable of seeing beyond our moon was built in 1609, by Galileo Galilei. ...
... These are the kind of instruments used to discover our galaxy before satellite imaging was available. The first telescope capable of seeing beyond our moon was built in 1609, by Galileo Galilei. ...
Pocket Planetarium V17N3.indd
... an hour-and-a-half before daybreak and is a suitable target for small telescopes. Its atmospheric cloud bands and four Galilean moons are always an impressive sight. The crescent Moon will be 7 degrees to the right of Jupiter on the morning of August 3, and 5 ½ degrees to the right of the giant plan ...
... an hour-and-a-half before daybreak and is a suitable target for small telescopes. Its atmospheric cloud bands and four Galilean moons are always an impressive sight. The crescent Moon will be 7 degrees to the right of Jupiter on the morning of August 3, and 5 ½ degrees to the right of the giant plan ...
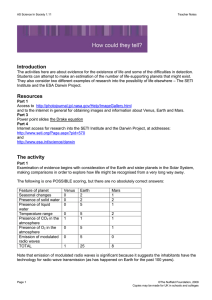
instructor notes: week 2
... planetary orbits are envisaged as circular for simplicity. Even circular orbits are sufficient for understanding the difference between sidereal (star) period of a planet, Psid = time to orbit the Sun, and its synodic period, Psyn = time to complete a cycle of phases as viewed from Earth. The relati ...
... planetary orbits are envisaged as circular for simplicity. Even circular orbits are sufficient for understanding the difference between sidereal (star) period of a planet, Psid = time to orbit the Sun, and its synodic period, Psyn = time to complete a cycle of phases as viewed from Earth. The relati ...
Learning About Stars
... http://www.redorbit.com/modules/reflib/article_images/6_15cc05865f89c4801c5ff2a85d74a93c.jpg ...
... http://www.redorbit.com/modules/reflib/article_images/6_15cc05865f89c4801c5ff2a85d74a93c.jpg ...
Planet Facts Matching Cards
... It is the only planet to have retrograde rotation, which means that it spins from East to West (EW), the opposite of the other planets. ...
... It is the only planet to have retrograde rotation, which means that it spins from East to West (EW), the opposite of the other planets. ...
Ice Giant Neptune Frontlines Potentially Hazardous Asteroid
... also broadcast live celestial events from partner observatories in Arizona, Japan, Hawaii, Cypress, Dubai, South Africa, Australia, New Zealand and Norway. Slooh’s free live broadcasts of potentially hazardous asteroids (PHAs), comets, transits, eclipses, solar activity etc. feature narration by a ...
... also broadcast live celestial events from partner observatories in Arizona, Japan, Hawaii, Cypress, Dubai, South Africa, Australia, New Zealand and Norway. Slooh’s free live broadcasts of potentially hazardous asteroids (PHAs), comets, transits, eclipses, solar activity etc. feature narration by a ...
- Europhysics News
... The huge diversity in the physical and orbital properties of exoplanets forces us to reconsider the model of planetary formation currently accepted for the solar system. This model is based upon the properties of planetary orbits, mostly coplanar, circular and concentric around the Sun. Following th ...
... The huge diversity in the physical and orbital properties of exoplanets forces us to reconsider the model of planetary formation currently accepted for the solar system. This model is based upon the properties of planetary orbits, mostly coplanar, circular and concentric around the Sun. Following th ...
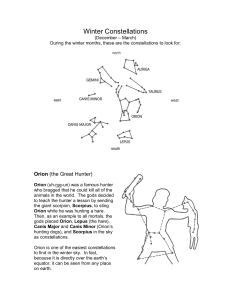
seven winter constellations
... animals in the world. The gods decided to teach the hunter a lesson by sending the giant scorpion, Scorpius, to sting Orion while he was hunting a hare. Then, as an example to all mortals, the gods placed Orion, Lepus (the hare), Canis Major and Canis Minor (Orion’s hunting dogs), and Scorpius in th ...
... animals in the world. The gods decided to teach the hunter a lesson by sending the giant scorpion, Scorpius, to sting Orion while he was hunting a hare. Then, as an example to all mortals, the gods placed Orion, Lepus (the hare), Canis Major and Canis Minor (Orion’s hunting dogs), and Scorpius in th ...
Aquarius (constellation)
Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for ""water-carrier"" or ""cup-carrier"", and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♒), a representation of water.Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac (the sun's apparent path). It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Eridanus the river.