Hertzsprung-Russell Diagrams
... Hertzsprung - Russell Diagram The Hertzsprung -Russell (H-R) Diagram is a graph that plots stars color (spectral type or surface temperature) vs. its luminosity (intrinsic brightness or absolute magnitude). On it, astronomers plot stars' color, temperature, luminosity, spectral type, and evolutiona ...
... Hertzsprung - Russell Diagram The Hertzsprung -Russell (H-R) Diagram is a graph that plots stars color (spectral type or surface temperature) vs. its luminosity (intrinsic brightness or absolute magnitude). On it, astronomers plot stars' color, temperature, luminosity, spectral type, and evolutiona ...
The Role of Gravity in Orbital Motion
... Here we see that given any mass of a larger object M at a given distance r, we can calculate the speed needed by the smaller object to break out of orbit. Supplemental escape velocity: Variable speed: The students can discover their “escape” speed from the system. Using the 1 meter distance trajecto ...
... Here we see that given any mass of a larger object M at a given distance r, we can calculate the speed needed by the smaller object to break out of orbit. Supplemental escape velocity: Variable speed: The students can discover their “escape” speed from the system. Using the 1 meter distance trajecto ...
Geoscience Astronomy Formative on Stellar Evolution and
... the speed of light d. Many astronomers believe that black dwarfs a. are hotter than white dwarfs c. are more massive than white dwarfs b. are more dense than white dwarfs d. do not exist yet A rapidly spinning neutron star that emits bursts of radio and optical energy is a a. supernova c. black hole ...
... the speed of light d. Many astronomers believe that black dwarfs a. are hotter than white dwarfs c. are more massive than white dwarfs b. are more dense than white dwarfs d. do not exist yet A rapidly spinning neutron star that emits bursts of radio and optical energy is a a. supernova c. black hole ...
milkyway - University of Pittsburgh
... spectrum: new spring snow seen in early morning light • Color temperature 4840K • Bluer than incandescent lights (3000K), redder than white on a TV/noon light (6500K): our eyes treat both as white • Handouts: Canva-Paper (OK substitute for snow); galaxy colors relative to different light sources ...
... spectrum: new spring snow seen in early morning light • Color temperature 4840K • Bluer than incandescent lights (3000K), redder than white on a TV/noon light (6500K): our eyes treat both as white • Handouts: Canva-Paper (OK substitute for snow); galaxy colors relative to different light sources ...
KEY Distance, Areas, Volumes-A sense of size and scale from the E
... The stars we see in the night sky are all from our galaxy-the Milky Way. The farthest object in the night sky is a smudge of light from our neighboring galaxy—the Andromeda Galaxy. Is our neighboring galaxy 2.5 light years away or 2.5 million light years away? Is a light year a distance or a time? ...
... The stars we see in the night sky are all from our galaxy-the Milky Way. The farthest object in the night sky is a smudge of light from our neighboring galaxy—the Andromeda Galaxy. Is our neighboring galaxy 2.5 light years away or 2.5 million light years away? Is a light year a distance or a time? ...
134-Notes-a
... Where the last two forms of (1.17) can only be used if the distance d is in parsecs. Often you will see the difference between the apparent and absolute magnitudes denoted via ...
... Where the last two forms of (1.17) can only be used if the distance d is in parsecs. Often you will see the difference between the apparent and absolute magnitudes denoted via ...
HST Paα Survey of the Galactic Center – Seeking the Missing
... We find that many of the Paα-emitting stars are located outside of the three young massive star clusters. As we mentioned previously, they are evolved massive stars with ages of a few Myr. Studying their origin can help us understand the star formation mode within the GC. Two third of these field Pa ...
... We find that many of the Paα-emitting stars are located outside of the three young massive star clusters. As we mentioned previously, they are evolved massive stars with ages of a few Myr. Studying their origin can help us understand the star formation mode within the GC. Two third of these field Pa ...
Stellar population models in the Near-Infrared Meneses
... well suited for studying stellar populations in unresolved galaxies, which are located sufficiently far away from us that it is not possible to distinguish individual stars. They are particularly useful for studying the old and intermediate-age stellar populations in galaxies, which are relatively f ...
... well suited for studying stellar populations in unresolved galaxies, which are located sufficiently far away from us that it is not possible to distinguish individual stars. They are particularly useful for studying the old and intermediate-age stellar populations in galaxies, which are relatively f ...
REVIEWS 18 years of science with the Hubble Space Telescope Julianne J. Dalcanton
... scales of a given system. Are we observing a faint object that happens to be close, or a bright object that is much farther away? Moreover, even when we can make reasonable assumptions about an object’s distance, we frequently lack the precision needed for critical cosmological tests. Over the past ...
... scales of a given system. Are we observing a faint object that happens to be close, or a bright object that is much farther away? Moreover, even when we can make reasonable assumptions about an object’s distance, we frequently lack the precision needed for critical cosmological tests. Over the past ...
BINARY STARS
... compact objects. These refer to stellar objects with extremely high densities, which may be white dwarfs, neutron stars or black holes, all of them have masses of the order of one to ten times the solar mass, compressed to sizes comparable to the diameters of the Earth, a metropolitan city, and Hong ...
... compact objects. These refer to stellar objects with extremely high densities, which may be white dwarfs, neutron stars or black holes, all of them have masses of the order of one to ten times the solar mass, compressed to sizes comparable to the diameters of the Earth, a metropolitan city, and Hong ...
The Initial Mass Function (IMF) Continued
... truncated by reionization. The minimum masses that could cool and collapse, ~108 M~ => ~106 M~ in stars, are strongly suggestive of present day GCs. • DM simulations can reproduce many of the properties of low metallicity cluster populations • High metallicity clusters are much more complicated – fo ...
... truncated by reionization. The minimum masses that could cool and collapse, ~108 M~ => ~106 M~ in stars, are strongly suggestive of present day GCs. • DM simulations can reproduce many of the properties of low metallicity cluster populations • High metallicity clusters are much more complicated – fo ...
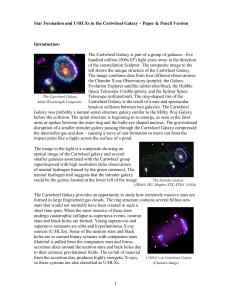
Cartwheel Galaxy - Chandra X
... 8. Is there an X-ray candidate for an active galactic nucleus (AGN) in Arp 147? Explain. 9. Why might there not be new star formation in the elliptical galaxy on the left? 10. A study of ULXs has determined that very few X-ray sources with luminosity greater than 1040 erg s−1 remain after ~15 Myr a ...
... 8. Is there an X-ray candidate for an active galactic nucleus (AGN) in Arp 147? Explain. 9. Why might there not be new star formation in the elliptical galaxy on the left? 10. A study of ULXs has determined that very few X-ray sources with luminosity greater than 1040 erg s−1 remain after ~15 Myr a ...
Supernova and Supernova Remnants lec 1-2
... Euclidean space so that we measure a total flux F (measured in ...
... Euclidean space so that we measure a total flux F (measured in ...
AN INTERSTELLAR CLOUD WITH A HIGH CON
... CN line, R(O) of the (0, 0) band in the B 2 ~+---? X 2 ~+ systellJ, at "A 3874.61 A, as measured by Dunham (194J) in seven stars, does not exceed 7 mA in strength, while the R(l) line at "A 3874.00 A is between two and three times weaker and the P(l) line is only marginally detected. The absorption ...
... CN line, R(O) of the (0, 0) band in the B 2 ~+---? X 2 ~+ systellJ, at "A 3874.61 A, as measured by Dunham (194J) in seven stars, does not exceed 7 mA in strength, while the R(l) line at "A 3874.00 A is between two and three times weaker and the P(l) line is only marginally detected. The absorption ...
Chandra and NIR Observations of Galactic HII Regions
... drive instabilities and X-ray emitting shocks. • The O stars in NGC 6611 are to be contrasted with those in the younger Orion Nebula Cluster with hard, time-variable X-rays and higher LX/Lbol, most likely produced by magnetic activity. ...
... drive instabilities and X-ray emitting shocks. • The O stars in NGC 6611 are to be contrasted with those in the younger Orion Nebula Cluster with hard, time-variable X-rays and higher LX/Lbol, most likely produced by magnetic activity. ...
WORD - Astrophysics
... impossible from the ground, supplying proper motions and distances. An ELT complements and thus strengthens the capabilities of ALMA, which focuses on analyses of the dust and gas content of galaxies. In this Chapter we describe the impact that a 50-100m ELT will have on our understanding of the for ...
... impossible from the ground, supplying proper motions and distances. An ELT complements and thus strengthens the capabilities of ALMA, which focuses on analyses of the dust and gas content of galaxies. In this Chapter we describe the impact that a 50-100m ELT will have on our understanding of the for ...
Logarithmic Scale
... As in the case with pH, multiplying the results by ten is purely for convenience. This way the majority of sounds we examine in decibels will fall in to a range between 0 and 120 rather than 0 and 12. A note about the Richter Scale. Charles Richter introduced his scale in 1935 in order to differentia ...
... As in the case with pH, multiplying the results by ten is purely for convenience. This way the majority of sounds we examine in decibels will fall in to a range between 0 and 120 rather than 0 and 12. A note about the Richter Scale. Charles Richter introduced his scale in 1935 in order to differentia ...
Multiwavelength Astronomy: Your World in Different Lights
... These are two versions of the same image, with the same scale of temperature, but the right picture has a larger range of colors to show the same range in temperature. When there are more colors in the same temperature range, you can easily detect more detail about small temperature differences. Of ...
... These are two versions of the same image, with the same scale of temperature, but the right picture has a larger range of colors to show the same range in temperature. When there are more colors in the same temperature range, you can easily detect more detail about small temperature differences. Of ...
Solution
... the red one must be smaller. But by Stefan-Boltzmann's Law, its luminosity/area must also be smaller, and they are the same size. So the red one is less luminous. 3. ( T F ) Using parallax, astronomers can now reliably measure the distance of most of the stars in our galaxy. False. Sad to say, most ...
... the red one must be smaller. But by Stefan-Boltzmann's Law, its luminosity/area must also be smaller, and they are the same size. So the red one is less luminous. 3. ( T F ) Using parallax, astronomers can now reliably measure the distance of most of the stars in our galaxy. False. Sad to say, most ...
the magellanic clouds newsletter - Keele University Astrophysics
... ranging from 5.8 to 20 K after removing sources with the 1% largest temperature estimates. Using seven independent methods, reliable distance estimates have been obtained for 5574 sources, which allows us to derive their physical properties such as their mass, physical size, mean density and luminos ...
... ranging from 5.8 to 20 K after removing sources with the 1% largest temperature estimates. Using seven independent methods, reliable distance estimates have been obtained for 5574 sources, which allows us to derive their physical properties such as their mass, physical size, mean density and luminos ...
Description of Pictures In the Dome
... to be left over from the formation of the cluster (hence the alternate name Maia Nebula after the star Maia), but is now known to be an unrelated dust cloud in the interstellar medium that the stars are currently passing through. Astronomers estimate that the cluster will survive for about another 2 ...
... to be left over from the formation of the cluster (hence the alternate name Maia Nebula after the star Maia), but is now known to be an unrelated dust cloud in the interstellar medium that the stars are currently passing through. Astronomers estimate that the cluster will survive for about another 2 ...
Student Worksheet
... After you learn how to classify galaxies, you will be able to explain what this statement means. When scientists see objects in nature that share some features, but not others, they find that grouping, or classifying them is a good idea. First they must decide what scheme or plan they will use to de ...
... After you learn how to classify galaxies, you will be able to explain what this statement means. When scientists see objects in nature that share some features, but not others, they find that grouping, or classifying them is a good idea. First they must decide what scheme or plan they will use to de ...
Stars in Motion
... The image contains two spectra; the image of one spectrum is horizontally cut in half by the other. The thin, light colored band running down the horizontal centerline of the image is the absorption spectrum of the (spectral type A) star being observed. Dark vertical lines in this band represent abs ...
... The image contains two spectra; the image of one spectrum is horizontally cut in half by the other. The thin, light colored band running down the horizontal centerline of the image is the absorption spectrum of the (spectral type A) star being observed. Dark vertical lines in this band represent abs ...
Cosmic distance ladder
The cosmic distance ladder (also known as the extragalactic distance scale) is the succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects. A real direct distance measurement of an astronomical object is possible only for those objects that are ""close enough"" (within about a thousand parsecs) to Earth. The techniques for determining distances to more distant objects are all based on various measured correlations between methods that work at close distances and methods that work at larger distances. Several methods rely on a standard candle, which is an astronomical object that has a known luminosity.The ladder analogy arises because no one technique can measure distances at all ranges encountered in astronomy. Instead, one method can be used to measure nearby distances, a second can be used to measure nearby to intermediate distances, and so on. Each rung of the ladder provides information that can be used to determine the distances at the next higher rung.