The Universe - the Scientia Review
... classified as elliptical. Because of their brightness, we usually can’t see any features in these galaxies. Some elliptical galaxies have only a hundred million stars, while others contain as many as one trillion stars, most of This picture of the M87 galaxy clearly which are older and shows the bri ...
... classified as elliptical. Because of their brightness, we usually can’t see any features in these galaxies. Some elliptical galaxies have only a hundred million stars, while others contain as many as one trillion stars, most of This picture of the M87 galaxy clearly which are older and shows the bri ...
sun.galaxy.notes
... But what determines the size of a star? Gravity wants to crush the star So why doesn’t it? Because the outward pressure Or force of energy from Fusion balances out the inward force of gravity This keeps the star in a state of balance or equilibrium! ...
... But what determines the size of a star? Gravity wants to crush the star So why doesn’t it? Because the outward pressure Or force of energy from Fusion balances out the inward force of gravity This keeps the star in a state of balance or equilibrium! ...
Central Massive Objects: The Stellar Nuclei – Black Hole
... megamasers, along with measurements of their stellar velocity dispersion. These galaxies lie below the M–σ relation, show ing a large scatter (see Figure 3). Moreover, active galactic nuclei (AGN) diagnostics help to measure black hole masses at the low-mass end. The future for black hole detection ...
... megamasers, along with measurements of their stellar velocity dispersion. These galaxies lie below the M–σ relation, show ing a large scatter (see Figure 3). Moreover, active galactic nuclei (AGN) diagnostics help to measure black hole masses at the low-mass end. The future for black hole detection ...
SouthamptonTalkPitkin - LIGO dcc
... • Lots of exciting science can be uncovered with GWs • Searches for many source types are well tested on initial GW detector data • Advanced detectors are on schedule to begin ...
... • Lots of exciting science can be uncovered with GWs • Searches for many source types are well tested on initial GW detector data • Advanced detectors are on schedule to begin ...
- newmanlib.ibri.org
... universe is not infinite), OR the really distant stars whose images would cover every speck of the sky have not been burning long enough for their light to get here yet (so the universe hasn't always existed). 3. The visible universe is probably only some 10-20 billion years old. This appears to be ...
... universe is not infinite), OR the really distant stars whose images would cover every speck of the sky have not been burning long enough for their light to get here yet (so the universe hasn't always existed). 3. The visible universe is probably only some 10-20 billion years old. This appears to be ...
Spectroscopy PPT
... Spectra (rainbows of diffracted light) can come from a (hot) glowing solid, a glowing liquid or a glowing gas (star). ...
... Spectra (rainbows of diffracted light) can come from a (hot) glowing solid, a glowing liquid or a glowing gas (star). ...
Sterrenstelsels en Cosmologie Docent: M. Franx, kamer 425
... magnitude (which would be appropriate for a star). Hence we measure the amount of light per area on the sky. This is called the surface brightness. It is often expressed as magnitude per square arcsec. How to measure average surface brightness profile ? Measure the intensity on ellipses of (nearly) ...
... magnitude (which would be appropriate for a star). Hence we measure the amount of light per area on the sky. This is called the surface brightness. It is often expressed as magnitude per square arcsec. How to measure average surface brightness profile ? Measure the intensity on ellipses of (nearly) ...
HR Diagram Explorer Worksheet
... stars we perceive as bright in the night sky really bright?” (hint: You may find the options labeled both the nearest and brightest stars and the overlap useful.) ...
... stars we perceive as bright in the night sky really bright?” (hint: You may find the options labeled both the nearest and brightest stars and the overlap useful.) ...
PowerPoint - Mark Kidger
... • In the early-1950s, only 8 radio sources in the sky had been identified. • A race started to identify objects, particularly from the new 3rd Cambridge (3C) catalogue of radio sources. • Many were found to be faint galaxies, but a few defied identification. • In 1960 Tom Matthews and John Bolton id ...
... • In the early-1950s, only 8 radio sources in the sky had been identified. • A race started to identify objects, particularly from the new 3rd Cambridge (3C) catalogue of radio sources. • Many were found to be faint galaxies, but a few defied identification. • In 1960 Tom Matthews and John Bolton id ...
General Module information
... Explain why fusion of light nuclei releases energy in terms of the binding energy per nucleon and its dependence on atomic mass. Explain qualitatively what the “Gamow peak” is and why it occurs. Recognise the equations for the three reaction processes: the p-p reaction, the CNO cycle and the triple- ...
... Explain why fusion of light nuclei releases energy in terms of the binding energy per nucleon and its dependence on atomic mass. Explain qualitatively what the “Gamow peak” is and why it occurs. Recognise the equations for the three reaction processes: the p-p reaction, the CNO cycle and the triple- ...
distance
... as photographed by Edwin Hubble using the then-new 100 inch telescope on Mt. Wilson, outside LA. World’s largest at the time. ...
... as photographed by Edwin Hubble using the then-new 100 inch telescope on Mt. Wilson, outside LA. World’s largest at the time. ...
CoRoT Observations of O Stars: Diverse Origins of Variability
... At the moment we can only speculate about the possible causes of this red noise in O-type stars. One possibility is that it is caused by the sub-surface convection zone found in theoretical modeling (Cantiello et al. 2009). This zone is assumed to be responsible for a number of surface effects, such ...
... At the moment we can only speculate about the possible causes of this red noise in O-type stars. One possibility is that it is caused by the sub-surface convection zone found in theoretical modeling (Cantiello et al. 2009). This zone is assumed to be responsible for a number of surface effects, such ...
the life cycle of stars - North American Montessori Center
... universe began. Then gravity forced the atoms to join together into ever larger clusters. Those clusters grew large enough that their gravity attracted other groups of atoms, until stars eventually formed. Those stars attracted other stars until small galaxies formed. Those galaxies attracted other ...
... universe began. Then gravity forced the atoms to join together into ever larger clusters. Those clusters grew large enough that their gravity attracted other groups of atoms, until stars eventually formed. Those stars attracted other stars until small galaxies formed. Those galaxies attracted other ...
An introduction to photometry and photometric measurements Henry
... • In this case, A is a constant like the exposure time, Z is the instrumental zero point and kX is the extinction correction. • This is a simple least-squares fit. But in general a system of equations will have to be solved: ...
... • In this case, A is a constant like the exposure time, Z is the instrumental zero point and kX is the extinction correction. • This is a simple least-squares fit. But in general a system of equations will have to be solved: ...
G060324-00 - DCC
... Elliptical Star forming Elliptical Star forming Galaxy cluster Faint star forming galaxy ...
... Elliptical Star forming Elliptical Star forming Galaxy cluster Faint star forming galaxy ...
US - Real Science
... In most starbursts the surge in starbirth is _________ when two galaxies come too close together. Mutual attraction _______ the galaxies causes immense turmoil in their gas and ____, and triggers the burst of star formation. NGC ______ appearance shows it has seen troubled times. Its spiral ____ lo ...
... In most starbursts the surge in starbirth is _________ when two galaxies come too close together. Mutual attraction _______ the galaxies causes immense turmoil in their gas and ____, and triggers the burst of star formation. NGC ______ appearance shows it has seen troubled times. Its spiral ____ lo ...
Scorpius: The Scorpion Σκορπιος Amber Perrine Physics 1040 MWF
... binoculars. It has a magnitude of 3.3 with the highest degree of concentration toward the center. It contains about 80 stars, with a distance of 980 light years. Ptolemy described it as the “nebula following the sting of Scorpius.” M7’s age is estimated at about 220 million years old and has a combi ...
... binoculars. It has a magnitude of 3.3 with the highest degree of concentration toward the center. It contains about 80 stars, with a distance of 980 light years. Ptolemy described it as the “nebula following the sting of Scorpius.” M7’s age is estimated at about 220 million years old and has a combi ...
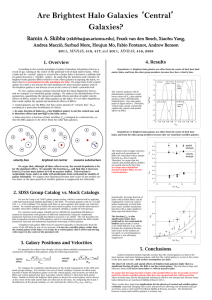
Ramin A. Skibba - Southern California Center for Galaxy Evolution
... We use the Yang et al. (2007) galaxy group catalog, which is constructed by applying a DM halo-based group-finding algorithm to the SDSS. We include galaxies with mr=-18 and 0.01 < z < 0.20, yielding 7234 groups with three or more galaxies that satisfy our selection criteria. We exclude groups in wh ...
... We use the Yang et al. (2007) galaxy group catalog, which is constructed by applying a DM halo-based group-finding algorithm to the SDSS. We include galaxies with mr=-18 and 0.01 < z < 0.20, yielding 7234 groups with three or more galaxies that satisfy our selection criteria. We exclude groups in wh ...
Hubble Redshift - at www.arxiv.org.
... Recent measurements of Hubble redshift from supernovae are inconsistent with the standard theoretical model of an expanding Friedmann universe. Figure 1 shows the Hubble redshift for 37 supernovae measured by Riess et al.1 illustrating that a positive cosmological constant must be added to the equat ...
... Recent measurements of Hubble redshift from supernovae are inconsistent with the standard theoretical model of an expanding Friedmann universe. Figure 1 shows the Hubble redshift for 37 supernovae measured by Riess et al.1 illustrating that a positive cosmological constant must be added to the equat ...
... of the main sequence, consistent with moderate (",20 per cent) contamination of the secondary light by an accretion disc. We use the K magnitudes to estimate the distances of the stars. We show that most lie within about 400 pc, and only two of the stars in our sample (RU LMi and DO Leo) are convinc ...
Cepheus (constellation)
... supergiant star 980 light-years from Earth. It was discovered to be variable by John Goodricke in 1784. It varies between 3.5m and 4.4m over a period of 5 days and 9 hours. The Cepheids are a class of pulsating variable stars; Delta Cephei has a minimum size of 40 solar diameters and a maximum size ...
... supergiant star 980 light-years from Earth. It was discovered to be variable by John Goodricke in 1784. It varies between 3.5m and 4.4m over a period of 5 days and 9 hours. The Cepheids are a class of pulsating variable stars; Delta Cephei has a minimum size of 40 solar diameters and a maximum size ...
Red Shift - The General Science Journal
... frequency as at the source. Even this relationship cannot continue indefinitely. At some point the slowing and the separating functions must diverge and affect frequency. One reason would be the existence of many other gravitation sources. The divergence leads to the slowing having more effect upon ...
... frequency as at the source. Even this relationship cannot continue indefinitely. At some point the slowing and the separating functions must diverge and affect frequency. One reason would be the existence of many other gravitation sources. The divergence leads to the slowing having more effect upon ...
Powerpoint slides
... the Andromeda Galaxy. How far away does the audience think the Andromeda Galaxy is from the Milky Way? After their experience with stars within the galaxy, many audience members will try to send your second volunteer to another city! Surprisingly enough, the answer is eight feet, or approximately 20 ...
... the Andromeda Galaxy. How far away does the audience think the Andromeda Galaxy is from the Milky Way? After their experience with stars within the galaxy, many audience members will try to send your second volunteer to another city! Surprisingly enough, the answer is eight feet, or approximately 20 ...
sections 16-18 instructor notes
... ii. by extrapolating the versus σΠ2 curve to its
extreme values for globular clusters. This technique also
has uncertainties owing to the unknown rate of rotation
for the globular cluster system about the Galactic centre,
as well as to the possible existence of two distinct groups
of globulars. ...
... ii. by extrapolating the
Cosmic distance ladder
The cosmic distance ladder (also known as the extragalactic distance scale) is the succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects. A real direct distance measurement of an astronomical object is possible only for those objects that are ""close enough"" (within about a thousand parsecs) to Earth. The techniques for determining distances to more distant objects are all based on various measured correlations between methods that work at close distances and methods that work at larger distances. Several methods rely on a standard candle, which is an astronomical object that has a known luminosity.The ladder analogy arises because no one technique can measure distances at all ranges encountered in astronomy. Instead, one method can be used to measure nearby distances, a second can be used to measure nearby to intermediate distances, and so on. Each rung of the ladder provides information that can be used to determine the distances at the next higher rung.