June 2015 - Bristol Astronomical Society
... first find the orange star Arcturus and continue down to find the white, first magnitude star, Spica, in Virgo. Saturn, a little brighter than Spica, lies in Libra down to its lower left and will appear slightly yellow in colour. Held steady, binoculars should enable you to see Saturn's brightest mo ...
... first find the orange star Arcturus and continue down to find the white, first magnitude star, Spica, in Virgo. Saturn, a little brighter than Spica, lies in Libra down to its lower left and will appear slightly yellow in colour. Held steady, binoculars should enable you to see Saturn's brightest mo ...
Formation of the Most Distant & Luminous Quasars
... – Both BHs and host galaxies build up through hierarchical mergers. – BHs accrete gas under Eddington limit in a selfregulated manner owing to feedback. • Our model should provide a viable mechanism for other luminous quasars, no exotic process is needed. ...
... – Both BHs and host galaxies build up through hierarchical mergers. – BHs accrete gas under Eddington limit in a selfregulated manner owing to feedback. • Our model should provide a viable mechanism for other luminous quasars, no exotic process is needed. ...
2_ISM - UCT Astronomy Department
... observing the same (standard) source several time during the night with a wide variety in zenith distances – usually well known for established Observatories. ...
... observing the same (standard) source several time during the night with a wide variety in zenith distances – usually well known for established Observatories. ...
Lecture 12: Evolution of the Galaxy
... the ages of stars in clusters from their HR diagrams. The metallicity increased rapidly in the first few × 108 yr, but only slowly thereafter. ...
... the ages of stars in clusters from their HR diagrams. The metallicity increased rapidly in the first few × 108 yr, but only slowly thereafter. ...
Gaps
... • Fast HB rotation, although maybe not present in all clusters, is a fairly common feature. ...
... • Fast HB rotation, although maybe not present in all clusters, is a fairly common feature. ...
L7-Potentials-orbits
... Constants of Motion – functions of phase-space coordinates and time which are constant along the orbit C (x,v,t) = const where v = dx/dt In phase-space of 2n dimensions, there are always 2n independent constants of motion. We will see in spherical potentials, there are 4 constants of motion (2 dimen ...
... Constants of Motion – functions of phase-space coordinates and time which are constant along the orbit C (x,v,t) = const where v = dx/dt In phase-space of 2n dimensions, there are always 2n independent constants of motion. We will see in spherical potentials, there are 4 constants of motion (2 dimen ...
Hubble Does Double-Duty Science: Finding Planets and
... solar flare behavior. Based on the star’s brightness, we saw modest flares in the brighter stars (flares increase of 10% or less in the star’s brightness) and larger flares in the fainter stars. A surprising fraction (85%) of flaring stars showed underlying variations, despite being a small componen ...
... solar flare behavior. Based on the star’s brightness, we saw modest flares in the brighter stars (flares increase of 10% or less in the star’s brightness) and larger flares in the fainter stars. A surprising fraction (85%) of flaring stars showed underlying variations, despite being a small componen ...
Dark Matter Concept Questions
... 6. Do your results support the following statement? “It is reasonable to expect that stars orbit around the gravitational mass contained within the radius of their orbit in the same way that planets orbit around the Sun.” Discuss. 7. Explain the shape of your plot for measured speed against orbital ...
... 6. Do your results support the following statement? “It is reasonable to expect that stars orbit around the gravitational mass contained within the radius of their orbit in the same way that planets orbit around the Sun.” Discuss. 7. Explain the shape of your plot for measured speed against orbital ...
instructor notes: weeks 9/10
... Surveys of the spatial distribution of galaxies indicate that they are not as “homogeneous” as sometimes thought. The location and brightness of galaxies in this view indicate the patchy nature of their distribution. ...
... Surveys of the spatial distribution of galaxies indicate that they are not as “homogeneous” as sometimes thought. The location and brightness of galaxies in this view indicate the patchy nature of their distribution. ...
Turning AGN Microlensing From a Curiosity Into a Tool
... • Computationally challenging to allow stars to move – we need ~3 GByte to analyze a systems at 2 wavelengths with static patterns, but ~300 GBytes if we allow the stars to move and need an animated sequence of patterns. Probably doable on shared memory machines (and we have experimented with this), ...
... • Computationally challenging to allow stars to move – we need ~3 GByte to analyze a systems at 2 wavelengths with static patterns, but ~300 GBytes if we allow the stars to move and need an animated sequence of patterns. Probably doable on shared memory machines (and we have experimented with this), ...
16.1 A Little History
... ble explanations, the most intriguing possibility is that stars more massive than ∼ 17M may collapse ‘quietly’ to form black holes and either very faint supernovae or no supernova at all. ...
... ble explanations, the most intriguing possibility is that stars more massive than ∼ 17M may collapse ‘quietly’ to form black holes and either very faint supernovae or no supernova at all. ...
Lecture 8: Spiral Structure
... This model pictures spiral arms not as material arms at all but rather as the result of density waves moving through the Galaxy’s disk. The spiral structure of a galaxy is regarded as a wave pattern resulting from gravitational instabilities. The density wave moves through the stellar and interstell ...
... This model pictures spiral arms not as material arms at all but rather as the result of density waves moving through the Galaxy’s disk. The spiral structure of a galaxy is regarded as a wave pattern resulting from gravitational instabilities. The density wave moves through the stellar and interstell ...
a thermonuclear flame has almost completed TEN SECONDS AFTER IGNITION,
... reaches the density of an atomic nucleus. Like a crystal vase falling onto a concrete floor, the collapsing material releases enough gravitational potential energy to blow the rest of the star apart. An alternative emerged in 1960, when Fred Hoyle of the University of Cambridge and Willy Fowler of Ca ...
... reaches the density of an atomic nucleus. Like a crystal vase falling onto a concrete floor, the collapsing material releases enough gravitational potential energy to blow the rest of the star apart. An alternative emerged in 1960, when Fred Hoyle of the University of Cambridge and Willy Fowler of Ca ...
Recent Advances in Astrometry with the VLBA
... Effects of Increasing Q0 • Reduces kinematic distances: Dk by 15%, hence… Molecular cloud sizes (R D) by 15% Young star luminosities: L R2 by 30% (increasing YSO ages) Cloud masses (from column density & size): M R2 by 30% • Milky Way’s dark matter halo mass: M (Vmax) 2 RVir Vmax Q0 & RV ...
... Effects of Increasing Q0 • Reduces kinematic distances: Dk by 15%, hence… Molecular cloud sizes (R D) by 15% Young star luminosities: L R2 by 30% (increasing YSO ages) Cloud masses (from column density & size): M R2 by 30% • Milky Way’s dark matter halo mass: M (Vmax) 2 RVir Vmax Q0 & RV ...
The Milky Way II AST 112
... and gas to the ISM. • This material expands, cools, and collapses back into stars… • … and on and on and on. ...
... and gas to the ISM. • This material expands, cools, and collapses back into stars… • … and on and on and on. ...
aaswinter07ppt
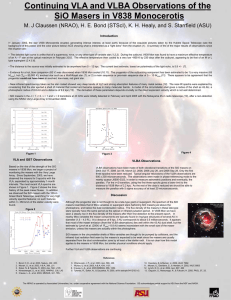
... masers resembles that of Mira variables or supergiant stars harboring SiO masers just above the photosphere, and below the dust condensation radius. The flux density of the masers in these late-type stars typically have the same period as the optical or infrared pulsation period. In V838 Mon we have ...
... masers resembles that of Mira variables or supergiant stars harboring SiO masers just above the photosphere, and below the dust condensation radius. The flux density of the masers in these late-type stars typically have the same period as the optical or infrared pulsation period. In V838 Mon we have ...
The correct answers are written in bold, italic and underlined. The
... • The core of a massive star is gradually transformed into iron by thermonuclear fusion reactions until it collapses, causing the outer layers to explode off the star. • Helium shell flashes push the outer layers of an asymptotic giant branch star out into space, leaving behind a stellar remnant. Ty ...
... • The core of a massive star is gradually transformed into iron by thermonuclear fusion reactions until it collapses, causing the outer layers to explode off the star. • Helium shell flashes push the outer layers of an asymptotic giant branch star out into space, leaving behind a stellar remnant. Ty ...
The Tip of the Red Giant Branch and Distance of the Magellanic
... not make any attempt to estimate this error because we lack information for that purpose (we would need spectra and/or UBVRIJHKL photometry on a sample of stars). For the AGB star models from Groenewegen and collaborators, we can estimate part of this error. The (J − KS ) colour does not provide eno ...
... not make any attempt to estimate this error because we lack information for that purpose (we would need spectra and/or UBVRIJHKL photometry on a sample of stars). For the AGB star models from Groenewegen and collaborators, we can estimate part of this error. The (J − KS ) colour does not provide eno ...
Task - Illustrative Mathematics
... when they are placed in increasing order. On the other hand, outliers can have a dramatic impact on the mean, especially if the data set is small or if these outliers are several orders of magnitude larger than most other data points. This is made particularly clear in the case of the distance of th ...
... when they are placed in increasing order. On the other hand, outliers can have a dramatic impact on the mean, especially if the data set is small or if these outliers are several orders of magnitude larger than most other data points. This is made particularly clear in the case of the distance of th ...
Galactic Archaeology: Current Surveys
... It was clear from their apparently contradictory conclusions that it was not possible that both ELS and SZ could be correct. We now have a better understanding of the biases that can arise in proper-motion selected samples such as that used by ELS (see, for example, Bond 1970; Carney et al. 1989). W ...
... It was clear from their apparently contradictory conclusions that it was not possible that both ELS and SZ could be correct. We now have a better understanding of the biases that can arise in proper-motion selected samples such as that used by ELS (see, for example, Bond 1970; Carney et al. 1989). W ...
night watch - Warren Astronomical Society
... -2The best method for determining the radius of Pluto, as it is for Neptune, is to observe a stellar occultation. It was predicted that Pluto would pass near a 15th magnitude star in 1965, and so the passage was observed very closely by several observatories to see if the star would be occulted. We ...
... -2The best method for determining the radius of Pluto, as it is for Neptune, is to observe a stellar occultation. It was predicted that Pluto would pass near a 15th magnitude star in 1965, and so the passage was observed very closely by several observatories to see if the star would be occulted. We ...
CAPSTONE-poster
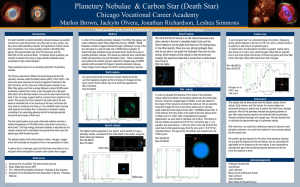
... Our team decided to explore planetary nebulae because we wanted to know how were they formed, why they had so many colors, why they were called planetary nebulae, the significance of their names, their composition, how many possibly existed in the Milky Way galaxy, their approximate age, their first ...
... Our team decided to explore planetary nebulae because we wanted to know how were they formed, why they had so many colors, why they were called planetary nebulae, the significance of their names, their composition, how many possibly existed in the Milky Way galaxy, their approximate age, their first ...
To Measure the Sky: An Introduction to Observational Astronomy.
... happens. The rhythms of the spinning and orbiting Earth gave astronomy an early and intimate connection to timekeeping. Because our Universe is always changing, astronomers need to know what time it is. The ‘‘fixed stars’’ are an old metaphor for the unchanging and eternal, but positions of real cele ...
... happens. The rhythms of the spinning and orbiting Earth gave astronomy an early and intimate connection to timekeeping. Because our Universe is always changing, astronomers need to know what time it is. The ‘‘fixed stars’’ are an old metaphor for the unchanging and eternal, but positions of real cele ...
Cosmic distance ladder
The cosmic distance ladder (also known as the extragalactic distance scale) is the succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects. A real direct distance measurement of an astronomical object is possible only for those objects that are ""close enough"" (within about a thousand parsecs) to Earth. The techniques for determining distances to more distant objects are all based on various measured correlations between methods that work at close distances and methods that work at larger distances. Several methods rely on a standard candle, which is an astronomical object that has a known luminosity.The ladder analogy arises because no one technique can measure distances at all ranges encountered in astronomy. Instead, one method can be used to measure nearby distances, a second can be used to measure nearby to intermediate distances, and so on. Each rung of the ladder provides information that can be used to determine the distances at the next higher rung.