Checklist for Geo- vs. Heliocentric Model of Universe
... around the Sun The is no obvious explanation for why objects fall to the ground in a model in which the Earth is not centrally located; only later would Newton explain gravity in this context The Earth moves, so the apparent lack of stellar parallax must be due to huge stellar distances; parallax sh ...
... around the Sun The is no obvious explanation for why objects fall to the ground in a model in which the Earth is not centrally located; only later would Newton explain gravity in this context The Earth moves, so the apparent lack of stellar parallax must be due to huge stellar distances; parallax sh ...
Early-type stars in the core of the young open cluster Westerlund 2
... cluster displays significant photometric variability above 1% at the 1-σ level. The twelve brightest O-type stars are found to have spectral types between O3 and O6.5, significantly earlier than previously thought. Conclusions. The distance of the early-type stars in Westerlund 2 is established to b ...
... cluster displays significant photometric variability above 1% at the 1-σ level. The twelve brightest O-type stars are found to have spectral types between O3 and O6.5, significantly earlier than previously thought. Conclusions. The distance of the early-type stars in Westerlund 2 is established to b ...
Q1. Describe, in as much detail as you can: • the evidence that the
... Satellites fitted with various telescopes orbit the Earth. These telescopes detect different types of electromagnetic radiation. Why are telescopes that detect different types of electromagnetic waves used to observe the Universe? ...
... Satellites fitted with various telescopes orbit the Earth. These telescopes detect different types of electromagnetic radiation. Why are telescopes that detect different types of electromagnetic waves used to observe the Universe? ...
Image filtering
... background in a regular grid of background meshes (“background map”), and interpolating these values to create a smooth image of the background. The background map has to be filtered to avoid oscillations of the interpolation around bright sources (the background map is under-sampled with respect ...
... background in a regular grid of background meshes (“background map”), and interpolating these values to create a smooth image of the background. The background map has to be filtered to avoid oscillations of the interpolation around bright sources (the background map is under-sampled with respect ...
Longitude by the Method of Lunar Distance
... confining celestial spheres of the earth-centered Ptolemaic theory and into the vast expanse of the Copernican universe. In 1611 Galileo devised tables of his newly discovered moons of Jupiter, which could be used to determine time and thus the longitude of the observer. These tables worked in theor ...
... confining celestial spheres of the earth-centered Ptolemaic theory and into the vast expanse of the Copernican universe. In 1611 Galileo devised tables of his newly discovered moons of Jupiter, which could be used to determine time and thus the longitude of the observer. These tables worked in theor ...
Discovery of White Dwarfs—8 Oct
... Main-sequence or dwarf stars Giants Horizontal-branch stars White dwarfs are too faint for these observations. A star lives a long time as a dwarf. It is on the main sequence. When it runs out of fuel, it becomes a giant and subsequently “traces out the giant branch.” ...
... Main-sequence or dwarf stars Giants Horizontal-branch stars White dwarfs are too faint for these observations. A star lives a long time as a dwarf. It is on the main sequence. When it runs out of fuel, it becomes a giant and subsequently “traces out the giant branch.” ...
MillionaireGame__Science_Review
... TRUE! Some matter remains after the explosion, and the shrunken core can become either a neutron star or a black hole. ...
... TRUE! Some matter remains after the explosion, and the shrunken core can become either a neutron star or a black hole. ...
The Evolution of Galaxy - Tufts Institute of Cosmology
... pebbles, into a swimming pool. The balloon represents the merging group: the water is gas, and the pebbles are galaxies. The swimming pool is the main cluster. When the balloon hits the water in the pool, it ruptures. Its own water stays at the surface and mixes very slowly, but the pebbles can trav ...
... pebbles, into a swimming pool. The balloon represents the merging group: the water is gas, and the pebbles are galaxies. The swimming pool is the main cluster. When the balloon hits the water in the pool, it ruptures. Its own water stays at the surface and mixes very slowly, but the pebbles can trav ...
aaswinter06
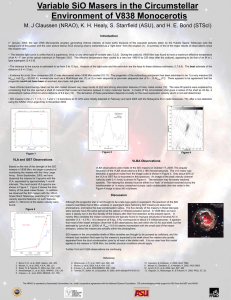
... masers resembles that of Mira variables or supergiant stars harboring SiO masers just above the photosphere, and below the dust condensation radius. The flux density of the masers in these late-type stars typically have the same period as the optical or infrared pulsation period. In V838 Mon we have ...
... masers resembles that of Mira variables or supergiant stars harboring SiO masers just above the photosphere, and below the dust condensation radius. The flux density of the masers in these late-type stars typically have the same period as the optical or infrared pulsation period. In V838 Mon we have ...
The Primeval Populations of the Ultra
... than that of any globular cluster, the age determination must rely upon theoretical isochrones (see §3.2), but a comparison to M92 is still instructive. In our analysis, the largest uncertainties are the distances of the UFDs relative to the globular cluster calibrators of our isochrone library, wit ...
... than that of any globular cluster, the age determination must rely upon theoretical isochrones (see §3.2), but a comparison to M92 is still instructive. In our analysis, the largest uncertainties are the distances of the UFDs relative to the globular cluster calibrators of our isochrone library, wit ...
슬라이드 1
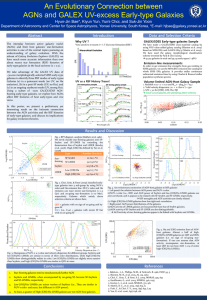
... advent of Galaxy Evolution Explorer (GALEX), we have much more accurate information than ever about recent star formation (RSF) histories of early-type galaxies in the local universe (z < 0.2). ...
... advent of Galaxy Evolution Explorer (GALEX), we have much more accurate information than ever about recent star formation (RSF) histories of early-type galaxies in the local universe (z < 0.2). ...
83-98
... DL Cas, BM Per, TX Cyg, X Cyg, CK Sct and UZ Sct using high-dispersion spectra and fine analysis. However, for X Cyg the estimate of HP is higher than the one derived by LL by 0.18 dex which is surprising. The differences in phases can partly account for the discrepancy. The observations of HP were ...
... DL Cas, BM Per, TX Cyg, X Cyg, CK Sct and UZ Sct using high-dispersion spectra and fine analysis. However, for X Cyg the estimate of HP is higher than the one derived by LL by 0.18 dex which is surprising. The differences in phases can partly account for the discrepancy. The observations of HP were ...
wing galaxies: a formation mechanism of the clumpy irregular galaxy
... is made for the data at PA = 0° through the clump B. The component trapped by the intruder is also seen in the model result. However, this component is not discriminated from the intrude in the observation. In the right panels, we show the velocity field of the intruder. The distance is measured fro ...
... is made for the data at PA = 0° through the clump B. The component trapped by the intruder is also seen in the model result. However, this component is not discriminated from the intrude in the observation. In the right panels, we show the velocity field of the intruder. The distance is measured fro ...
Document
... Very compressed and rich star clusters Compressed clusters of small and large (i.e., faint and bright) stars ...
... Very compressed and rich star clusters Compressed clusters of small and large (i.e., faint and bright) stars ...
Resolved SPs : simulations
... The description of the details in the shape of the tracks, and the evolutionary lifetimes (use normalized independent variable) The description of photometric errors, blending and completeness (evaluate crowding conditions: if there is more than 1 star per resolution element the photometry is bad; c ...
... The description of the details in the shape of the tracks, and the evolutionary lifetimes (use normalized independent variable) The description of photometric errors, blending and completeness (evaluate crowding conditions: if there is more than 1 star per resolution element the photometry is bad; c ...
Abstracts - Space Telescope Science Institute
... HST/WFC3 Observations of the Grand Design Spiral M83: Star Clusters, Supernova Remnants, and More The face-on grand design spiral galaxy M83 (d=4.6 Mpc) is an actively star-forming galaxy, with spiral arms filled with giant H II regions and an intense nuclear starburst. The galaxy itself is a verita ...
... HST/WFC3 Observations of the Grand Design Spiral M83: Star Clusters, Supernova Remnants, and More The face-on grand design spiral galaxy M83 (d=4.6 Mpc) is an actively star-forming galaxy, with spiral arms filled with giant H II regions and an intense nuclear starburst. The galaxy itself is a verita ...
IAU-Perraut-2013 - Putting A Stars into Context
... Coupled with spectroscopy, optical interferometry can allow kinematics studies of A stars’ environments. Going beyong angular diameter measurements allows limbdarkening to be derived and besides surfaces of fast rotators to be ...
... Coupled with spectroscopy, optical interferometry can allow kinematics studies of A stars’ environments. Going beyong angular diameter measurements allows limbdarkening to be derived and besides surfaces of fast rotators to be ...
observation reports
... 21:40 UT (22:40 local) Aligned ETX with Altair and Alpheratz. I checked up on several variables, and R Cygni was now equal to the 9.9 field star in brightness. Chi Cygni had now sunk to 8.3, and was becoming difficult to find in the rich field. A new one for me was R Draconis, which this time was ne ...
... 21:40 UT (22:40 local) Aligned ETX with Altair and Alpheratz. I checked up on several variables, and R Cygni was now equal to the 9.9 field star in brightness. Chi Cygni had now sunk to 8.3, and was becoming difficult to find in the rich field. A new one for me was R Draconis, which this time was ne ...
Stars in the Sky Stars in the Sky
... that light travels through space in 1 year. Because the speed of light through space is about 300,000 km/s, it travels approximately 9.46 trillion kilometers in 1 year! Figure 6 below illustrates how far away some stars that we see really are. Even after astronomers figured out that stars were far a ...
... that light travels through space in 1 year. Because the speed of light through space is about 300,000 km/s, it travels approximately 9.46 trillion kilometers in 1 year! Figure 6 below illustrates how far away some stars that we see really are. Even after astronomers figured out that stars were far a ...
Astrometry - Stony Brook Astronomy
... Aberra=ons shig the en=re field, and so do not generally affect the rela=ve posi=ons of objects. You need to account for these aberra=ons if you need to point the telescope with arcsecond accuracy. In ...
... Aberra=ons shig the en=re field, and so do not generally affect the rela=ve posi=ons of objects. You need to account for these aberra=ons if you need to point the telescope with arcsecond accuracy. In ...
26.3 Life Cycles of Stars
... hydrogen, gravity gains the upper hand over pressure, and the core starts to shrink. • The core temperature rises enough to cause the hydrogen in a shell outside the core to begin fusion. • The energy flowing outward increases, causing the outer regions of the star to expand. The expanding atmospher ...
... hydrogen, gravity gains the upper hand over pressure, and the core starts to shrink. • The core temperature rises enough to cause the hydrogen in a shell outside the core to begin fusion. • The energy flowing outward increases, causing the outer regions of the star to expand. The expanding atmospher ...
Document
... On the other hand, they lack spiral arms, and generally contain very little gas and dust, like elliptical galaxies. Hubble put them at the intersection between spiral and elliptical galaxies in his classification diagram (see figure on the next slide). Though sometimes called “transition galaxies,” ...
... On the other hand, they lack spiral arms, and generally contain very little gas and dust, like elliptical galaxies. Hubble put them at the intersection between spiral and elliptical galaxies in his classification diagram (see figure on the next slide). Though sometimes called “transition galaxies,” ...
INTERSTELLAR MedLab
... 6. The following are sample spectra: each set contains one spectrum representing the nebula and the other represents the spectrum of an associated star. Label each set of spectra as being representative of a reflection nebula or emission nebula and defend your selection. ...
... 6. The following are sample spectra: each set contains one spectrum representing the nebula and the other represents the spectrum of an associated star. Label each set of spectra as being representative of a reflection nebula or emission nebula and defend your selection. ...
Solutions to Homework #6, AST 203, Spring 2012
... c) How many galaxies are there in the observable Universe? Here you can assume that the average distance between galaxies is comparable to the distance between the Milky Way and Andromeda (2.5 mega light-years). Do this calculation for both Universes. (10 points) Solution: Let us assume that the av ...
... c) How many galaxies are there in the observable Universe? Here you can assume that the average distance between galaxies is comparable to the distance between the Milky Way and Andromeda (2.5 mega light-years). Do this calculation for both Universes. (10 points) Solution: Let us assume that the av ...
Our galaxy - School of Physics
... Shapley concluded that the Galaxy must extend far beyond the portion that had been mapped, and that the globular clusters must mark the true centre of the Galaxy. This suggested the Galaxy was much larger than we thought. ...
... Shapley concluded that the Galaxy must extend far beyond the portion that had been mapped, and that the globular clusters must mark the true centre of the Galaxy. This suggested the Galaxy was much larger than we thought. ...
Cosmic distance ladder
The cosmic distance ladder (also known as the extragalactic distance scale) is the succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects. A real direct distance measurement of an astronomical object is possible only for those objects that are ""close enough"" (within about a thousand parsecs) to Earth. The techniques for determining distances to more distant objects are all based on various measured correlations between methods that work at close distances and methods that work at larger distances. Several methods rely on a standard candle, which is an astronomical object that has a known luminosity.The ladder analogy arises because no one technique can measure distances at all ranges encountered in astronomy. Instead, one method can be used to measure nearby distances, a second can be used to measure nearby to intermediate distances, and so on. Each rung of the ladder provides information that can be used to determine the distances at the next higher rung.