Document
... first needing to know its distance. c. Can vary in brightness (as long as it always has the same average luminosity). d. Has a known absolute magnitude. e. Always gives off the same amount of energy, regardless of distance from us. ...
... first needing to know its distance. c. Can vary in brightness (as long as it always has the same average luminosity). d. Has a known absolute magnitude. e. Always gives off the same amount of energy, regardless of distance from us. ...
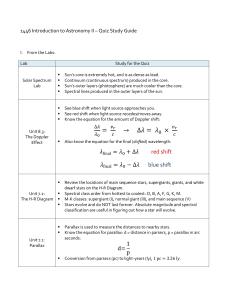
red shift blue shift
... Spectral class order from hottest to coolest: O, B, A, F, G, K, M. M-K classes: supergiant (I), normal giant (III), and main sequence (V) Stars evolve and do NOT last forever. Absolute magnitude and spectral classification are useful in figuring out how a star will evolve. ...
... Spectral class order from hottest to coolest: O, B, A, F, G, K, M. M-K classes: supergiant (I), normal giant (III), and main sequence (V) Stars evolve and do NOT last forever. Absolute magnitude and spectral classification are useful in figuring out how a star will evolve. ...
ASTRO 346 - SPRING 2007
... a) How far apart are galaxies (what is the average separation)? Historically, why was it so hard to get distances of galaxies beyond the local group? Why do we have to use a distance "Distance Ladder"? What ‘rung’ of the ladder got us out to the galaxies? ...
... a) How far apart are galaxies (what is the average separation)? Historically, why was it so hard to get distances of galaxies beyond the local group? Why do we have to use a distance "Distance Ladder"? What ‘rung’ of the ladder got us out to the galaxies? ...
Thursday October 1 - Montana State University
... we can find its distance. • A star of known luminosity is called a standard candle. • More on this later... ...
... we can find its distance. • A star of known luminosity is called a standard candle. • More on this later... ...
Distances
... Our knowledge of astronomical distances is built on a interconnected web of absolute and relative distance measurements. Relative measurements are used to build a “scale model” of the universe with correct proportions. Absolute measurements are used to determine the scale factor needed to express th ...
... Our knowledge of astronomical distances is built on a interconnected web of absolute and relative distance measurements. Relative measurements are used to build a “scale model” of the universe with correct proportions. Absolute measurements are used to determine the scale factor needed to express th ...
Support worksheet – Topic 3 Questions
... Star X has apparent magnitude 5.2 and star Y apparent magnitude 3.2. Calculate the b ratio of apparent brightness X . ...
... Star X has apparent magnitude 5.2 and star Y apparent magnitude 3.2. Calculate the b ratio of apparent brightness X . ...
The Stellar Luminosity Function
... gives the distances in light years, the formula had to be modified to M =m+5-5 logD/3.26 . Th e absolute magnitudes were then rounded to the nearest whole magnitude and then plotted. (See fig.1 .) The sun's absolute magnitude is 4.8. It can be seen readily that there are only 3 stars within the 16 l ...
... gives the distances in light years, the formula had to be modified to M =m+5-5 logD/3.26 . Th e absolute magnitudes were then rounded to the nearest whole magnitude and then plotted. (See fig.1 .) The sun's absolute magnitude is 4.8. It can be seen readily that there are only 3 stars within the 16 l ...
Distance measurement in astronomy
... This relationship, named after the two American Astronomers who discovered it, is not yet widely used because of lack of reliable data. It states that the more luminous a galaxy the faster it rotates. Therefore measurement of the rotational speed of galaxies using the Doppler effect gives a way of d ...
... This relationship, named after the two American Astronomers who discovered it, is not yet widely used because of lack of reliable data. It states that the more luminous a galaxy the faster it rotates. Therefore measurement of the rotational speed of galaxies using the Doppler effect gives a way of d ...
Stellar Distances and Magnitudes
... • The spectral type (class) of a star gives us temperature information, but we don’t know its luminosity. • To get the luminosity, we must know the distance! • Remember the inverse square law! ...
... • The spectral type (class) of a star gives us temperature information, but we don’t know its luminosity. • To get the luminosity, we must know the distance! • Remember the inverse square law! ...
1_Introduction
... First star to have its parallax angle measured: 61 Cygni (in the year 1838). Parallax angle = 0.287 arcseconds Distance = 1 parsec / 0.287 = 3.48 parsecs ...
... First star to have its parallax angle measured: 61 Cygni (in the year 1838). Parallax angle = 0.287 arcseconds Distance = 1 parsec / 0.287 = 3.48 parsecs ...
hw5
... A creature’s likelyhood of surviving changes in their environment over time depends on how quickly they can adapt to those changes. An intelligent creature can adapt very quickly to changes through use of tools and rational behavior. p. 370 RQ# 3 How can astronomers use variable stars to find distan ...
... A creature’s likelyhood of surviving changes in their environment over time depends on how quickly they can adapt to those changes. An intelligent creature can adapt very quickly to changes through use of tools and rational behavior. p. 370 RQ# 3 How can astronomers use variable stars to find distan ...
Earth
... standard distance from Earth) from 20 pc. • Since the star will be “closer”, it will be brighter. • A brighter star has a smaller magnitude • Thus, we expect an absolute magnitude less than ...
... standard distance from Earth) from 20 pc. • Since the star will be “closer”, it will be brighter. • A brighter star has a smaller magnitude • Thus, we expect an absolute magnitude less than ...
parallax and triangulation
... How Far Away are Stars & Other Celestial Bodies? • Use Stellarium to observe the sky and discuss what observations you might be able to use to determine which objects are closest to Earth. • Do size and brightness always lead to accurate conclusions about the distances between Earth and objects out ...
... How Far Away are Stars & Other Celestial Bodies? • Use Stellarium to observe the sky and discuss what observations you might be able to use to determine which objects are closest to Earth. • Do size and brightness always lead to accurate conclusions about the distances between Earth and objects out ...
distances_in_space
... How Astronomers Measure Distances • Triangulation is how astronomers measure distances to objects in the solar system and beyond • A baseline gives us a starting point which is used for comparisons • The diameter of Earth is often used by astronomers, which is 1.3 x 104 km ▫ This value can then be ...
... How Astronomers Measure Distances • Triangulation is how astronomers measure distances to objects in the solar system and beyond • A baseline gives us a starting point which is used for comparisons • The diameter of Earth is often used by astronomers, which is 1.3 x 104 km ▫ This value can then be ...
here
... measure the speed of light. His attempt involved two observers positioned in two towers that were about 10km apart. The idea was that the first observer opens a shutter in a lantern and then as soon as the second observer sees the light from the first lantern, opens his shutter. Galileo would then m ...
... measure the speed of light. His attempt involved two observers positioned in two towers that were about 10km apart. The idea was that the first observer opens a shutter in a lantern and then as soon as the second observer sees the light from the first lantern, opens his shutter. Galileo would then m ...
Astronomical Distance Ladder
... d cluster d t sin This proper motion technique is capable of giving reliable distances up to around 800 parsecs. With the distances to many stars in the galaxy calculated by parallax different ways to calculate distance was needed to extend the astronomical distance ladder. It was also discovere ...
... d cluster d t sin This proper motion technique is capable of giving reliable distances up to around 800 parsecs. With the distances to many stars in the galaxy calculated by parallax different ways to calculate distance was needed to extend the astronomical distance ladder. It was also discovere ...
Cosmic Distance Ladder
... • Edwin Hubble determined a Cepheid Variable in Andromeda Galaxy. • Used Leavitt’s method to find the distance. • Andromeda is much distant than the estimated size of our galaxy! ...
... • Edwin Hubble determined a Cepheid Variable in Andromeda Galaxy. • Used Leavitt’s method to find the distance. • Andromeda is much distant than the estimated size of our galaxy! ...
Astronomy Quiz #1 Answers
... -this means that the wave lengths facing us/toward us are longer (like colour red), showing stars are moving away from us/each other -diagram should be of 2 visible spectra with lines; first one is the original, second one should show that they shifted towards the red end of the spectrum a. What doe ...
... -this means that the wave lengths facing us/toward us are longer (like colour red), showing stars are moving away from us/each other -diagram should be of 2 visible spectra with lines; first one is the original, second one should show that they shifted towards the red end of the spectrum a. What doe ...
Cosmic Distance Ladder
... • Edwin Hubble determined a Cepheid Variable in Andromeda Galaxy. • Used Leavitt’s method to find the distance. • Conclusion: Andromeda is much distant than the estimated size of our galaxy! ...
... • Edwin Hubble determined a Cepheid Variable in Andromeda Galaxy. • Used Leavitt’s method to find the distance. • Conclusion: Andromeda is much distant than the estimated size of our galaxy! ...
Cosmic Distance Ladder
... distance from the Sun in terms of the distance of the Earth from the Sun, an accurate absolute value of this distance had not been calculated. Astronomical Unit (AU): The Earth-Sun distance = 150 Million km=1.5E13 cm ...
... distance from the Sun in terms of the distance of the Earth from the Sun, an accurate absolute value of this distance had not been calculated. Astronomical Unit (AU): The Earth-Sun distance = 150 Million km=1.5E13 cm ...
Cosmic distance ladder
The cosmic distance ladder (also known as the extragalactic distance scale) is the succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects. A real direct distance measurement of an astronomical object is possible only for those objects that are ""close enough"" (within about a thousand parsecs) to Earth. The techniques for determining distances to more distant objects are all based on various measured correlations between methods that work at close distances and methods that work at larger distances. Several methods rely on a standard candle, which is an astronomical object that has a known luminosity.The ladder analogy arises because no one technique can measure distances at all ranges encountered in astronomy. Instead, one method can be used to measure nearby distances, a second can be used to measure nearby to intermediate distances, and so on. Each rung of the ladder provides information that can be used to determine the distances at the next higher rung.