Lecture16
... distance, we could find their luminosity. We can measure the distance to stars with parallax (our old friend). ...
... distance, we could find their luminosity. We can measure the distance to stars with parallax (our old friend). ...
Stars, Galaxies & Universe
... • During nuclear fusion, what does hydrogen fuse into? • helium • What is graphed on the H-R diagram? • brightness & temperature ...
... • During nuclear fusion, what does hydrogen fuse into? • helium • What is graphed on the H-R diagram? • brightness & temperature ...
How Big Is Our Universe? - Harvard
... Knowing these distances helped find the true scale of the entire solar system for the first time. Halley knew that every 121 years the planet Venus passes in front of the Sun. Venus’ position, relative to the Sun behind it, appears very different when viewed from two different places on Earth. How d ...
... Knowing these distances helped find the true scale of the entire solar system for the first time. Halley knew that every 121 years the planet Venus passes in front of the Sun. Venus’ position, relative to the Sun behind it, appears very different when viewed from two different places on Earth. How d ...
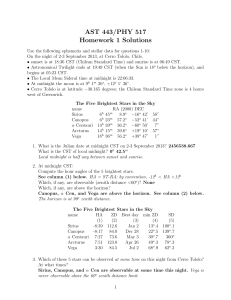
AST 443/PHY 517 Homework 1 Solutions
... 4. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? Sirius, at about 44.3 degrees 5. The sidereal time at midnight advances by 3m 56s each day. What are the best days to observe these targets? See column (3) above. 6. What is the minimum zenith distance for each star? Se ...
... 4. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? Sirius, at about 44.3 degrees 5. The sidereal time at midnight advances by 3m 56s each day. What are the best days to observe these targets? See column (3) above. 6. What is the minimum zenith distance for each star? Se ...
Chapter 18 Study Guide
... Red 8. What type of star has a high temperature but a low luminosity? (use H-R Diagram to determine) White dwarf 9. What type of star has a low temperature but a high luminosity? (use H-R Diagram to determine) Red supergiant 10. According to the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, what relationship exist b ...
... Red 8. What type of star has a high temperature but a low luminosity? (use H-R Diagram to determine) White dwarf 9. What type of star has a low temperature but a high luminosity? (use H-R Diagram to determine) Red supergiant 10. According to the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, what relationship exist b ...
Reach_for_the_stars_final_questions.doc
... 9. Vega, Altair, and Regulus are flattened at the poles and bulging at the equator. What are the reasons for this ? (2 pts) ______________________________________________________________________________ 10. Which star, excluding the sun, is the closest to Earth? How far is it (to .1 light years)? (2 ...
... 9. Vega, Altair, and Regulus are flattened at the poles and bulging at the equator. What are the reasons for this ? (2 pts) ______________________________________________________________________________ 10. Which star, excluding the sun, is the closest to Earth? How far is it (to .1 light years)? (2 ...
OCR Physics A Refer to the Physics A datasheet for data, formulae
... b The table below gives the velocity and distance of five galaxies observed in different constellations. Galaxy in constellation of ...
... b The table below gives the velocity and distance of five galaxies observed in different constellations. Galaxy in constellation of ...
File - The Physics Doctor
... State what is meant by redshift, and explain how it allows the distance to the galaxy to be ...
... State what is meant by redshift, and explain how it allows the distance to the galaxy to be ...
Expanding Universe Lab
... The Hubble Law tells us that our Universe is expanding. We observe galaxies, find their distances and their velocities, and find that they are all moving away from us. The more distant the galaxy, the faster it is moving away. From this information, we can estimate the age of our Universe. We assume ...
... The Hubble Law tells us that our Universe is expanding. We observe galaxies, find their distances and their velocities, and find that they are all moving away from us. The more distant the galaxy, the faster it is moving away. From this information, we can estimate the age of our Universe. We assume ...
1” “Sky-Notes” of the Open University Astronomy Club. April 2006. 1
... a large hazy patch reveals a beautiful scattering of moderate to faint stars. This is the Coma star cluster (Mel 111) best seen in binoculars and well worth a photograph. 2 Com ds (6.0, 7.5) separation 3.6". Use high power when seeing is good. 24 Com ds. (5.0,6.5) separation 20.3" Wide contrasting y ...
... a large hazy patch reveals a beautiful scattering of moderate to faint stars. This is the Coma star cluster (Mel 111) best seen in binoculars and well worth a photograph. 2 Com ds (6.0, 7.5) separation 3.6". Use high power when seeing is good. 24 Com ds. (5.0,6.5) separation 20.3" Wide contrasting y ...
Exercise 4
... 3. Absolute magnitude is related to luminosity. Apparent magnitude depends on brightness which in turn depends on luminosity and distance. 4. Recall: L = 4R2 T4.Thus luminosity depends on size R and surface temperature T. ...
... 3. Absolute magnitude is related to luminosity. Apparent magnitude depends on brightness which in turn depends on luminosity and distance. 4. Recall: L = 4R2 T4.Thus luminosity depends on size R and surface temperature T. ...
Astronomy 103
... The brightest stars have magnitudes around 0. The faintest you can see are around 6. ...
... The brightest stars have magnitudes around 0. The faintest you can see are around 6. ...
Stars
... universe such as stars and galaxies. (8.13B) explain the use of light years to describe distances in the universe. (8.13C) research and describe historical scientific theories of the origin of the ...
... universe such as stars and galaxies. (8.13B) explain the use of light years to describe distances in the universe. (8.13C) research and describe historical scientific theories of the origin of the ...
Angular size and resolution - RIT Center for Imaging Science
... – with binoculars, can easily see shapes/shading on Moon’s surface (angular sizes of 10's of arcseconds) • To see further detail you can use small telescope w/ magnification of 100-300 – can distinguish large craters w/ small telescope – angular sizes of a few arcseconds ...
... – with binoculars, can easily see shapes/shading on Moon’s surface (angular sizes of 10's of arcseconds) • To see further detail you can use small telescope w/ magnification of 100-300 – can distinguish large craters w/ small telescope – angular sizes of a few arcseconds ...
File - 5th Grade Science Almost done!!!!!!!!!
... • The first thing the students do when they enter the room is write down the homework (see next slide) in stone-silence. • After about 20 to 30 seconds of silence I tell the students “Please begin the warm up.” • Please go through the ppt with the students. Students will have to write items in blue ...
... • The first thing the students do when they enter the room is write down the homework (see next slide) in stone-silence. • After about 20 to 30 seconds of silence I tell the students “Please begin the warm up.” • Please go through the ppt with the students. Students will have to write items in blue ...
Ch. 17 (RGs & WDs)
... 2. Use spectral class to estimate luminosity 3. Apply inverse-square law to find distance ...
... 2. Use spectral class to estimate luminosity 3. Apply inverse-square law to find distance ...
Hubblecast Episode 48: Deep Observations of the Andromeda
... unprecedented detail. Most of the stars in this image are outside the Milky Way and lie over two million light-years away. Its one of the deepest, most detailed images ever made of a galaxy outside our own. ...
... unprecedented detail. Most of the stars in this image are outside the Milky Way and lie over two million light-years away. Its one of the deepest, most detailed images ever made of a galaxy outside our own. ...
Document
... • It is convenient to measure planetary distances using the Astronomical Unit, or AU. • 1 AU = average distance between the Earth and the Sun. • 1 AU ~ 150 million km ~ 93 million miles. ...
... • It is convenient to measure planetary distances using the Astronomical Unit, or AU. • 1 AU = average distance between the Earth and the Sun. • 1 AU ~ 150 million km ~ 93 million miles. ...
Microsoft Power Point version
... What is the most important property of a star? • A star’s most important property is its mass, which determines its luminosity and spectral type at each stage of its life. What are the three major classes of binary star systems? • A visual binary is a pair of orbiting stars that we can see distinctl ...
... What is the most important property of a star? • A star’s most important property is its mass, which determines its luminosity and spectral type at each stage of its life. What are the three major classes of binary star systems? • A visual binary is a pair of orbiting stars that we can see distinctl ...
16. Properties of Stars
... What is the most important property of a star? • A star’s most important property is its mass, which determines its luminosity and spectral type at each stage of its life. What are the three major classes of binary star systems? • A visual binary is a pair of orbiting stars that we can see distinctl ...
... What is the most important property of a star? • A star’s most important property is its mass, which determines its luminosity and spectral type at each stage of its life. What are the three major classes of binary star systems? • A visual binary is a pair of orbiting stars that we can see distinctl ...
White dwarfs - University of Toronto
... see the papers in Nature (vol 443, p 283 and p 308) A Type Ia supernova more than twice as bright as others of its type has been observed, suggesting it arose from a star that managed to grow more massive than the Chandrasekhar limit. This mass cut-off was thought to make all such supernovae explode ...
... see the papers in Nature (vol 443, p 283 and p 308) A Type Ia supernova more than twice as bright as others of its type has been observed, suggesting it arose from a star that managed to grow more massive than the Chandrasekhar limit. This mass cut-off was thought to make all such supernovae explode ...
Mathematics (P)review
... To get the rate at which the pressure increases with depth: (1) Draw in a line that fits the data points the best (2) Get the coordinates of two arbitrary points on the line (3) Use the coordinates to find the slope of the line ...
... To get the rate at which the pressure increases with depth: (1) Draw in a line that fits the data points the best (2) Get the coordinates of two arbitrary points on the line (3) Use the coordinates to find the slope of the line ...
Chapter 17 Measuring the Stars
... parallax, but does use spectroscopy in finding the distance to a star. 1. Measure the star’s apparent magnitude and spectral class 2. Use spectral class to estimate luminosity ...
... parallax, but does use spectroscopy in finding the distance to a star. 1. Measure the star’s apparent magnitude and spectral class 2. Use spectral class to estimate luminosity ...
Cosmic distance ladder
The cosmic distance ladder (also known as the extragalactic distance scale) is the succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects. A real direct distance measurement of an astronomical object is possible only for those objects that are ""close enough"" (within about a thousand parsecs) to Earth. The techniques for determining distances to more distant objects are all based on various measured correlations between methods that work at close distances and methods that work at larger distances. Several methods rely on a standard candle, which is an astronomical object that has a known luminosity.The ladder analogy arises because no one technique can measure distances at all ranges encountered in astronomy. Instead, one method can be used to measure nearby distances, a second can be used to measure nearby to intermediate distances, and so on. Each rung of the ladder provides information that can be used to determine the distances at the next higher rung.