the 82nd arthur h. compton lecture series
... ➢ Type Ia SNe come from explosions of white dwarfs in binary systems and do not show signs of He, but strong Si absorption. ➢ Type II SNe show H in the spectra. Subtypes are IIP, IIn, IIL. ➢ Type Ib/c SNe have lost their H (Ib) and sometimes also He (Ic) envelopes. ➢ Most supernova light curves are ...
... ➢ Type Ia SNe come from explosions of white dwarfs in binary systems and do not show signs of He, but strong Si absorption. ➢ Type II SNe show H in the spectra. Subtypes are IIP, IIn, IIL. ➢ Type Ib/c SNe have lost their H (Ib) and sometimes also He (Ic) envelopes. ➢ Most supernova light curves are ...
The Transient Radio Sky Astrophysical and Artificial
... 4. Ly-a absorbers: galaxian magnetic field evolution over cosmic time 5. Cosmic web: the magnetized intergalactic medium ...
... 4. Ly-a absorbers: galaxian magnetic field evolution over cosmic time 5. Cosmic web: the magnetized intergalactic medium ...
Night Sky Course Stars and Star Clusters within the
... All stars in a cluster are about the same distance from us. If they are sufficiently close to us, the stars exhibit proper motion – and over the course of a decade will appear on an image at a slightly different position against the further background of stars.Historically, using the Moving Cluster ...
... All stars in a cluster are about the same distance from us. If they are sufficiently close to us, the stars exhibit proper motion – and over the course of a decade will appear on an image at a slightly different position against the further background of stars.Historically, using the Moving Cluster ...
File
... Visible nebulae that you placed yellow labels are located nearby the Solar System and invisible nebulae (but seen in radio wavelength) that you placed silver labels are located far from our Solar System. Visible light emitted from far nebulae are absorbed by foreground gas and dust in the space and ...
... Visible nebulae that you placed yellow labels are located nearby the Solar System and invisible nebulae (but seen in radio wavelength) that you placed silver labels are located far from our Solar System. Visible light emitted from far nebulae are absorbed by foreground gas and dust in the space and ...
PoA Examples Sheet 3
... 7. A source of ionising radiation is located at a distance R from a star surrounded by a neutral protoplanetary disc. A neutral disc wind feeds gas into an ionisation front which cuts the line between the star and the ionising source at at a distance rI from the star. Explain why (in the limit R >> ...
... 7. A source of ionising radiation is located at a distance R from a star surrounded by a neutral protoplanetary disc. A neutral disc wind feeds gas into an ionisation front which cuts the line between the star and the ionising source at at a distance rI from the star. Explain why (in the limit R >> ...
The radial scale length of the Milky Way
... Key words: Galaxy: structure – Galaxy: fundamental parameters – infrared: stars ...
... Key words: Galaxy: structure – Galaxy: fundamental parameters – infrared: stars ...
Physics- HSC- Module 9.7 Astrophysics
... Below is a list of parallax measurements of nine of the brightest stars in the southern skies. It is you task to convert these angular measurements into distance measurement from Earth. ...
... Below is a list of parallax measurements of nine of the brightest stars in the southern skies. It is you task to convert these angular measurements into distance measurement from Earth. ...
Assignment 10
... ____ 18. Today we know that what all quasars have in common is that they appear to be small sources of energy with a. strong radio emission b. variations in luminosity with a period of seconds c. redshifts that indicate they are far away d. tremendous proper motion (apparent motion across the sky) e ...
... ____ 18. Today we know that what all quasars have in common is that they appear to be small sources of energy with a. strong radio emission b. variations in luminosity with a period of seconds c. redshifts that indicate they are far away d. tremendous proper motion (apparent motion across the sky) e ...
1_Introduction
... atoms, galaxies, and us to form. (Speaking to an audience of humans, I make no apologies ...
... atoms, galaxies, and us to form. (Speaking to an audience of humans, I make no apologies ...
The Night Sky September 2016 - Bridgend Astronomical Society
... Between Beta and Gamma Lyra lies a beautiful object called the Ring Nebula. It is the 57th object in the Messier Catalogue and so is also called M57. Such objects are called planetary nebulae as in a telescope they show a disc, rather like a planet. But in fact they are the remnants of stars, simila ...
... Between Beta and Gamma Lyra lies a beautiful object called the Ring Nebula. It is the 57th object in the Messier Catalogue and so is also called M57. Such objects are called planetary nebulae as in a telescope they show a disc, rather like a planet. But in fact they are the remnants of stars, simila ...
Electromagnetic Waves - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... positions slightly as the Earth moves around the Sun. These stars shift because they are closer to Earth—this parallax effect can be used to determine the distance to our nearest stars. ...
... positions slightly as the Earth moves around the Sun. These stars shift because they are closer to Earth—this parallax effect can be used to determine the distance to our nearest stars. ...
Astronomy (stars, galaxies and the Universe)
... cause different constellations to be seen at different times of the year Stars located above the north and south poles, called circumpolar stars, appear to move in circles above the horizon each night Astronomers use constellations as landmarks to locate other objects in the sky ...
... cause different constellations to be seen at different times of the year Stars located above the north and south poles, called circumpolar stars, appear to move in circles above the horizon each night Astronomers use constellations as landmarks to locate other objects in the sky ...
Stars - Barrington 220
... Some people think that stars, once in the sky, they can never die. They actually have a lifespan, just like us. Infact, if you see a star being born, your great, great grandchildren wouldn’t even get to see that same star die. It takes millions of years for a star to die. When a star, such as the Su ...
... Some people think that stars, once in the sky, they can never die. They actually have a lifespan, just like us. Infact, if you see a star being born, your great, great grandchildren wouldn’t even get to see that same star die. It takes millions of years for a star to die. When a star, such as the Su ...
Star Life Cycle
... 2. How can one locate the center of our galaxy as we orbit the sun and the sun orbits the galaxy? 3. Is our solar system moving away from the center of our galaxy? 4. How many years does it take the sun to orbit the center of the galaxy? 5. The Milky Way is part of a set of about 30 galaxies known a ...
... 2. How can one locate the center of our galaxy as we orbit the sun and the sun orbits the galaxy? 3. Is our solar system moving away from the center of our galaxy? 4. How many years does it take the sun to orbit the center of the galaxy? 5. The Milky Way is part of a set of about 30 galaxies known a ...
Class II Supernova
... Supernova? •It will produce as much energy in it’s time span, then the sun will in its lifetime. •It is not uncommon for a supernova to outshine an entire galaxy. •Quite rare, but sometimes 1 supernova will trigger another one to start. •A type II must have from 3-9 solar masses. ...
... Supernova? •It will produce as much energy in it’s time span, then the sun will in its lifetime. •It is not uncommon for a supernova to outshine an entire galaxy. •Quite rare, but sometimes 1 supernova will trigger another one to start. •A type II must have from 3-9 solar masses. ...
TEKS 8.13 A, B, and C
... together by gravity. Galaxies are scattered throughout the universe. Galaxies are so far away that we can’t make out individual stars. They vary greatly in size and shape. Until the 1920s astronomers did not have a classification system for galaxies. An astronomer, Edwin Hubble decided to group the ...
... together by gravity. Galaxies are scattered throughout the universe. Galaxies are so far away that we can’t make out individual stars. They vary greatly in size and shape. Until the 1920s astronomers did not have a classification system for galaxies. An astronomer, Edwin Hubble decided to group the ...
Lecture 29: Ellipticals and Irregulars
... Proposed systematic subclasses, but many irregulars defy classification. Significant dwarf irregular population, classified as “dI” Examples: Large and Small Magellanic Clouds ...
... Proposed systematic subclasses, but many irregulars defy classification. Significant dwarf irregular population, classified as “dI” Examples: Large and Small Magellanic Clouds ...
MS Word
... Stars such as Capella are called giants because of their size. In this next part you will actually calculate the true radius of a Capella based upon the latest results using optical interferometers. These telescopes are able to resolve the miniscule angular sizes of distant stars. In conjunction wit ...
... Stars such as Capella are called giants because of their size. In this next part you will actually calculate the true radius of a Capella based upon the latest results using optical interferometers. These telescopes are able to resolve the miniscule angular sizes of distant stars. In conjunction wit ...
Astronomy (stars, galaxies and the Universe)
... cause different constellations to be seen at different times of the year Stars located above the north and south poles, called circumpolar stars, appear to move in circles above the horizon each night Astronomers use constellations as landmarks to locate other objects in the sky ...
... cause different constellations to be seen at different times of the year Stars located above the north and south poles, called circumpolar stars, appear to move in circles above the horizon each night Astronomers use constellations as landmarks to locate other objects in the sky ...
G. Kacprzak "Galaxy-halo and gas connection 0.5 email
... Study Mg II quasar absorption line systems in order to understand the kinematics of halos probing distances out to 70 kpcs from the galaxies. Therefore the galaxies in our sample are selected by the known presence of Mg II absorption ...
... Study Mg II quasar absorption line systems in order to understand the kinematics of halos probing distances out to 70 kpcs from the galaxies. Therefore the galaxies in our sample are selected by the known presence of Mg II absorption ...
IB_Op_F_04 - Effectsmeister
... revolve around their common center of mass. The set of all binary systems are often divided into visual binaries, eclipsing binaries and spectroscopic binaries. Use the book to find the difference between these three cases. ...
... revolve around their common center of mass. The set of all binary systems are often divided into visual binaries, eclipsing binaries and spectroscopic binaries. Use the book to find the difference between these three cases. ...
Question 1 The star Regulus, in the constellation Leo, appears
... . The star Regulus, in the constellation Leo, appears brighter through a blue filter than it does through a yellow filter. Suppose that a second star is found that has the same brightness as Regulus through the blue filter but is brighter than Regulus through the yellow filter. From this informati ...
... . The star Regulus, in the constellation Leo, appears brighter through a blue filter than it does through a yellow filter. Suppose that a second star is found that has the same brightness as Regulus through the blue filter but is brighter than Regulus through the yellow filter. From this informati ...
01 - Awtrey Middle School
... 2. During which stage of the life cycle is a star a ball of gas and dust? a. first stage b. second stage c. third stage d. last stage 3. What gas does hydrogen change into as a star becomes hotter? a. uranium b. helium c. gravity d. carbon DIFFERENT TYPES OF STARS 4. Which of the following is NOT a ...
... 2. During which stage of the life cycle is a star a ball of gas and dust? a. first stage b. second stage c. third stage d. last stage 3. What gas does hydrogen change into as a star becomes hotter? a. uranium b. helium c. gravity d. carbon DIFFERENT TYPES OF STARS 4. Which of the following is NOT a ...
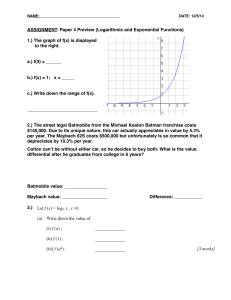
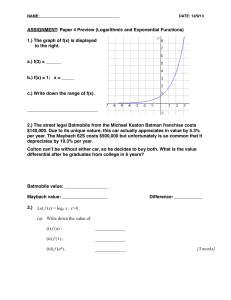
Let f (x) = log x , Let f (x) = loga x , x>0 . (a) Write down the value of (i
... 7.) As we learned in class, our Twinkle Twinkle little stars have apparent magnitude (brightness visible from Earth) and absolute magnitude (actual brightness exuded from the star). The equation is: m – M = log (d/10)5 where “m” is the apparent magnitude, “M” is the absolute magnitude, and “d” is th ...
... 7.) As we learned in class, our Twinkle Twinkle little stars have apparent magnitude (brightness visible from Earth) and absolute magnitude (actual brightness exuded from the star). The equation is: m – M = log (d/10)5 where “m” is the apparent magnitude, “M” is the absolute magnitude, and “d” is th ...
Let f (x) = log x , Let f (x) = loga x , x>0 . (a) Write down the value of (i
... 7.) As we learned in class, our Twinkle Twinkle little stars have apparent magnitude (brightness visible from Earth) and absolute magnitude (actual brightness exuded from the star). The equation is: m – M = log (d/10)5 where “m” is the apparent magnitude, “M” is the absolute magnitude, and “d” is th ...
... 7.) As we learned in class, our Twinkle Twinkle little stars have apparent magnitude (brightness visible from Earth) and absolute magnitude (actual brightness exuded from the star). The equation is: m – M = log (d/10)5 where “m” is the apparent magnitude, “M” is the absolute magnitude, and “d” is th ...
Cosmic distance ladder
The cosmic distance ladder (also known as the extragalactic distance scale) is the succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects. A real direct distance measurement of an astronomical object is possible only for those objects that are ""close enough"" (within about a thousand parsecs) to Earth. The techniques for determining distances to more distant objects are all based on various measured correlations between methods that work at close distances and methods that work at larger distances. Several methods rely on a standard candle, which is an astronomical object that has a known luminosity.The ladder analogy arises because no one technique can measure distances at all ranges encountered in astronomy. Instead, one method can be used to measure nearby distances, a second can be used to measure nearby to intermediate distances, and so on. Each rung of the ladder provides information that can be used to determine the distances at the next higher rung.