VISIT TO NORMAN LOCKYER OBSERVATORY IN SIDMOUTH
... galaxies M81 and M82 shown in the image below. M82 is undergoing a major burst of star formation and hence called a "starburst galaxy". They can be seen together using a low power eyepiece on a small telescope. ...
... galaxies M81 and M82 shown in the image below. M82 is undergoing a major burst of star formation and hence called a "starburst galaxy". They can be seen together using a low power eyepiece on a small telescope. ...
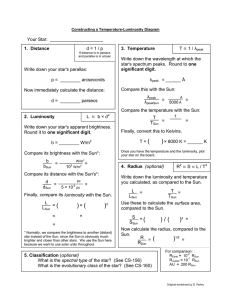
Your Star: _____________________ d = 1 / p
... In this exercise, we will use the observed properties (parallax, apparent brightness, and spectrum peak) of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns i ...
... In this exercise, we will use the observed properties (parallax, apparent brightness, and spectrum peak) of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns i ...
Lecture 17, PPT version
... Gamma rays are VERY high energy light, inherently rare for them to be emitted by astronomical objects Bursts discovered in early 1960’s, randomly distributed around the sky, a few per week, may have complex light curves, but they don’t repeat ...
... Gamma rays are VERY high energy light, inherently rare for them to be emitted by astronomical objects Bursts discovered in early 1960’s, randomly distributed around the sky, a few per week, may have complex light curves, but they don’t repeat ...
redshift parameter, z
... Like Seyferts, there are two kinds: Broad-line (BLRG) Narrow-line (NLRG) ...
... Like Seyferts, there are two kinds: Broad-line (BLRG) Narrow-line (NLRG) ...
Powerpoint - UIUC HEP Group
... due North (or due South), we can calculate our longitude. What time does each star One minute time accuracy leads to ¼° longitude accuracy (about 15 miles, depending on lattitude). The first sufficiently accurate (to 5 seconds during a transatlantic voyage) marine chronometer was tested by John Harr ...
... due North (or due South), we can calculate our longitude. What time does each star One minute time accuracy leads to ¼° longitude accuracy (about 15 miles, depending on lattitude). The first sufficiently accurate (to 5 seconds during a transatlantic voyage) marine chronometer was tested by John Harr ...
Packet 3
... 18b. Over what time period do to be to use this method? you need to measure parallax? _________________________ 19. When a star is more distant, what 2 measurements do scientists have to make to calculate the distance of a star from Earth? 18a. What is parallax? ...
... 18b. Over what time period do to be to use this method? you need to measure parallax? _________________________ 19. When a star is more distant, what 2 measurements do scientists have to make to calculate the distance of a star from Earth? 18a. What is parallax? ...
Fig.4
... J2310-437 (Fig.1) is hosted by an elliptical galaxy of z=0.0886, at the centre of a cluster of Abell richness class 0 (Ref.1), where Abell richness is the number of galaxies in a cluster that lie within the magnitude range m3 to m3+2 (m3 is the magnitude of the third brightest member of the cluster) ...
... J2310-437 (Fig.1) is hosted by an elliptical galaxy of z=0.0886, at the centre of a cluster of Abell richness class 0 (Ref.1), where Abell richness is the number of galaxies in a cluster that lie within the magnitude range m3 to m3+2 (m3 is the magnitude of the third brightest member of the cluster) ...
What constitutes the dark matter?
... N>1: quantum degenerate N=1: transition quantum-classical At r = 505 kpc = 1.6 million lightyear d = 2r = 3.2 million lightyear That is pretty large … ...
... N>1: quantum degenerate N=1: transition quantum-classical At r = 505 kpc = 1.6 million lightyear d = 2r = 3.2 million lightyear That is pretty large … ...
Lesson Plan: Supernova`s
... a supernova explosion happened near the Earth, we could see it in the sky even during the day. Supernova explosions happen rarely. In our own galaxy, the Milky Way, the last supernova happened in the year 1604. We can see supernovas in other galaxies too. Every year we see 300 supernovas in other ga ...
... a supernova explosion happened near the Earth, we could see it in the sky even during the day. Supernova explosions happen rarely. In our own galaxy, the Milky Way, the last supernova happened in the year 1604. We can see supernovas in other galaxies too. Every year we see 300 supernovas in other ga ...
pkt 14 Astrophysics
... the individual masses. This is useful as it allows us to determine the mass of single stars just by ...
... the individual masses. This is useful as it allows us to determine the mass of single stars just by ...
19 The Milky Way Galaxy
... throughout the Milky Way and trace their directions and distances. 2. Observe objects at radio and infrared wavelengths to circumvent the problem of optical obscuration, and catalog their directions and distances. 3. Trace the orbital velocities of objects in different directions relative to our pos ...
... throughout the Milky Way and trace their directions and distances. 2. Observe objects at radio and infrared wavelengths to circumvent the problem of optical obscuration, and catalog their directions and distances. 3. Trace the orbital velocities of objects in different directions relative to our pos ...
Astronomy 401 Lecture 4 Kinematics of the Milky Way 1 The local
... the atom emits a photon with wavelength 21.10611405413 cm, or frequency 1420.40575177 MHz. This transition is highly forbidden with an extremely small probability of 2.9 × 10−15 s−1 , which means that the time for a single isolated atom of neutral hydrogen to undergo this transition is around 10 mil ...
... the atom emits a photon with wavelength 21.10611405413 cm, or frequency 1420.40575177 MHz. This transition is highly forbidden with an extremely small probability of 2.9 × 10−15 s−1 , which means that the time for a single isolated atom of neutral hydrogen to undergo this transition is around 10 mil ...
–1– 1. The Salpeter Initial Mass Function The initial mass function is
... the seminal work of Miller & Scalo (1979). This goes in two steps. First, a present day mass function, PDMF or φ(logM) for main sequence stars is found. This is the number of stars per mass per unit area in the galaxy; it is integrated over the ”vertical” dimension of the disk. The PDMF is given by ...
... the seminal work of Miller & Scalo (1979). This goes in two steps. First, a present day mass function, PDMF or φ(logM) for main sequence stars is found. This is the number of stars per mass per unit area in the galaxy; it is integrated over the ”vertical” dimension of the disk. The PDMF is given by ...
CCD PHOTOMETRY OF OPEN STAR CLUSTER M67
... Catalogue stellar sizes of comparative stars do not appear in those equations anymore, because here general calibration equations for all the stars of the given field are concerned. 3 Results and discussion Colour-magnitude diagrams for the individual colour indexes (B-V), (V-R), (V-I) were created ...
... Catalogue stellar sizes of comparative stars do not appear in those equations anymore, because here general calibration equations for all the stars of the given field are concerned. 3 Results and discussion Colour-magnitude diagrams for the individual colour indexes (B-V), (V-R), (V-I) were created ...
Lecture 10: The Hertzsprung
... There is a mass-luminosity relation on the main sequence. We can use that + a sample of stars where we get all the stars within a certain distance of the Sun to figure out how many stars of what masses are out there. Answer: Lots of low-mass stars! Very few high-mass stars. This is something our the ...
... There is a mass-luminosity relation on the main sequence. We can use that + a sample of stars where we get all the stars within a certain distance of the Sun to figure out how many stars of what masses are out there. Answer: Lots of low-mass stars! Very few high-mass stars. This is something our the ...
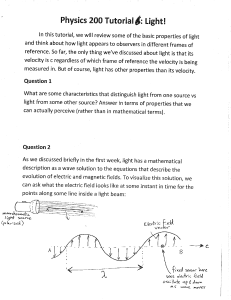
tutorial 6
... b) If the sheet is expanding at a rate such that it doubles in a time T and the distance between two galaxies is D at time 0, what is the distance between the galaxies at a later time t? (Hint: whot is the distance at time T, 2T, 3T, etc...) ...
... b) If the sheet is expanding at a rate such that it doubles in a time T and the distance between two galaxies is D at time 0, what is the distance between the galaxies at a later time t? (Hint: whot is the distance at time T, 2T, 3T, etc...) ...
NASAexplores 9-12 Lesson: Classified Stars - Science
... you while gazing into the night sky. The absolute magnitude and luminosity are used for that. They give you the relative brightness based on all of the stars being the same distance away from the earth. On this diagram, you do not see all of the individual stars. Since there are so many stars, only ...
... you while gazing into the night sky. The absolute magnitude and luminosity are used for that. They give you the relative brightness based on all of the stars being the same distance away from the earth. On this diagram, you do not see all of the individual stars. Since there are so many stars, only ...
Galaxies and the Universe bb
... Fate of the universe • Final fate depends on the average _______ of the universe • If the density is _____ than the critical density, then the universe would ________ • Current estimates point to _____ then the critical density and predict an _______________, or open, ...
... Fate of the universe • Final fate depends on the average _______ of the universe • If the density is _____ than the critical density, then the universe would ________ • Current estimates point to _____ then the critical density and predict an _______________, or open, ...
Monthly Target Matrix Excel
... Each month the sky presents us with a dazzling assortment of spectacular objects on which to train our telescopes: variable stars, nebulae, galaxies, and clusters of galaxies, to name a few. As the Earth makes its yearly trip aroundthe Sun, different objects slide into view in the nighttime sky. Any ...
... Each month the sky presents us with a dazzling assortment of spectacular objects on which to train our telescopes: variable stars, nebulae, galaxies, and clusters of galaxies, to name a few. As the Earth makes its yearly trip aroundthe Sun, different objects slide into view in the nighttime sky. Any ...
Light Years
... Light Years Activity Distances in space are so large that it does not make sense to use a typical unit such as kilometers or miles. Instead, astronomers use a special unit called a light year to measure the distances between stars and galaxies. A light year is the distance that light travels in one ...
... Light Years Activity Distances in space are so large that it does not make sense to use a typical unit such as kilometers or miles. Instead, astronomers use a special unit called a light year to measure the distances between stars and galaxies. A light year is the distance that light travels in one ...
smallest exoplanet - Forsyth Astronomical Society
... In the six years the Cassini spacecraft has been orbiting Saturn and taking detailed images of its ring and many moons, it has helped answer many questions about this planetary system, but also revealed new mysteries for scientists to puzzle over. One of the most important unknowns is the tiny moon ...
... In the six years the Cassini spacecraft has been orbiting Saturn and taking detailed images of its ring and many moons, it has helped answer many questions about this planetary system, but also revealed new mysteries for scientists to puzzle over. One of the most important unknowns is the tiny moon ...
Cosmic distance ladder
The cosmic distance ladder (also known as the extragalactic distance scale) is the succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects. A real direct distance measurement of an astronomical object is possible only for those objects that are ""close enough"" (within about a thousand parsecs) to Earth. The techniques for determining distances to more distant objects are all based on various measured correlations between methods that work at close distances and methods that work at larger distances. Several methods rely on a standard candle, which is an astronomical object that has a known luminosity.The ladder analogy arises because no one technique can measure distances at all ranges encountered in astronomy. Instead, one method can be used to measure nearby distances, a second can be used to measure nearby to intermediate distances, and so on. Each rung of the ladder provides information that can be used to determine the distances at the next higher rung.