ENGINEERING_THERMODYNAMICS
... If there is no chemical reaction or transfer of matter form one part of the system to another is called Chemical equilibrium 18. Explain Thermal equilibrium. If the temperature difference between the system and surroundings is zero then it is in Thermal equilibrium. 19. Define Zeroth law of Thermody ...
... If there is no chemical reaction or transfer of matter form one part of the system to another is called Chemical equilibrium 18. Explain Thermal equilibrium. If the temperature difference between the system and surroundings is zero then it is in Thermal equilibrium. 19. Define Zeroth law of Thermody ...
Understanding pV Diagrams and Calculating Work Done
... The first law of thermodynamics is the statement of the law of conservation of energy in its most general form. You can apply it to any situation in which you are concerned with changes in the internal energy of a system, with heat flow into or out of a system, and/or with work done by or on a syste ...
... The first law of thermodynamics is the statement of the law of conservation of energy in its most general form. You can apply it to any situation in which you are concerned with changes in the internal energy of a system, with heat flow into or out of a system, and/or with work done by or on a syste ...
15 Thermodynamics - Wright State University
... • Define the first law of thermodynamics. • Describe how conservation of energy relates to the first law of thermodynamics. • Identify instances of the first law of thermodynamics working in everyday situations, including biological metabolism. • Calculate changes in the internal energy of a system, ...
... • Define the first law of thermodynamics. • Describe how conservation of energy relates to the first law of thermodynamics. • Identify instances of the first law of thermodynamics working in everyday situations, including biological metabolism. • Calculate changes in the internal energy of a system, ...
Poultry House Temperature Control Using Fuzzy-PID
... Although proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controllers are widely used advanced method in the process industry, their effectiveness is often limited due to poor tuning. The manual tuning of PID controllers, which requires optimization of three parameters, is a time-consuming task. To address th ...
... Although proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controllers are widely used advanced method in the process industry, their effectiveness is often limited due to poor tuning. The manual tuning of PID controllers, which requires optimization of three parameters, is a time-consuming task. To address th ...
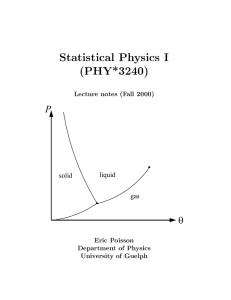
Equilibrium Statistical Mechanics
... If fixed no energy is transmitted from one subsystem to the other in the form of work. If adiabatic, no heat flow. Impermeable, no particle flow. ...
... If fixed no energy is transmitted from one subsystem to the other in the form of work. If adiabatic, no heat flow. Impermeable, no particle flow. ...
Exergy: the quality of energy
... contribution of the irreversibility’s to the entropy increase and is called the irreversible entropy increase (or entropy production) indicated as ∆Sirrev. So, from the second law it appears that any closed system can be characterised by the property “entropy”; the change of this property during a t ...
... contribution of the irreversibility’s to the entropy increase and is called the irreversible entropy increase (or entropy production) indicated as ∆Sirrev. So, from the second law it appears that any closed system can be characterised by the property “entropy”; the change of this property during a t ...
Construction of microcanonical entropy on
... As mentioned above the density of states is definite positive ω > 0; also, by definition, the volume " is non-negative. Hence their ratio kB T = "/ω is non-negative. This means that, within the microcanonical formalism, negative temperatures are inadmissible. Often the present microcanonical scenari ...
... As mentioned above the density of states is definite positive ω > 0; also, by definition, the volume " is non-negative. Hence their ratio kB T = "/ω is non-negative. This means that, within the microcanonical formalism, negative temperatures are inadmissible. Often the present microcanonical scenari ...
an improved heat soak calculation for mechanical seals
... heat soak from viscous process fluids and buffer/barrier fluids. In general, heat soak to fluids more viscous than water will be less than the default API estimate for heat soak. Except for viscosity, all other fluid properties can be combined into the fluid property factor, m6. This factor includes ...
... heat soak from viscous process fluids and buffer/barrier fluids. In general, heat soak to fluids more viscous than water will be less than the default API estimate for heat soak. Except for viscosity, all other fluid properties can be combined into the fluid property factor, m6. This factor includes ...
Document
... between the system and surroundings Heat exchange occurs when system and surroundings have a difference in temperature Temperature is the measure of the amount of thermal energy within a sample of matter Heat flows from matter with high temperature to matter with low temperature until both objects r ...
... between the system and surroundings Heat exchange occurs when system and surroundings have a difference in temperature Temperature is the measure of the amount of thermal energy within a sample of matter Heat flows from matter with high temperature to matter with low temperature until both objects r ...
Slajd 1
... reactants products refers to the H when the specified number of moles of reactants, all at standard states, are converted completely to the specified number of moles of products, all at standard states. ...
... reactants products refers to the H when the specified number of moles of reactants, all at standard states, are converted completely to the specified number of moles of products, all at standard states. ...
Chapter 5 13edx
... • Usually we have no way of knowing the internal energy of a system; finding that value is simply too complex a problem. • However, we do know that the internal energy of a system is independent of the path by which the system achieved that state. – In the system below, the water could have reached ...
... • Usually we have no way of knowing the internal energy of a system; finding that value is simply too complex a problem. • However, we do know that the internal energy of a system is independent of the path by which the system achieved that state. – In the system below, the water could have reached ...
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry
... • Usually we have no way of knowing the internal energy of a system; finding that value is simply too complex a problem. • However, we do know that the internal energy of a system is independent of the path by which the system achieved that state. – In the system below, the water could have reached ...
... • Usually we have no way of knowing the internal energy of a system; finding that value is simply too complex a problem. • However, we do know that the internal energy of a system is independent of the path by which the system achieved that state. – In the system below, the water could have reached ...
book - University of Guelph Physics
... Let us examine how a system reaches equilibrium. Imagine that a certain quantity of gas, initially confined to a small portion of a box, is allowed to slowly fill the entire box by flowing through a porous membrane. (We assume that initially, the rest of the box contains a vacuum.) As long as the ga ...
... Let us examine how a system reaches equilibrium. Imagine that a certain quantity of gas, initially confined to a small portion of a box, is allowed to slowly fill the entire box by flowing through a porous membrane. (We assume that initially, the rest of the box contains a vacuum.) As long as the ga ...
PHY 1150 - Concepts of Physics
... 1) Explain how the ‘acceleration due to gravity’ is dependant upon the size, mass, ‘density’ and shape of a body in the presence of air resistance and demonstrate how the ‘terminal velocity’ of a given body falling in air may be altered. 2) State the values for the acceleration due to gravity in the ...
... 1) Explain how the ‘acceleration due to gravity’ is dependant upon the size, mass, ‘density’ and shape of a body in the presence of air resistance and demonstrate how the ‘terminal velocity’ of a given body falling in air may be altered. 2) State the values for the acceleration due to gravity in the ...
Chem - Andhra University
... Heat changes, Enthalpy, reversible changes, maximum work. Heat capacities at constant pressure and volume, adiabatic changes. Heat of Reaction, heat of Formation, Heat of Combustion, Thermo-chemical Laws, effect of temperature on Heat of Reaction. Second law of Thermodynamics, spontaneous processes, ...
... Heat changes, Enthalpy, reversible changes, maximum work. Heat capacities at constant pressure and volume, adiabatic changes. Heat of Reaction, heat of Formation, Heat of Combustion, Thermo-chemical Laws, effect of temperature on Heat of Reaction. Second law of Thermodynamics, spontaneous processes, ...
Heat

In physics, heat is energy in a process of transfer between a system and its surroundings, other than as work or with the transfer of matter. When there is a suitable physical pathway, heat flows from a hotter body to a colder one. The pathway can be direct, as in conduction and radiation, or indirect, as in convective circulation.Because it refers to a process of transfer between two systems, the system of interest, and its surroundings considered as a system, heat is not a state or property of a single system. If heat transfer is slow and continuous, so that the temperature of the system of interest remains well defined, it can sometimes be described by a process function.Kinetic theory explains heat as a macroscopic manifestation of the motions and interactions of microscopic constituents such as molecules and photons.In calorimetry, sensible heat is defined with respect to a specific chosen state variable of the system, such as pressure or volume. Sensible heat transferred into or out of the system under study causes change of temperature while leaving the chosen state variable unchanged. Heat transfer that occurs with the system at constant temperature and that does change that particular state variable is called latent heat with respect to that variable. For infinitesimal changes, the total incremental heat transfer is then the sum of the latent and sensible heat increments. This is a basic paradigm for thermodynamics, and was important in the historical development of the subject.The quantity of energy transferred as heat is a scalar expressed in an energy unit such as the joule (J) (SI), with a sign that is customarily positive when a transfer adds to the energy of a system. It can be measured by calorimetry, or determined by calculations based on other quantities, relying on the first law of thermodynamics.