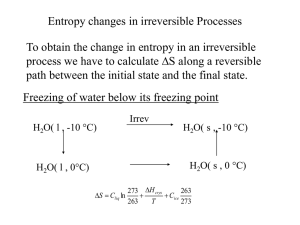
Determination of the enthalpy of combustion with a calorimetric
... Set up the experiment as shown in Fig. 1. Pulverise the substance to be combusted in a mortar and pestle. Subsequently weigh approximately 400 mg into a weighing dish. Cut an approximately 10 cm long length from the iron wire and weigh it to the nearest mg. Position it in the guide grooves of the pe ...
... Set up the experiment as shown in Fig. 1. Pulverise the substance to be combusted in a mortar and pestle. Subsequently weigh approximately 400 mg into a weighing dish. Cut an approximately 10 cm long length from the iron wire and weigh it to the nearest mg. Position it in the guide grooves of the pe ...
Lecture 9
... the system. (Many systems in different states might have the same volume.) Once the current state is known, we do know all of these variables’ values. How the system arrived at its current state, does not affect these values. Heat and work are not state variables. ...
... the system. (Many systems in different states might have the same volume.) Once the current state is known, we do know all of these variables’ values. How the system arrived at its current state, does not affect these values. Heat and work are not state variables. ...
Lecture 2
... A rising piston, a rotating shaft, and an electric wire crossing the system boundaries are all associated with work interactions Formal sign convention: Heat transfer to a system and work done by a system are positive; heat transfer from a system and work done on a system are negative. Alterna ...
... A rising piston, a rotating shaft, and an electric wire crossing the system boundaries are all associated with work interactions Formal sign convention: Heat transfer to a system and work done by a system are positive; heat transfer from a system and work done on a system are negative. Alterna ...
the work done is
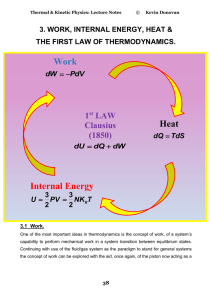
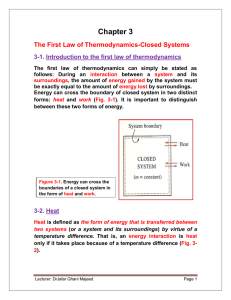
... The first law of thermodynamics can simply be stated as follows: During an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy gained by the system must be exactly equal to the amount of energy lost by surroundings. Energy can cross the boundary of closed system in two distinct f ...
... The first law of thermodynamics can simply be stated as follows: During an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy gained by the system must be exactly equal to the amount of energy lost by surroundings. Energy can cross the boundary of closed system in two distinct f ...
Chapter 1: Introductory Concepts, Units, and Definitions
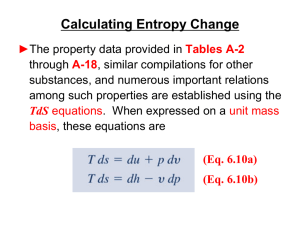
... Notice from the steam property tables that we have also included three new properties: internal energy u [kJ/kg], enthalpy h [kJ/kg], and entropy s [kJ/kg.K] all of which will be defined as needed in future sections. At this stage we note that the 3 equations relating quality and specific volume ca ...
... Notice from the steam property tables that we have also included three new properties: internal energy u [kJ/kg], enthalpy h [kJ/kg], and entropy s [kJ/kg.K] all of which will be defined as needed in future sections. At this stage we note that the 3 equations relating quality and specific volume ca ...
Entropy, free energy and equilibrium
... Matter disperses – gas fills a container, two liquids mix Heat disperses – hot object cools on cold surface Motion disperses – a ball stops bouncing The reverses of these three well known processes never occur spontaneously ...
... Matter disperses – gas fills a container, two liquids mix Heat disperses – hot object cools on cold surface Motion disperses – a ball stops bouncing The reverses of these three well known processes never occur spontaneously ...
Thermodynamic Considerations in Animal Nutrition Department of
... Department of Zoology, University of Georgia, Athens, Georgia 30601 SYNOPSIS. Acquisition of energy is a prime objective of the search for nutrition. The energy budget of a population or trophic level comprises the sum of energy gains and losses by each individual organism. Since these energy exchan ...
... Department of Zoology, University of Georgia, Athens, Georgia 30601 SYNOPSIS. Acquisition of energy is a prime objective of the search for nutrition. The energy budget of a population or trophic level comprises the sum of energy gains and losses by each individual organism. Since these energy exchan ...
First Law of Thermodynamics – Basic Concepts
... In fact, a reversible process is considered to proceed from the initial state to the final state through an infinite series of infinitesimally small stages. At the initial, final and all intermediate stages, the system is in equilibrium state. This is so because an infinitesimal change in the state ...
... In fact, a reversible process is considered to proceed from the initial state to the final state through an infinite series of infinitesimally small stages. At the initial, final and all intermediate stages, the system is in equilibrium state. This is so because an infinitesimal change in the state ...
ONSAGER`S VARIATIONAL PRINCIPLE AND ITS APPLICATIONS
... The microcanonical ensemble is of fundamental value while the canonical ensemble is more widely used. For more details, see C. Kittel, Elementary Statistical Physics. The energy is a constant of motion for a conservative system. If the energy of the system is prescribed to be in the range δE at E0 , ...
... The microcanonical ensemble is of fundamental value while the canonical ensemble is more widely used. For more details, see C. Kittel, Elementary Statistical Physics. The energy is a constant of motion for a conservative system. If the energy of the system is prescribed to be in the range δE at E0 , ...
Chapter 4: Energy Analysis of Closed Systems
... Before the first law of thermodynamics can be applied to systems, ways to calculate the change in internal energy of the substance enclosed by the system boundary must be determined. For real substances like water, the property tables are used to find the internal energy change. For ideal gases the ...
... Before the first law of thermodynamics can be applied to systems, ways to calculate the change in internal energy of the substance enclosed by the system boundary must be determined. For real substances like water, the property tables are used to find the internal energy change. For ideal gases the ...
Heat

In physics, heat is energy in a process of transfer between a system and its surroundings, other than as work or with the transfer of matter. When there is a suitable physical pathway, heat flows from a hotter body to a colder one. The pathway can be direct, as in conduction and radiation, or indirect, as in convective circulation.Because it refers to a process of transfer between two systems, the system of interest, and its surroundings considered as a system, heat is not a state or property of a single system. If heat transfer is slow and continuous, so that the temperature of the system of interest remains well defined, it can sometimes be described by a process function.Kinetic theory explains heat as a macroscopic manifestation of the motions and interactions of microscopic constituents such as molecules and photons.In calorimetry, sensible heat is defined with respect to a specific chosen state variable of the system, such as pressure or volume. Sensible heat transferred into or out of the system under study causes change of temperature while leaving the chosen state variable unchanged. Heat transfer that occurs with the system at constant temperature and that does change that particular state variable is called latent heat with respect to that variable. For infinitesimal changes, the total incremental heat transfer is then the sum of the latent and sensible heat increments. This is a basic paradigm for thermodynamics, and was important in the historical development of the subject.The quantity of energy transferred as heat is a scalar expressed in an energy unit such as the joule (J) (SI), with a sign that is customarily positive when a transfer adds to the energy of a system. It can be measured by calorimetry, or determined by calculations based on other quantities, relying on the first law of thermodynamics.