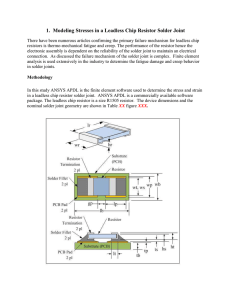
R eduction(1 3 ).pdf
... focus our attention on a particular time, which we choose to be t = 0. How should we represent the system in macroscopic terms (given we do not know the microstate of the system at that time)? The principal macroscopic quantity is the total energy of the system, E. By fixing this value, we restrict ...
... focus our attention on a particular time, which we choose to be t = 0. How should we represent the system in macroscopic terms (given we do not know the microstate of the system at that time)? The principal macroscopic quantity is the total energy of the system, E. By fixing this value, we restrict ...
Project_FEA.doc
... /unloading criteria. It assumes that plastic flow occurs at all non-zero stress values. The Anand model represents the non-linear rate dependent stress-strain relation of solder. The model uses a single scalar internal variable (s), called the deformation resistance that corresponds to the isotropic ...
... /unloading criteria. It assumes that plastic flow occurs at all non-zero stress values. The Anand model represents the non-linear rate dependent stress-strain relation of solder. The model uses a single scalar internal variable (s), called the deformation resistance that corresponds to the isotropic ...
Dislocations
... ● there is an interfacial or grain boundary energy similar to the surface energy just described. The magnitude of this energy depends on the degree of misorientation, being larger for high-angle boundaries. ● impurity atoms often preferentially segregate along these boundaries because of their highe ...
... ● there is an interfacial or grain boundary energy similar to the surface energy just described. The magnitude of this energy depends on the degree of misorientation, being larger for high-angle boundaries. ● impurity atoms often preferentially segregate along these boundaries because of their highe ...
Amorphous to Tetragonal Zirconia
... spectral positions of these peaks, however, cannot be attributed to any specific ionic state, due to the finite uncertainty involved in deconvolution in the background of complex envelop of density of states. Hence, these peaks are referred to Zr+ζ, 0 ≤ |ζ| < 4, with varying (2.8−3.2 eV) spin orbit sp ...
... spectral positions of these peaks, however, cannot be attributed to any specific ionic state, due to the finite uncertainty involved in deconvolution in the background of complex envelop of density of states. Hence, these peaks are referred to Zr+ζ, 0 ≤ |ζ| < 4, with varying (2.8−3.2 eV) spin orbit sp ...
Module
... Metals have free valance electrons which are responsible for their good thermal and electrical conductivity. Metals readily loose their electrons to form positive ions. The metallic bond is held by electrostatic force between delocalized electrons and positive ions. Metals are primarily used in the ...
... Metals have free valance electrons which are responsible for their good thermal and electrical conductivity. Metals readily loose their electrons to form positive ions. The metallic bond is held by electrostatic force between delocalized electrons and positive ions. Metals are primarily used in the ...
Introduction to Modern Physics PHYX 2710
... Position—where you are in space (L or meter) Velocity—how fast position is changing with time (LT-1 or m/s) Acceleration—how fast velocity is changing with time (LT-2 or m/s2) Force— what is required to change to motion of a body (MLT-2 or kg-m/s2 or N) Inertia (mass)— a measure of the force needed ...
... Position—where you are in space (L or meter) Velocity—how fast position is changing with time (LT-1 or m/s) Acceleration—how fast velocity is changing with time (LT-2 or m/s2) Force— what is required to change to motion of a body (MLT-2 or kg-m/s2 or N) Inertia (mass)— a measure of the force needed ...
Hybridization of atomic orbitals In general VSEPR predicts the
... Hybridization of atomic orbitals In general VSEPR predicts the shape of molecules and ions accurately CH4 : tetrahedral Four equal bonds with equal HCH angles A covalent bond is formed by sharing two electrons by two atoms Imagine an orbital (containing 1 electron) from one atom overlaps with an orb ...
... Hybridization of atomic orbitals In general VSEPR predicts the shape of molecules and ions accurately CH4 : tetrahedral Four equal bonds with equal HCH angles A covalent bond is formed by sharing two electrons by two atoms Imagine an orbital (containing 1 electron) from one atom overlaps with an orb ...
RGch10
... Revision Notes: exponential decay processes Summary Diagrams: Radioactive decay used as a clock, Half-life and time constant decay of charge, current or potential difference with time for a capacitor (plotted both directly and logarithmically) Revision Notes: exponential decay processes Summary Diag ...
... Revision Notes: exponential decay processes Summary Diagrams: Radioactive decay used as a clock, Half-life and time constant decay of charge, current or potential difference with time for a capacitor (plotted both directly and logarithmically) Revision Notes: exponential decay processes Summary Diag ...
dual-valent
... The electronic structure of SFO in the G-AF state is consistent with metallic conductivity with a low density of states (DOS) at the Fermi level (EF ). The partial DOS analysis shows that the Fe 3d and O 2p states are energetically degenerate leading to covalent interaction between them. However, as ...
... The electronic structure of SFO in the G-AF state is consistent with metallic conductivity with a low density of states (DOS) at the Fermi level (EF ). The partial DOS analysis shows that the Fe 3d and O 2p states are energetically degenerate leading to covalent interaction between them. However, as ...
Chem 1202
... Calorimetry = measurement of heat flow q. A calorimeter is an apparatus that measures heat flow q. Heat capacity = the amount of heat required to change the temperature of an object by 1 centigrade degree (°C or K). The units of heat capacity are J/deg. The increase in T measures the increased kinet ...
... Calorimetry = measurement of heat flow q. A calorimeter is an apparatus that measures heat flow q. Heat capacity = the amount of heat required to change the temperature of an object by 1 centigrade degree (°C or K). The units of heat capacity are J/deg. The increase in T measures the increased kinet ...
An availability approach to thermal energy recovery in vehicles
... Abstract: Availability is a well-established and widely recognized way of describing the work-producing potential of energy systems. A first-law analysis is helpful in setting the energy context and ensuring that energy flows balance, but it is a second-law analysis based on availability that places a ...
... Abstract: Availability is a well-established and widely recognized way of describing the work-producing potential of energy systems. A first-law analysis is helpful in setting the energy context and ensuring that energy flows balance, but it is a second-law analysis based on availability that places a ...
Heat transfer physics

Heat transfer physics describes the kinetics of energy storage, transport, and transformation by principal energy carriers: phonons (lattice vibration waves), electrons, fluid particles, and photons. Heat is energy stored in temperature-dependent motion of particles including electrons, atomic nuclei, individual atoms, and molecules. Heat is transferred to and from matter by the principal energy carriers. The state of energy stored within matter, or transported by the carriers, is described by a combination of classical and quantum statistical mechanics. The energy is also transformed (converted) among various carriers.The heat transfer processes (or kinetics) are governed by the rates at which various related physical phenomena occur, such as (for example) the rate of particle collisions in classical mechanics. These various states and kinetics determine the heat transfer, i.e., the net rate of energy storage or transport. Governing these process from the atomic level (atom or molecule length scale) to macroscale are the laws of thermodynamics, including conservation of energy.