IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE)
... Understanding the electro-thermal responses of different conducting materials facilitate the integrity assessment as well as effective manipulation capability in material selection for modern micro-electronic devices. To meet the requirements of extreme performance under various complex working cond ...
... Understanding the electro-thermal responses of different conducting materials facilitate the integrity assessment as well as effective manipulation capability in material selection for modern micro-electronic devices. To meet the requirements of extreme performance under various complex working cond ...
Optical Properties
... The answer is “Metals are materials with a positive thermal coefficient of resistivity”. What this means is that when the temperature of the metal is raised, its resistance increases. Other materials which can also conduct charge, such as ionic conductors and semiconductors, actually lower their res ...
... The answer is “Metals are materials with a positive thermal coefficient of resistivity”. What this means is that when the temperature of the metal is raised, its resistance increases. Other materials which can also conduct charge, such as ionic conductors and semiconductors, actually lower their res ...
Syllabus
... courses across the country Medical Council of India The Medical Council of India (MCI) recommends the following syllabus for National Eligibility-cum-Entrance Test for admission to MBBS courses across the country (NEETUG) after review of various State syllabi as well as those prepared by CBSE, NCERT ...
... courses across the country Medical Council of India The Medical Council of India (MCI) recommends the following syllabus for National Eligibility-cum-Entrance Test for admission to MBBS courses across the country (NEETUG) after review of various State syllabi as well as those prepared by CBSE, NCERT ...
Chapter 2
... placed so that they can exchange energy. The most important property of the temperature is its tendency to become equal. For example, if we put a hot and a cold body into thermal contact, the temperature of the hot body decreases and the temperature of the cold body increases until both bodies are a ...
... placed so that they can exchange energy. The most important property of the temperature is its tendency to become equal. For example, if we put a hot and a cold body into thermal contact, the temperature of the hot body decreases and the temperature of the cold body increases until both bodies are a ...
Fundamentals of Thermodynamics Applied to Thermal
... will start at a higher temperature. There is a direct correspondence between pressure and temperature during a phase change process, which is known as the saturation curve. For each substance, including water, there is a specific temperature where a phase change will occur at a given pressure. Conve ...
... will start at a higher temperature. There is a direct correspondence between pressure and temperature during a phase change process, which is known as the saturation curve. For each substance, including water, there is a specific temperature where a phase change will occur at a given pressure. Conve ...
Chapter 1: Introduction
... Fluid Mechanics and Flow Classification Hydrodynamics: flow of fluids for which density is constant such as liquids and low-speed gases. If in addition fluid properties are constant, temperature and heat transfer effects are uncoupled such that they can be treated separately. Examples: hydraulics, l ...
... Fluid Mechanics and Flow Classification Hydrodynamics: flow of fluids for which density is constant such as liquids and low-speed gases. If in addition fluid properties are constant, temperature and heat transfer effects are uncoupled such that they can be treated separately. Examples: hydraulics, l ...
A family of intracules, a conjecture and the electron correlation... z* Peter M. W. Gill,* Deborah L. Crittenden,w
... HF theory often yields fairly accurate predictions of molecular structure but it is less satisfactory for most other properties. In particular, its mean-field treatment of electron motion cannot account properly for the formation of an electron pair during bond formation and it is therefore usually n ...
... HF theory often yields fairly accurate predictions of molecular structure but it is less satisfactory for most other properties. In particular, its mean-field treatment of electron motion cannot account properly for the formation of an electron pair during bond formation and it is therefore usually n ...
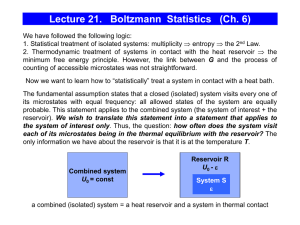
Lecture 21. Boltzmann Statistics (Ch. 6)
... Consider a system of N particles with only 3 possible energy levels separated by (let the ground state energy be 0). The system occupies a fixed volume V and is in thermal equilibrium with a reservoir at temperature T. Ignore interactions between particles and assume that Boltzmann statistics appl ...
... Consider a system of N particles with only 3 possible energy levels separated by (let the ground state energy be 0). The system occupies a fixed volume V and is in thermal equilibrium with a reservoir at temperature T. Ignore interactions between particles and assume that Boltzmann statistics appl ...
Heat transfer physics

Heat transfer physics describes the kinetics of energy storage, transport, and transformation by principal energy carriers: phonons (lattice vibration waves), electrons, fluid particles, and photons. Heat is energy stored in temperature-dependent motion of particles including electrons, atomic nuclei, individual atoms, and molecules. Heat is transferred to and from matter by the principal energy carriers. The state of energy stored within matter, or transported by the carriers, is described by a combination of classical and quantum statistical mechanics. The energy is also transformed (converted) among various carriers.The heat transfer processes (or kinetics) are governed by the rates at which various related physical phenomena occur, such as (for example) the rate of particle collisions in classical mechanics. These various states and kinetics determine the heat transfer, i.e., the net rate of energy storage or transport. Governing these process from the atomic level (atom or molecule length scale) to macroscale are the laws of thermodynamics, including conservation of energy.