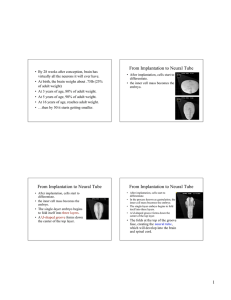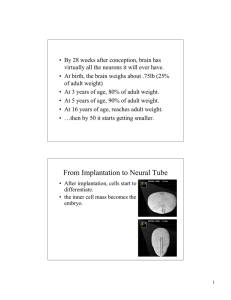
From Implantation to Neural Tube
... The Brain and Experience Plasticity- The capacity of the brain to be affected by experience. • Experience-expectant plasticity • Experience-dependent plasticity – Neural connections are created and reorganized throughout life as a function of individual experience. – Highly specialized effects can o ...
... The Brain and Experience Plasticity- The capacity of the brain to be affected by experience. • Experience-expectant plasticity • Experience-dependent plasticity – Neural connections are created and reorganized throughout life as a function of individual experience. – Highly specialized effects can o ...
AP Psychology
... 19. Why is the thalamus often thought to be part of the brainstem, and what is its function? 20. Where is the cerebellum located, and what is its function? 21. Identify the four parts of the limbic system and describe the function of each 22. The cerebral cortex is the area 1/10 of an inch all aroun ...
... 19. Why is the thalamus often thought to be part of the brainstem, and what is its function? 20. Where is the cerebellum located, and what is its function? 21. Identify the four parts of the limbic system and describe the function of each 22. The cerebral cortex is the area 1/10 of an inch all aroun ...
Document
... single perception (cognition). • The second function constructs a spatial coordinate system to represent the world around us. ...
... single perception (cognition). • The second function constructs a spatial coordinate system to represent the world around us. ...
Media Release
... games have their roots in neural networks inspired by information processing in the brain. In a Review published June 14 in Trends in Cognitive Sciences, researchers from Google DeepMind and Stanford University update a theory originally developed to explain how humans and other animals learn - and ...
... games have their roots in neural networks inspired by information processing in the brain. In a Review published June 14 in Trends in Cognitive Sciences, researchers from Google DeepMind and Stanford University update a theory originally developed to explain how humans and other animals learn - and ...
1244509Health Nervous System 2012
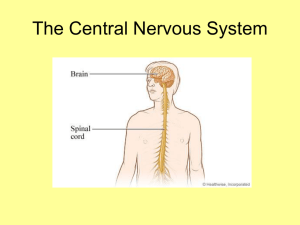
... The brain’s best friend ◦ Relays messages from all parts of the body to the brain……. ◦ THEN, it receives the message from the brain and relays the brain’s message to muscles, glands, etc. **** The spinal cord is like a bad gossiper, but in a ...
... The brain’s best friend ◦ Relays messages from all parts of the body to the brain……. ◦ THEN, it receives the message from the brain and relays the brain’s message to muscles, glands, etc. **** The spinal cord is like a bad gossiper, but in a ...
The Nervous System
... Parkinson’s Disease – degeneration of nerve cells in the brain that produce dopamine; leads to uncoordinated muscular movement Multiple Sclerosis – auto-immune disease; destruction of nerve cell insulation Alzheimer’s – mental deterioration usually associated with age Epilepsy – sudden episo ...
... Parkinson’s Disease – degeneration of nerve cells in the brain that produce dopamine; leads to uncoordinated muscular movement Multiple Sclerosis – auto-immune disease; destruction of nerve cell insulation Alzheimer’s – mental deterioration usually associated with age Epilepsy – sudden episo ...
psychology - Eagan High School
... The brain has no pain, because there are no nerves that register pain within the brain itself, neurosurgeons can probe the brain while a patient is conscious. They can then use feedback from the patient to identify important regions, such as those used for speech. The brain has the largest area of u ...
... The brain has no pain, because there are no nerves that register pain within the brain itself, neurosurgeons can probe the brain while a patient is conscious. They can then use feedback from the patient to identify important regions, such as those used for speech. The brain has the largest area of u ...
the brain - Cloudfront.net
... 4. The more you repeat something the more brain space is dedicated to it. For example, in musicians the part of the brain that controls fingers used to play an instrument is up to 130% larger than in a non-musician. ...
... 4. The more you repeat something the more brain space is dedicated to it. For example, in musicians the part of the brain that controls fingers used to play an instrument is up to 130% larger than in a non-musician. ...
Louise Comely`s
... In her book, “A Student’s Brain”, Kathie Nunley outlines 4 key education principles linking neuroscience to education: 1. attention. ...
... In her book, “A Student’s Brain”, Kathie Nunley outlines 4 key education principles linking neuroscience to education: 1. attention. ...
SRS values
... the students decide what they want to learn and what they want to do. It’s a place where we consider the needs of the students, as a group and as individuals, and encourage them to participate in the learning process all the time. Leo Jones 2007 Cambridge University Press ...
... the students decide what they want to learn and what they want to do. It’s a place where we consider the needs of the students, as a group and as individuals, and encourage them to participate in the learning process all the time. Leo Jones 2007 Cambridge University Press ...
Slide 1
... – Axon: extends from cell body, carries electrical potential, sends a chemical message to adjacent neurons via terminal buttons ...
... – Axon: extends from cell body, carries electrical potential, sends a chemical message to adjacent neurons via terminal buttons ...
Modification of brain circuits as a result of experience
... increased. • Correlated activity between presynaptic and postsynaptic cells strengthens synaptic connections between them. • Cells that fire together, wire together. Also used in learning and memory, called long term potentiation (LTP). ...
... increased. • Correlated activity between presynaptic and postsynaptic cells strengthens synaptic connections between them. • Cells that fire together, wire together. Also used in learning and memory, called long term potentiation (LTP). ...
X Period- Review for Brain test
... Upper brain- controls all human functions, example—thinking, personality ...
... Upper brain- controls all human functions, example—thinking, personality ...
Helping our Students REALLY Get it by Understanding
... Professor of Biology and Biochemistry at Case Western University, Director of UCITE (The University Center for Innovation in Teaching and Education), and Professor of a Human Learning and The Brain class. ...
... Professor of Biology and Biochemistry at Case Western University, Director of UCITE (The University Center for Innovation in Teaching and Education), and Professor of a Human Learning and The Brain class. ...
Chapter 3
... Neuroscience Deals with the biological bases of our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors Where are memories stored in the brain? How do we experience joy, anger, or desire? Why do drug addictions occur? Are there parts of the brain that have specialized functions? What causes mental illnesses ...
... Neuroscience Deals with the biological bases of our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors Where are memories stored in the brain? How do we experience joy, anger, or desire? Why do drug addictions occur? Are there parts of the brain that have specialized functions? What causes mental illnesses ...
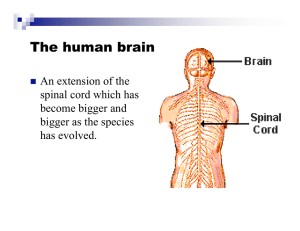
The human brain
... What changes in maturation is the connections between the neurons. On average, we lose about 20% of our neurons by the time we die. ...
... What changes in maturation is the connections between the neurons. On average, we lose about 20% of our neurons by the time we die. ...
sensory neurons
... 2. Impulse travels to spinal cord 3. Impulse sent to brain and back to hand. 4. Hand pulls back before pain is registered by brain ...
... 2. Impulse travels to spinal cord 3. Impulse sent to brain and back to hand. 4. Hand pulls back before pain is registered by brain ...
Ch 10 Brain Damage & Neuroplasticity (pt2)
... (Section of axon between the cut & the soma) If the axon cannot reestablish contact with a target, the neuron eventually dies ...
... (Section of axon between the cut & the soma) If the axon cannot reestablish contact with a target, the neuron eventually dies ...
Brain & Behavior
... • Tamping iron blew through his head • Memory and movement intact, could learn new things • But, personality changed ...
... • Tamping iron blew through his head • Memory and movement intact, could learn new things • But, personality changed ...
Document
... new topic or skill, they don’t have the basis from which to grow—on which to connect and construct—the dendrites for the higher levels of skill and knowledge. ...
... new topic or skill, they don’t have the basis from which to grow—on which to connect and construct—the dendrites for the higher levels of skill and knowledge. ...