The basic Hebb rule
... Anti-Hebbian plasticity • It causes synapses to decrease (rather than increase) in strength when there is simultaneous pre- and postsynaptic activity. • It is believed to be the predominant form of plasticity at synapses in mormyrid electric fish and those from parallel fibers to Purkinje cells in ...
... Anti-Hebbian plasticity • It causes synapses to decrease (rather than increase) in strength when there is simultaneous pre- and postsynaptic activity. • It is believed to be the predominant form of plasticity at synapses in mormyrid electric fish and those from parallel fibers to Purkinje cells in ...
Neurons
... to the axon terminals, referred to as firing. • After firing, each action potential is followed by a brief recharging period, known as the refractory period, when it can’t fire. • When the cell is capable of firing again, it has reached its resting potential, meaning it’s relaxed and ready to fire a ...
... to the axon terminals, referred to as firing. • After firing, each action potential is followed by a brief recharging period, known as the refractory period, when it can’t fire. • When the cell is capable of firing again, it has reached its resting potential, meaning it’s relaxed and ready to fire a ...
Focus On Vocabulary Chapter 02
... guts,” means the same thing!) Thus, when Myers states that being human takes a lot of nerve, the literal meaning in this context is that humans are made up of many, many nerves (the humor is derived from the double meaning). Glial cells are worker bees. Here, the analogy is to a beehive where the qu ...
... guts,” means the same thing!) Thus, when Myers states that being human takes a lot of nerve, the literal meaning in this context is that humans are made up of many, many nerves (the humor is derived from the double meaning). Glial cells are worker bees. Here, the analogy is to a beehive where the qu ...
Body Systems: Nervous and Sensory Systems
... reduces the spastic movements, it has been commonly used for 30 years Amytophic Lateral Sclerosis- A terminal neurological disorder characterized by progressive generation of motor cells in the Spine and Brain. It has no known cause as it occurs in 95% of patients without a family history. It eventu ...
... reduces the spastic movements, it has been commonly used for 30 years Amytophic Lateral Sclerosis- A terminal neurological disorder characterized by progressive generation of motor cells in the Spine and Brain. It has no known cause as it occurs in 95% of patients without a family history. It eventu ...
Chapter 11
... consists of fibers called nerve tracts; provide 2-way communication b/t brain & s.c.; • 2 types: 1. ascending – *In the medulla, fibers cross over ...
... consists of fibers called nerve tracts; provide 2-way communication b/t brain & s.c.; • 2 types: 1. ascending – *In the medulla, fibers cross over ...
424 brain mechanisms in language, cognition, and
... sophisticated approach to hemispheric specialization. Some thirty years ago, Pribrarn initiated a program of research aimed at the production of animal models of the agnosias. (Since, at that time, animals had not yet been shown to use signs, aphasias were not considered suitable for modeling-and ev ...
... sophisticated approach to hemispheric specialization. Some thirty years ago, Pribrarn initiated a program of research aimed at the production of animal models of the agnosias. (Since, at that time, animals had not yet been shown to use signs, aphasias were not considered suitable for modeling-and ev ...
PowerPoint Slides
... their nervous system to perform these behaviours. •An appropriate model/simulation of the nervous system should be able to produce similar responses and behaviours in artificial systems. •The nervous system is build by relatively simple units, the neurons, so copying their behavior and functionality ...
... their nervous system to perform these behaviours. •An appropriate model/simulation of the nervous system should be able to produce similar responses and behaviours in artificial systems. •The nervous system is build by relatively simple units, the neurons, so copying their behavior and functionality ...
Lecture 12
... Neurons within the nervous system link to form circuits with specific functions. In the brain, neural networks create affective and cognitive behaviors. Signaling within these pathways creates thinking, language, feeling, learning, and memory. The brain exhibits plasticity, the ability to change con ...
... Neurons within the nervous system link to form circuits with specific functions. In the brain, neural networks create affective and cognitive behaviors. Signaling within these pathways creates thinking, language, feeling, learning, and memory. The brain exhibits plasticity, the ability to change con ...
“It`s all in your head”
... Case of R.M. • Transferred to Neurosurgery, started on Dexamethasone • Craniotomy for excision of brain tumour 3 days later ...
... Case of R.M. • Transferred to Neurosurgery, started on Dexamethasone • Craniotomy for excision of brain tumour 3 days later ...
Chapter 2 Review Notes
... Describe the parts of a neuron, and explain how its impulses are generated. A neuron consists of a cell body and branching fibers: The dendrite fibers receive information from sensory receptors or other neurons, and the axon fibers pass that information along to other neurons. A layer of fatty tissu ...
... Describe the parts of a neuron, and explain how its impulses are generated. A neuron consists of a cell body and branching fibers: The dendrite fibers receive information from sensory receptors or other neurons, and the axon fibers pass that information along to other neurons. A layer of fatty tissu ...
Ascolot Lesson #5 - 2015 Brain-Machine
... signals from and transmitting them to neurons. Long the McGuffins of science fiction, from The Terminal Man to The Matrix, brain chips are now being used or tested as treatments for epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, paralysis, blindness and other disorders. Decades ago Delgado carried out experiments t ...
... signals from and transmitting them to neurons. Long the McGuffins of science fiction, from The Terminal Man to The Matrix, brain chips are now being used or tested as treatments for epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, paralysis, blindness and other disorders. Decades ago Delgado carried out experiments t ...
The Evolution of the Brain Neurons are quite distinct from other body
... In most cells, such depolarization would not spread far, certainly not to neighboring cells. But a few changes in the shape and arrangement of cells (in just the way that neurons are fashioned) permits depolarization to propagate quickly from one neuron to the next, and allows it to travel quickly a ...
... In most cells, such depolarization would not spread far, certainly not to neighboring cells. But a few changes in the shape and arrangement of cells (in just the way that neurons are fashioned) permits depolarization to propagate quickly from one neuron to the next, and allows it to travel quickly a ...
USC Brain Project Specific Aims
... The Prey-Selector Model of Didday Consider how the frog's brain might select one of several visually presented prey objects. The task: to design a distributed network (not a serial scan strategy) that could take a position-tagged "foodness array" and ensure that usually the strongest region of acti ...
... The Prey-Selector Model of Didday Consider how the frog's brain might select one of several visually presented prey objects. The task: to design a distributed network (not a serial scan strategy) that could take a position-tagged "foodness array" and ensure that usually the strongest region of acti ...
Webster transitions class 2 slides
... The brain is an 'anticipation machine' (Siegel 1999). It is designed to help us navigate our way, providing expectations of likely outcomes and holding knowledge of our environment. Based on the images we form of a prototype episode: for example, how the other person's face looked, how I feel in my ...
... The brain is an 'anticipation machine' (Siegel 1999). It is designed to help us navigate our way, providing expectations of likely outcomes and holding knowledge of our environment. Based on the images we form of a prototype episode: for example, how the other person's face looked, how I feel in my ...
The Nervous System
... synapses. When synapses are created to a high degree through new experiences, they allow the central nervous system to send and receive messages much more quickly between nerve cells. Like neurogenesis, synaptogenesis continues into adulthood. ...
... synapses. When synapses are created to a high degree through new experiences, they allow the central nervous system to send and receive messages much more quickly between nerve cells. Like neurogenesis, synaptogenesis continues into adulthood. ...
Research from University of Miami and Tetra Discovery Shows
... Phosphodiesterase 4B Inhibitor, was authored by Coleen M. Atkins, Ph.D., Associate Professor, Department of Neurological Surgery, University of Miami, along with W. Dalton Dietrich, Ph.D., Scientific Director, The Miami Project and Kinetic Concepts Distinguished Chair in Neurosurgery, Senior Assoc ...
... Phosphodiesterase 4B Inhibitor, was authored by Coleen M. Atkins, Ph.D., Associate Professor, Department of Neurological Surgery, University of Miami, along with W. Dalton Dietrich, Ph.D., Scientific Director, The Miami Project and Kinetic Concepts Distinguished Chair in Neurosurgery, Senior Assoc ...
Too little
... excitatory and inhibitory signals from many neurons. When the excitatory signals minus the inhibitory signals exceed a minimum intensity (threshold) the neuron fires an action potential. Gas vs. brake pedals of a car!!!! ...
... excitatory and inhibitory signals from many neurons. When the excitatory signals minus the inhibitory signals exceed a minimum intensity (threshold) the neuron fires an action potential. Gas vs. brake pedals of a car!!!! ...
05First2yearsBiosocial
... • If starving, the body stops growing, but not the brain • The brain is the last part of the body to be damaged by malnutrition ...
... • If starving, the body stops growing, but not the brain • The brain is the last part of the body to be damaged by malnutrition ...
Adolescents Brain Development
... the brain that is involved in thinking about other people’s emotions and thought when considering a course of action – less able to imagine emotional reactions and to read the emotions of other which can led to misunderstandings and over reactions • The ability to hold in mind an intention to carry ...
... the brain that is involved in thinking about other people’s emotions and thought when considering a course of action – less able to imagine emotional reactions and to read the emotions of other which can led to misunderstandings and over reactions • The ability to hold in mind an intention to carry ...
Document
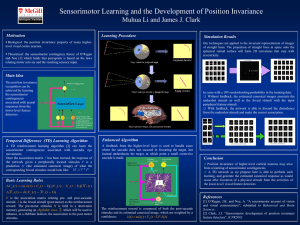
... Biological: the position invariance property of many higherlevel visual cortex neurons. ...
... Biological: the position invariance property of many higherlevel visual cortex neurons. ...
Brain Anatomy - Southwest High School
... rhythmically or rhythmically to a metronome and going back and forth…What kind of scan? ...
... rhythmically or rhythmically to a metronome and going back and forth…What kind of scan? ...
ACP Level 2 Lesson Twelve
... spinal column. Connections which happen between two or more neurons is called a synapse. Okay, so far? It’s not brain surgery is it… neurology that is? Oh wait, it is! I definitely think it is easier than the muscles lesson though, there is less Latin to pronounce! Let’s have a probe round the brain ...
... spinal column. Connections which happen between two or more neurons is called a synapse. Okay, so far? It’s not brain surgery is it… neurology that is? Oh wait, it is! I definitely think it is easier than the muscles lesson though, there is less Latin to pronounce! Let’s have a probe round the brain ...
Applications of computer science in the life sciences
... The agent chooses an action a, based on its estimates of the values of possible future states, Q(s, a) The agent performs the action, and observes the new state s! , and receives a reward r The agent improves its estimate of the current value of each state and action using a “temporal difference” ru ...
... The agent chooses an action a, based on its estimates of the values of possible future states, Q(s, a) The agent performs the action, and observes the new state s! , and receives a reward r The agent improves its estimate of the current value of each state and action using a “temporal difference” ru ...