Nervous System Module - Year 2 Semester 1 Number of Credit – 8
... 2. List the errors of refraction, describe how they occur and explain the basis of correcting each of them. 3.Explain the term accommodation as applied to the eye. 4. Explain the basis of the accommodation-convergence reflex and pupillary light reflex. 5. Explain the principles underlying visual acu ...
... 2. List the errors of refraction, describe how they occur and explain the basis of correcting each of them. 3.Explain the term accommodation as applied to the eye. 4. Explain the basis of the accommodation-convergence reflex and pupillary light reflex. 5. Explain the principles underlying visual acu ...
Sensing Limb Movements in the Motor Cortex: How Humans Sense
... excites the muscle spindle afferents of the vibrated muscles and elicits an illusory limb movement. If we measure the brain activity while totally relaxed subjects experience illusory limb movements, we may detect brain areas that receive and process the kinesthetic afferent inputs. By taking advant ...
... excites the muscle spindle afferents of the vibrated muscles and elicits an illusory limb movement. If we measure the brain activity while totally relaxed subjects experience illusory limb movements, we may detect brain areas that receive and process the kinesthetic afferent inputs. By taking advant ...
Where is a Nose with Respect to a Foot? The Left
... flawlessly in all the other tasks. In contrast, 3 patients were found selectively impaired at matching body parts by function, whereas thirteen were impaired in either the hand laterality or real/imagined hand movement task despite being still able to perform normally on all other tasks. Thus, the co ...
... flawlessly in all the other tasks. In contrast, 3 patients were found selectively impaired at matching body parts by function, whereas thirteen were impaired in either the hand laterality or real/imagined hand movement task despite being still able to perform normally on all other tasks. Thus, the co ...
Introduction to Psychology, 7th Edition, James W. Kalat Chapter 3
... neurons. If a drug were injected into an animal that blocked dopamine from attaching to its receptors, what would happen to the postsynaptic neurons? ...
... neurons. If a drug were injected into an animal that blocked dopamine from attaching to its receptors, what would happen to the postsynaptic neurons? ...
The cognitive neuroscience of sustained attention
... the assessment of sustained attention (or vigilance) performance typically has utilized situations in which an observer is required to keep watch for inconspicuous signals over prolonged periods of time. The state of readiness to respond to rarely and unpredictably occurring signals is characterized ...
... the assessment of sustained attention (or vigilance) performance typically has utilized situations in which an observer is required to keep watch for inconspicuous signals over prolonged periods of time. The state of readiness to respond to rarely and unpredictably occurring signals is characterized ...
Corticosteroid–serotonin interactions in the
... response of the body to a demand’’, may also be described as any environmental change, either internal or external, that disturbs the maintenance of homeostasis (Leonard, 2005). The term ‘‘stress’’ can be used in two ways: either to identify events or circumstances that are perceived adversely (‘‘st ...
... response of the body to a demand’’, may also be described as any environmental change, either internal or external, that disturbs the maintenance of homeostasis (Leonard, 2005). The term ‘‘stress’’ can be used in two ways: either to identify events or circumstances that are perceived adversely (‘‘st ...
E ffects of different kinds of acute stress on nerve growth factor
... injection caused the rats to vocalize loudly. Rats were decapitated without anesthesia 1 h later, i.e., at 8 p.m. 2.2.2. Group 2 (moderate stress) Rats were grasped by the scruff at 7 p.m., lifted out of the cage, turned upside down and the tail was pulled for 30–60 s as for preparation of an intrap ...
... injection caused the rats to vocalize loudly. Rats were decapitated without anesthesia 1 h later, i.e., at 8 p.m. 2.2.2. Group 2 (moderate stress) Rats were grasped by the scruff at 7 p.m., lifted out of the cage, turned upside down and the tail was pulled for 30–60 s as for preparation of an intrap ...
The Evolution of Neuron Types and Cortical
... pathological changes subsequent to ablation, some studies also examined cortical projection systems in apes (Walker, 1938; Lassek and Wheatley, 1945; Kuypers, 1958; Jackson et al., 1969). After the 1950s, however, the amount of research directed toward understanding variation in the hominoid brain d ...
... pathological changes subsequent to ablation, some studies also examined cortical projection systems in apes (Walker, 1938; Lassek and Wheatley, 1945; Kuypers, 1958; Jackson et al., 1969). After the 1950s, however, the amount of research directed toward understanding variation in the hominoid brain d ...
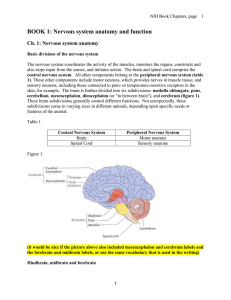
BOOK 1: Nervous system anatomy and function
... pumping artificial brain extracellular fluid through the inside of the probe, dopamine is collected and measured outside of the animal using very sensitive and selective instrumentation. Artificial brain extracellular fluid is pumped through the probe so that the composition of real brain extracellu ...
... pumping artificial brain extracellular fluid through the inside of the probe, dopamine is collected and measured outside of the animal using very sensitive and selective instrumentation. Artificial brain extracellular fluid is pumped through the probe so that the composition of real brain extracellu ...
full text - TReAD Lab
... received less scholarly attention than its neighbors, its function has recently become the subject of great interest. In particular, clinical scientists have become interested in its contributions to the control of motivated behavior and clinical pathologies such as Parkinson's disease (PD) and obse ...
... received less scholarly attention than its neighbors, its function has recently become the subject of great interest. In particular, clinical scientists have become interested in its contributions to the control of motivated behavior and clinical pathologies such as Parkinson's disease (PD) and obse ...
Goals of Explaining Brain Functions Underlying Anxiety Disorders
... • How do medications fit into this picture? • Three questions about medications: – How do they affect the anxiety response? – How do they affect the exposure process? • How do they affect the amygdala’s learning? ...
... • How do medications fit into this picture? • Three questions about medications: – How do they affect the anxiety response? – How do they affect the exposure process? • How do they affect the amygdala’s learning? ...
MATERNAL BEHAVIOUR IN LACTATING RATS STIMULATES c
... behaviour that included milk letdown. Both groups of dams had a similar number of 67,000 mol. wt glutamate decarboxylaseimmunoreactive cells in each site, although the number of 67,000 mol. wt glutamate decarboxylase-immunoreactive cells per microscopic ®eld was signi®cantly greater in the caudal ve ...
... behaviour that included milk letdown. Both groups of dams had a similar number of 67,000 mol. wt glutamate decarboxylaseimmunoreactive cells in each site, although the number of 67,000 mol. wt glutamate decarboxylase-immunoreactive cells per microscopic ®eld was signi®cantly greater in the caudal ve ...
Physiological Psychology - II Sem
... types of receptors, it is possible for a neuron to have excitatory effects on one set of target cells, inhibitory effects on others, and complex modulatory effects on others still. Nevertheless, it happens that the two most widely used neurotransmitters, glutamate and GABA, each have largely consist ...
... types of receptors, it is possible for a neuron to have excitatory effects on one set of target cells, inhibitory effects on others, and complex modulatory effects on others still. Nevertheless, it happens that the two most widely used neurotransmitters, glutamate and GABA, each have largely consist ...
Full version (PDF file)
... pressure but also elevated MT1 protein expression. It was hypothesized that the activation of melatonin receptors on endothelial cells would trigger NO production and contribute to blood pressure reduction (Paulis and Simko 2007). It seems, however, that melatonin receptors may regulate blood pressu ...
... pressure but also elevated MT1 protein expression. It was hypothesized that the activation of melatonin receptors on endothelial cells would trigger NO production and contribute to blood pressure reduction (Paulis and Simko 2007). It seems, however, that melatonin receptors may regulate blood pressu ...
- Journal of Adolescent Health
... the hippocampus in the pathophysiology of PTSS, specifically as they relate to learning from previous experience. Animal research has shown that one potential mechanism of damage to the hippocampus is through corticosterone, the animal analog to cortisol in humans, which can be neurotoxic if secreted ...
... the hippocampus in the pathophysiology of PTSS, specifically as they relate to learning from previous experience. Animal research has shown that one potential mechanism of damage to the hippocampus is through corticosterone, the animal analog to cortisol in humans, which can be neurotoxic if secreted ...
FREE Sample Here
... Identify the parts of the neuron and explain how neurons communicate with each other. Identify key neurotransmitters and describe their functions. Explain how an action potential is generated Explain the difference between agonists and antagonists. Describe how the nervous system is organized Descri ...
... Identify the parts of the neuron and explain how neurons communicate with each other. Identify key neurotransmitters and describe their functions. Explain how an action potential is generated Explain the difference between agonists and antagonists. Describe how the nervous system is organized Descri ...
Table of Contents
... – (CT) computerized tomography - computer enhanced Xray – (PET) positron emission tomography - radioactively tagged chemicals serve as markers of blood flow or metabolic activity in the brain that are monitored by X-ray – (MRI) magnetic resonance imaging - uses magnetic fields, radio waves, and comp ...
... – (CT) computerized tomography - computer enhanced Xray – (PET) positron emission tomography - radioactively tagged chemicals serve as markers of blood flow or metabolic activity in the brain that are monitored by X-ray – (MRI) magnetic resonance imaging - uses magnetic fields, radio waves, and comp ...
Control and Coordination
... react to changes in their environments. Their nervous systems help maintain homeostasis, or the regulation of their internal environments. For example, the goalie’s nervous system must signal his heart and breathing to slow down to restore homeostasis once he has blocked the shot. ...
... react to changes in their environments. Their nervous systems help maintain homeostasis, or the regulation of their internal environments. For example, the goalie’s nervous system must signal his heart and breathing to slow down to restore homeostasis once he has blocked the shot. ...
Dexterous Finger Movements in Primate Without Monosynaptic
... 100 mmHg and pCO2 at 4.0%. A drip of Ringer-glucose was given during the entire experiment, and the urinary bladder was emptied regularly. Atropin (0.5 mg), decadrone (4 mg), gentacine (1 ml) were given just after anesthesia. Atropin was given at intervals of 4 –5 h. The animals were paralyzed with ...
... 100 mmHg and pCO2 at 4.0%. A drip of Ringer-glucose was given during the entire experiment, and the urinary bladder was emptied regularly. Atropin (0.5 mg), decadrone (4 mg), gentacine (1 ml) were given just after anesthesia. Atropin was given at intervals of 4 –5 h. The animals were paralyzed with ...
The Big Picture File
... contours of the brain (called gyri and sulci) • The pia is pierced by blood vessels which travel to the brain and spinal cord, and its capillaries are responsible for nourishing the brain ...
... contours of the brain (called gyri and sulci) • The pia is pierced by blood vessels which travel to the brain and spinal cord, and its capillaries are responsible for nourishing the brain ...
Dimensions of integration in embedded and extended cognitive
... of human cognition, implying rather significant epistemological and methodological consequences for the philosophical and scientific study of human thought. 1.1 Parity and complementarity John Sutton (2010) has identified two distinct, but historically overlapping, waves in EMT. The first wave is mo ...
... of human cognition, implying rather significant epistemological and methodological consequences for the philosophical and scientific study of human thought. 1.1 Parity and complementarity John Sutton (2010) has identified two distinct, but historically overlapping, waves in EMT. The first wave is mo ...
The Cytoarchitectonic Map of Constantin von Economo and Georg N
... (1885–1975), working in the Psychiatric Clinic of Julius Wagner-Jauregg (1857–1940) at the University of Vienna, published their monumental Atlas and Textbook of Cytoarchitectonics of the Adult Human Cerebral Cortex, following in the footsteps of Theodor Meynert (1833–1892) and Korbinian Brodmann (1 ...
... (1885–1975), working in the Psychiatric Clinic of Julius Wagner-Jauregg (1857–1940) at the University of Vienna, published their monumental Atlas and Textbook of Cytoarchitectonics of the Adult Human Cerebral Cortex, following in the footsteps of Theodor Meynert (1833–1892) and Korbinian Brodmann (1 ...
Region-specific alterations of A-to-I RNA editing of
... processes.29 Alterations in the DLPFCx have been reported in mood disorders, both in vivo30,31 and postmortem.32 The ACCx is a major component of the ‘limbic system’ and is implicated in emotion, attention, mood states, motor and cognitive processes.33–35 We first investigated whether differences cou ...
... processes.29 Alterations in the DLPFCx have been reported in mood disorders, both in vivo30,31 and postmortem.32 The ACCx is a major component of the ‘limbic system’ and is implicated in emotion, attention, mood states, motor and cognitive processes.33–35 We first investigated whether differences cou ...
Increased prefrontal activity and reduced motor cortex
... studies have shown that imagery can be used to improve strength related tasks (Ranganathan et al., 2004), but it is still a controversial issue with large individual differences. Although, one must also remember that there are differences between motor imagery and execution, and it has been shown th ...
... studies have shown that imagery can be used to improve strength related tasks (Ranganathan et al., 2004), but it is still a controversial issue with large individual differences. Although, one must also remember that there are differences between motor imagery and execution, and it has been shown th ...