Brain Development and Behavior
... The cerebral cortex is the layer of the brain often referred to as gray matter. The cortex (thin layer of tissue) is gray because nerves in this area lack the insulation that makes most other parts of the brain appear to be white. The cortex covers the outer portion the ...
... The cerebral cortex is the layer of the brain often referred to as gray matter. The cortex (thin layer of tissue) is gray because nerves in this area lack the insulation that makes most other parts of the brain appear to be white. The cortex covers the outer portion the ...
2-3 nervous sys Sp13
... where learning, remembering and reasoning takes place The cerebral cortex ...
... where learning, remembering and reasoning takes place The cerebral cortex ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... and 31 spinal pairs from nerves that your go from spinal the cord called central spinal nervous nerves. to system Spinal your nerves are skeletal made up of muscles. bundles of The sensory autonomic and motor system neurons controls bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. F ...
... and 31 spinal pairs from nerves that your go from spinal the cord called central spinal nervous nerves. to system Spinal your nerves are skeletal made up of muscles. bundles of The sensory autonomic and motor system neurons controls bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. F ...
Nervous and Muscular System
... – Functions to: control the flow of messages between the brain and body; control breathing, swallowing, heart rate, blood pressure, consciousness; and identify if one is awake/alert or tired/sleepy ...
... – Functions to: control the flow of messages between the brain and body; control breathing, swallowing, heart rate, blood pressure, consciousness; and identify if one is awake/alert or tired/sleepy ...
Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences
... monkeys hold two pictures “in mind” (i.e., in working memory) simultaneously, neural activity for the two pictures line up on different places of 32 Hz “brain waves” across the neuron population. This may explain our severe limitation in thinking multiple thoughts at the same time, and suggests that ...
... monkeys hold two pictures “in mind” (i.e., in working memory) simultaneously, neural activity for the two pictures line up on different places of 32 Hz “brain waves” across the neuron population. This may explain our severe limitation in thinking multiple thoughts at the same time, and suggests that ...
The Nervous System - Primary Home Care
... Chronic Brain Syndrome (also called Alzheimer's-Type Dementia). In this condition large areas of neurons cease to function and the client cannot remember what just happened, has poor judgment, and has great fear and anxiety. Clients may forget who family and friends are, how to do simple tasks, and ...
... Chronic Brain Syndrome (also called Alzheimer's-Type Dementia). In this condition large areas of neurons cease to function and the client cannot remember what just happened, has poor judgment, and has great fear and anxiety. Clients may forget who family and friends are, how to do simple tasks, and ...
Basic Anatomy and Terminology of the Head and Brain Scalp and
... cerebral hemispheres. Each cerebral hemisphere controls the opposite side of the body. The surfaces of the cerebral hemispheres are convoluted. This means that the surfaces are folded in on themselves in many places. The convolutions allow for more surface area for the brain. The surface is called t ...
... cerebral hemispheres. Each cerebral hemisphere controls the opposite side of the body. The surfaces of the cerebral hemispheres are convoluted. This means that the surfaces are folded in on themselves in many places. The convolutions allow for more surface area for the brain. The surface is called t ...
the limbic system
... in the vertebrate central nervous system are contacted by thousands of synaptic terminals relaying information about the environment. The postsynaptic membrane at each synaptic terminal is the first place where information is processed as it converges on the dendrite. At the postsynaptic membrane of ...
... in the vertebrate central nervous system are contacted by thousands of synaptic terminals relaying information about the environment. The postsynaptic membrane at each synaptic terminal is the first place where information is processed as it converges on the dendrite. At the postsynaptic membrane of ...
The Brain
... People with primary visual agnosia may have one or several impairments in visual recognition without impairment of intelligence, motivation, and/or attention. Vision is almost always intact and the mind is clear. Some affected individuals do not have the ability to recognize familiar objects. They ...
... People with primary visual agnosia may have one or several impairments in visual recognition without impairment of intelligence, motivation, and/or attention. Vision is almost always intact and the mind is clear. Some affected individuals do not have the ability to recognize familiar objects. They ...
PHYSIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 2
... Endorphins were first discovered during the 1970s by researchers studying the effects of morphine and other opiates. To their surprise, the researchers learned there were special receptor sites for such drugs within the brain (Hughes et al., 1975). Why should such receptors exist? • Naturally occurr ...
... Endorphins were first discovered during the 1970s by researchers studying the effects of morphine and other opiates. To their surprise, the researchers learned there were special receptor sites for such drugs within the brain (Hughes et al., 1975). Why should such receptors exist? • Naturally occurr ...
Endocrine and nervous system - Glasgow Independent Schools
... 3. Axon: long projection that carries impulses away from cell body ...
... 3. Axon: long projection that carries impulses away from cell body ...
The Nervous System
... most of the sensory neurons and directing these impulses to the part of the brain where each will be interpreted. -Screens out less significant stimuli (prevents sensory overload) ...
... most of the sensory neurons and directing these impulses to the part of the brain where each will be interpreted. -Screens out less significant stimuli (prevents sensory overload) ...
Using_IntelXeonPhi_for_BrainResearchVisualization
... data analysis to enable insight, and specifically, ray-tracing can help to highlight areas of the circuits where cells touch each other and where synapses are being created. Using OSPRay’s ray tracing capability, using light, shadow, and depth of field effects that can simulate photo-realistic image ...
... data analysis to enable insight, and specifically, ray-tracing can help to highlight areas of the circuits where cells touch each other and where synapses are being created. Using OSPRay’s ray tracing capability, using light, shadow, and depth of field effects that can simulate photo-realistic image ...
PsychSim 5: PSYCHOLOGY`S TIMELINE
... and culture. The focus of the activity is a simulated experiment in which you will play the role of a researcher who is recording from “mirror neurons” in the premotor cortex of monkeys as they perform various tasks or watch others perform those tasks. Brain Regions Briefly describe the premotor c ...
... and culture. The focus of the activity is a simulated experiment in which you will play the role of a researcher who is recording from “mirror neurons” in the premotor cortex of monkeys as they perform various tasks or watch others perform those tasks. Brain Regions Briefly describe the premotor c ...
Understanding-the.. - Windsor C
... (space between neurons) – This is called a synaptic transmission ...
... (space between neurons) – This is called a synaptic transmission ...
The basics of brain communication
... What are the Basic Brain Structures and Their Functions? • Scientists Can Now Watch the Working Brain • The Brain Stem Houses the Basic Programs of Survival • The Cerebellum is Essential for Movement • Subcortical Structures Control Emotions and Appetitive Behaviors • The Cerebral Cortex Underlies C ...
... What are the Basic Brain Structures and Their Functions? • Scientists Can Now Watch the Working Brain • The Brain Stem Houses the Basic Programs of Survival • The Cerebellum is Essential for Movement • Subcortical Structures Control Emotions and Appetitive Behaviors • The Cerebral Cortex Underlies C ...
SHEEP BRAIN DISSECTION GUIDE
... (which is the inability to remember new information and experiences though previously-stored memories remain intact). The hippocampus and the medial temporal cortical areas which project to it are critical for long-term memory. The rat hippocampus is probably the single most studied brain structure ...
... (which is the inability to remember new information and experiences though previously-stored memories remain intact). The hippocampus and the medial temporal cortical areas which project to it are critical for long-term memory. The rat hippocampus is probably the single most studied brain structure ...
Introduction to Psychology - John Marshall High School
... MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer – generated images that distinguish among different types of soft tissue; allows us to see structures within the brain. ...
... MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer – generated images that distinguish among different types of soft tissue; allows us to see structures within the brain. ...
THE WORKING OF THE HUMAN BRAIN
... emotions, moods and perception Also involved in sleep, blood pressure, body temperature and the secretion of hormones Occurs throughout the body – especially in digestive system; only about 2% of the total amount in the body is present in the brain Produced from the amino acid Ltryptophane ...
... emotions, moods and perception Also involved in sleep, blood pressure, body temperature and the secretion of hormones Occurs throughout the body – especially in digestive system; only about 2% of the total amount in the body is present in the brain Produced from the amino acid Ltryptophane ...
Andrew Rosen - Chapter 3: The Brain and Nervous System Intro
... o Some cells function as motion detectors and only fire when an object is in motion o Some cells function as shape detectors that fire when a form is in view Multi-unit recording – Procedure using microelectrodes to record the activity of individual cells and then relies on computer analysis to exam ...
... o Some cells function as motion detectors and only fire when an object is in motion o Some cells function as shape detectors that fire when a form is in view Multi-unit recording – Procedure using microelectrodes to record the activity of individual cells and then relies on computer analysis to exam ...
Introduction to Brain Structure - Center for Behavioral Neuroscience
... ways this is accomplished is by the convolutions (folding) of the cerebral cortex. Thus more advanced animals tend to have a more complicated cerebral cortex. Animals with a relatively smooth cerebral cortex are called lissencephalic while animals with a very convoluted cerebral cortex are called gy ...
... ways this is accomplished is by the convolutions (folding) of the cerebral cortex. Thus more advanced animals tend to have a more complicated cerebral cortex. Animals with a relatively smooth cerebral cortex are called lissencephalic while animals with a very convoluted cerebral cortex are called gy ...
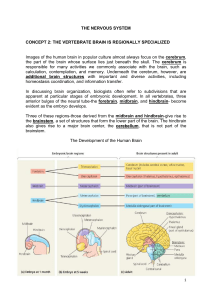
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN
... Images of the human brain in popular culture almost always focus on the cerebrum, the part of the brain whose surface lies just beneath the skull. The cerebrum is responsible for many activities we commonly associate with the brain, such as calculation, contemplation, and memory. Underneath the cere ...
... Images of the human brain in popular culture almost always focus on the cerebrum, the part of the brain whose surface lies just beneath the skull. The cerebrum is responsible for many activities we commonly associate with the brain, such as calculation, contemplation, and memory. Underneath the cere ...
11-5_TheMulti-CenterAspectOfMotorControl. _NagyD
... The basic function of the brain is to produce behaviours, which are, first and foremost, movements. Several different regions of the cerebral cortex are involved in controlling the body's movements. Similarly, in the human brain, planning for any given movement is done mainly in the forward portion ...
... The basic function of the brain is to produce behaviours, which are, first and foremost, movements. Several different regions of the cerebral cortex are involved in controlling the body's movements. Similarly, in the human brain, planning for any given movement is done mainly in the forward portion ...
Connectome

A connectome is a comprehensive map of neural connections in the brain, and may be thought of as its ""wiring diagram"". More broadly, a connectome would include the mapping of all neural connections within an organism's nervous system.The production and study of connectomes, known as connectomics, may range in scale from a detailed map of the full set of neurons and synapses within part or all of the nervous system of an organism to a macro scale description of the functional and structural connectivity between all cortical areas and subcortical structures. The term ""connectome"" is used primarily in scientific efforts to capture, map, and understand the organization of neural interactions within the brain.Research has successfully constructed the full connectome of one animal: the roundworm C. elegans (White et al., 1986, Varshney et al., 2011). Partial connectomes of a mouse retina and mouse primary visual cortex have also been successfully constructed. Bock et al.'s complete 12TB data set is publicly available at Open Connectome Project.The ultimate goal of connectomics is to map the human brain. This effort is pursued by the Human Connectome Project, sponsored by the National Institutes of Health, whose focus is to build a network map of the human brain in healthy, living adults.