
view - Queen`s University
... which form connections with the motor neurons after the synapse, and permit substantial processing of signals. But the direct projection from sensory afferents to motor neurons precludes such processing. Instead, the activity of these synapses (and other afferent synapses in the spinal cord) is regu ...
... which form connections with the motor neurons after the synapse, and permit substantial processing of signals. But the direct projection from sensory afferents to motor neurons precludes such processing. Instead, the activity of these synapses (and other afferent synapses in the spinal cord) is regu ...
Language Processing in the Brain
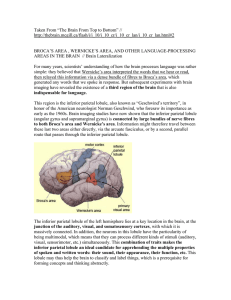
... Major lesions in the left parieto-occipital area can make someone unable to read and/or write while leaving their spoken-language abilities intact. In contrast, lesions in auditory associative areas such as Wernicke’s area will prevent someone both from understanding spoken language and from reading ...
... Major lesions in the left parieto-occipital area can make someone unable to read and/or write while leaving their spoken-language abilities intact. In contrast, lesions in auditory associative areas such as Wernicke’s area will prevent someone both from understanding spoken language and from reading ...
Chapter 21 - The Nervous System: Organization
... Reflexes are quick and produce behaviors that are typically beneficial. For example, when you fall, reflex arcs immediately act to extend your arm so that your arm prevents your head and body from hitting the ground. Some reflexes involve the brain, others do not. A whole series of responses may oc ...
... Reflexes are quick and produce behaviors that are typically beneficial. For example, when you fall, reflex arcs immediately act to extend your arm so that your arm prevents your head and body from hitting the ground. Some reflexes involve the brain, others do not. A whole series of responses may oc ...
Investigation of pathological mechanisms underlying the childhood
... Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) is the leading genetic cause of infant death, affecting around 1 in every 6,000 children. The condition is caused by loss of the Survival Motor Neuron (SMN) gene, which primarily results in a breakdown and loss of nerve cells (known as lower motor neurons) that connect ...
... Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) is the leading genetic cause of infant death, affecting around 1 in every 6,000 children. The condition is caused by loss of the Survival Motor Neuron (SMN) gene, which primarily results in a breakdown and loss of nerve cells (known as lower motor neurons) that connect ...
attachment-TheBrain[r] - U
... concentration, affecting the ability to recognize places, objects and people. It also receives and processes information about temperature, taste, touch, and movement coming from the rest of the body. Reading and arithmetic are also processed in this region and it affects ability to concentrate or f ...
... concentration, affecting the ability to recognize places, objects and people. It also receives and processes information about temperature, taste, touch, and movement coming from the rest of the body. Reading and arithmetic are also processed in this region and it affects ability to concentrate or f ...
Tuesday part A: Lecture - Computer Science
... Mary went to a restaurant for lunch. Afterwards she didn’t have enough money to buy the car she wanted. ...
... Mary went to a restaurant for lunch. Afterwards she didn’t have enough money to buy the car she wanted. ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... skin that a person can control – Sensory neurons which relay info about environment to CNS Reflex Arc – Motor neurons which initiate appropriate response ...
... skin that a person can control – Sensory neurons which relay info about environment to CNS Reflex Arc – Motor neurons which initiate appropriate response ...
Document
... The major structures of the basal ganglia (red-shaded areas) include the caudate nucleus, the subthalamic nucleus, the substantia nigra, the globus pallidus, and the putamen. The critical connections (inputs and outputs) of the basal ganglia are illustrated. ...
... The major structures of the basal ganglia (red-shaded areas) include the caudate nucleus, the subthalamic nucleus, the substantia nigra, the globus pallidus, and the putamen. The critical connections (inputs and outputs) of the basal ganglia are illustrated. ...
Activity Overview - Teacher Enrichment Initiatives
... cord and that they relay messages within the central nervous system. 4. The “Brain” processes the message and sends a message back to the foot to move off the rock. 5. The “Motor Neurons” must work together to send the message to the “Foot”. 6. When the “Foot” receives the message, it moves off the ...
... cord and that they relay messages within the central nervous system. 4. The “Brain” processes the message and sends a message back to the foot to move off the rock. 5. The “Motor Neurons” must work together to send the message to the “Foot”. 6. When the “Foot” receives the message, it moves off the ...
Neural underpinnings of superior action
... To dissociate the role of visual and motor action representations in experts’ action perception, in the present study we investigated whether the suppression of visual and motor areas in experts had different detrimental effects with respect to novices. We applied a temporal occlusion paradigm (adap ...
... To dissociate the role of visual and motor action representations in experts’ action perception, in the present study we investigated whether the suppression of visual and motor areas in experts had different detrimental effects with respect to novices. We applied a temporal occlusion paradigm (adap ...
Chapter 14 Brain Cranial Nerves
... • White matter (arbor vitae) visible in sagittal section • Connected to brainstem by cerebellar peduncles – superior peduncle = output to midbrain, thalamus, and cortex – middle peduncle = input from cerebral cortex and inner ear – inferior peduncle = spinocerebellar tracts (proprioception) ...
... • White matter (arbor vitae) visible in sagittal section • Connected to brainstem by cerebellar peduncles – superior peduncle = output to midbrain, thalamus, and cortex – middle peduncle = input from cerebral cortex and inner ear – inferior peduncle = spinocerebellar tracts (proprioception) ...
Nervous System Overview
... • Blood-brain barrier is endothelium that is permeable to lipidsoluble materials • alcohol, O2, CO2, nicotine and anesthetics • 3rd and 4th ventricles are breaks in the barrier where blood has direct access – monitors glucose, pH, osmolarity ...
... • Blood-brain barrier is endothelium that is permeable to lipidsoluble materials • alcohol, O2, CO2, nicotine and anesthetics • 3rd and 4th ventricles are breaks in the barrier where blood has direct access – monitors glucose, pH, osmolarity ...
L7-Brainstem Student..
... • (2) It has got center for cardiovascular, respiratory & autonomic regulation . • (3) It has centers for Brainstem Reflexes , such as cough reflex , gag reflex , swallowing , and vomiting ; + visual & auditory orientation reflexes (required for head movements. through Superior & Inferior Colliculi ...
... • (2) It has got center for cardiovascular, respiratory & autonomic regulation . • (3) It has centers for Brainstem Reflexes , such as cough reflex , gag reflex , swallowing , and vomiting ; + visual & auditory orientation reflexes (required for head movements. through Superior & Inferior Colliculi ...
Anatomy
... Learn about nervous system function by doing Rhbit simulations. Rhbit is a frog with only 8 neurons created at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. You are allowed to stimulate, inhibit or record from any of the 8 neurons. Brain imagine techniques such as PET scans and MRI are described on one ...
... Learn about nervous system function by doing Rhbit simulations. Rhbit is a frog with only 8 neurons created at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. You are allowed to stimulate, inhibit or record from any of the 8 neurons. Brain imagine techniques such as PET scans and MRI are described on one ...
9.14 Lecture 16: Descending Pathways and Evolution Notes
... Why would diaschisis effects of lesions of one of the descending pathways in the study be greater in humans than in the monkeys? What are major manifestations of such effects? After recovery of spinal reflexes, the enduring effects ...
... Why would diaschisis effects of lesions of one of the descending pathways in the study be greater in humans than in the monkeys? What are major manifestations of such effects? After recovery of spinal reflexes, the enduring effects ...
THE CEREBRAL CORTEX
... bound up with the prodigious abundance and unusual wealth of forms of the so-called neurons with the short axons. ...
... bound up with the prodigious abundance and unusual wealth of forms of the so-called neurons with the short axons. ...
Biology and Behaviour 40s
... • Type: Case Study, single subject, non-random sample, instrumental – it sought to construct/confirm a hypothesis regarding localization of inhibition in the brain as well as explaining the phenomena of his changed behaviour by what his brain injury turned out to be once they could perform an autops ...
... • Type: Case Study, single subject, non-random sample, instrumental – it sought to construct/confirm a hypothesis regarding localization of inhibition in the brain as well as explaining the phenomena of his changed behaviour by what his brain injury turned out to be once they could perform an autops ...
Reflex Arc - Cloudfront.net
... heat, pressure, etc.) in your environment COMPREHEND – Interneurons: connect sensory neurons to motor neurons; located in the brain/spinal cord RESPOND – Motor neurons: make your muscles respond (taking your hand away from something hot) ...
... heat, pressure, etc.) in your environment COMPREHEND – Interneurons: connect sensory neurons to motor neurons; located in the brain/spinal cord RESPOND – Motor neurons: make your muscles respond (taking your hand away from something hot) ...
The Biology of Mind
... Neurons do NOT touch each other- the space in between is call the synapse. ...
... Neurons do NOT touch each other- the space in between is call the synapse. ...
Summary of the Opening Conference
... A “silent hero” which stood in the background of many talks was the mirror. That there are neurons in the brain of the monkey and most probably in that of humans as well that do not only engage in performing actions but also in perceiving them, gave rise to multiple speculations about the mechanism ...
... A “silent hero” which stood in the background of many talks was the mirror. That there are neurons in the brain of the monkey and most probably in that of humans as well that do not only engage in performing actions but also in perceiving them, gave rise to multiple speculations about the mechanism ...
The Nervous System - Marshall Middle
... body's information gatherer, storage center and control system. It can respond to stimuli, transmit nerve impulses, and activate muscles. It collects information about the external conditions in relation to the body's external state, analyzes this information, and initiates appropriate responses to ...
... body's information gatherer, storage center and control system. It can respond to stimuli, transmit nerve impulses, and activate muscles. It collects information about the external conditions in relation to the body's external state, analyzes this information, and initiates appropriate responses to ...
Ontology of Actions
... a helicopter first starts its engine, then takes off, flies, lands at another point, and turns off its engine. This recognizer will recognize events that we would characterize as ’the helicopter flies to a point P and lands there’. If there are several helicopters in the world then they must have on ...
... a helicopter first starts its engine, then takes off, flies, lands at another point, and turns off its engine. This recognizer will recognize events that we would characterize as ’the helicopter flies to a point P and lands there’. If there are several helicopters in the world then they must have on ...


![attachment-TheBrain[r] - U](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009855576_1-24ac3687f395c1b24e4bd94b77fcff5f-300x300.png)



















