Autism and Computational Simulations
... Reading words and seeing the drawing invokes similar brain activations, presumably reflecting semantics of concepts. Although individual variance is significant similar activations are found in brains of different people, a classifier may still be trained on pooled data. Model trained on ~10 fMRI sc ...
... Reading words and seeing the drawing invokes similar brain activations, presumably reflecting semantics of concepts. Although individual variance is significant similar activations are found in brains of different people, a classifier may still be trained on pooled data. Model trained on ~10 fMRI sc ...
PDF file
... Motor layer – Layer two develops using steps 1,2, and 4 above, but there is not top-down input, so Eq. 1 does not have a top-down part. The response z(2) is computed in the same way otherwise, with its own parameter k (2) controlling the number of non-inhibited neurons. When the network is being tra ...
... Motor layer – Layer two develops using steps 1,2, and 4 above, but there is not top-down input, so Eq. 1 does not have a top-down part. The response z(2) is computed in the same way otherwise, with its own parameter k (2) controlling the number of non-inhibited neurons. When the network is being tra ...
09_chapter_3
... SVC and nu-SVC, and the former one was selected for these studies. More concretely, [Hsu et al., 2007] is a practical guidance provided by Lin’s group to explain how to implement C-SVC to yield good performance, including data scaling, the use of an RBF kernel, parameter selection by cross-validatio ...
... SVC and nu-SVC, and the former one was selected for these studies. More concretely, [Hsu et al., 2007] is a practical guidance provided by Lin’s group to explain how to implement C-SVC to yield good performance, including data scaling, the use of an RBF kernel, parameter selection by cross-validatio ...
Keynotes - IEEE Computer Society
... developed for handwriting and speech recognition. Examples of such key concepts are the Bayes decision rule for minimum error rate and probabilistic approaches to acoustic modelling (e.g. hidden Markov models) and language modelling. Recently the accuracy of handwriting and speech recognition could ...
... developed for handwriting and speech recognition. Examples of such key concepts are the Bayes decision rule for minimum error rate and probabilistic approaches to acoustic modelling (e.g. hidden Markov models) and language modelling. Recently the accuracy of handwriting and speech recognition could ...
Descision making
... • The strength of each connection is calculated from the product of the preand postsynaptic activities, scaled by a “learning rate” a (which determines how fast connection weights change). Δwij = a * g[i] * f[j]. • The linear associator stores associations between a pattern of neural activations in ...
... • The strength of each connection is calculated from the product of the preand postsynaptic activities, scaled by a “learning rate” a (which determines how fast connection weights change). Δwij = a * g[i] * f[j]. • The linear associator stores associations between a pattern of neural activations in ...
Chapter 4
... When does life begin? British Warnock Committee (1984) suggested experimentation on the human embryo within the first 14 days of its development. 1. Because before this time implantation in the uterus is not complete; 2. Because only after this time do the embryo cells lose their so-called ‘totip ...
... When does life begin? British Warnock Committee (1984) suggested experimentation on the human embryo within the first 14 days of its development. 1. Because before this time implantation in the uterus is not complete; 2. Because only after this time do the embryo cells lose their so-called ‘totip ...
for neural fate
... Inductive Signals They affect/determine which genes are expressed in a cell. 1920s-Spemann & Mangold Before Gastrulation, they transplant the DLB from a pigmented animal to a non pigmented one and they place it in the ventral ectoderm. ...
... Inductive Signals They affect/determine which genes are expressed in a cell. 1920s-Spemann & Mangold Before Gastrulation, they transplant the DLB from a pigmented animal to a non pigmented one and they place it in the ventral ectoderm. ...
Bimal K
... The hidden layer functions to associate the input and output layers. The input and output layers (defined as buffers) have neurons equal to the respective number of signals. The input layer neurons do not have transfer function, but there is scale factor in each input to normalize the input signals. ...
... The hidden layer functions to associate the input and output layers. The input and output layers (defined as buffers) have neurons equal to the respective number of signals. The input layer neurons do not have transfer function, but there is scale factor in each input to normalize the input signals. ...
Cell division and migration in a `genotype` for neural networks (Cell
... In the developmental model described in Nolfi and Parisi (1992; in press) what is simulated is the process of neural growth. Neural networks are viewed as physical objects in bidimensional space and not, as is usually done, as purely topological structures. Neurons are assigned physical positions in ...
... In the developmental model described in Nolfi and Parisi (1992; in press) what is simulated is the process of neural growth. Neural networks are viewed as physical objects in bidimensional space and not, as is usually done, as purely topological structures. Neurons are assigned physical positions in ...
Machine Learning in Board Games
... [4]. “Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction”, A. Barto. MIT Press, 1998. Available online at: http://webdocs.cs.ualberta.ca/~sutton/book/the-book.html [5]. “Evolving Neural Networks to Play Checkers without Relying on Expert Knowledge”, K. Chellapilla and D. Fogel, IEEE Transactions on Neural Netw ...
... [4]. “Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction”, A. Barto. MIT Press, 1998. Available online at: http://webdocs.cs.ualberta.ca/~sutton/book/the-book.html [5]. “Evolving Neural Networks to Play Checkers without Relying on Expert Knowledge”, K. Chellapilla and D. Fogel, IEEE Transactions on Neural Netw ...
Module 4 Neural and Hormonal Systems
... The autonomic nervous system controls our glands and the muscles of our internal organs, influencing such functions as glandular activity, heartbeat, and digestion. It may be consciously overridden. The sympathetic nervous system arouses and expends energy. Heartrate, blood pressure, digestion, bloo ...
... The autonomic nervous system controls our glands and the muscles of our internal organs, influencing such functions as glandular activity, heartbeat, and digestion. It may be consciously overridden. The sympathetic nervous system arouses and expends energy. Heartrate, blood pressure, digestion, bloo ...
nips2.frame - /marty/papers/drotdil
... receptive field. Regions of maximum weights in direction-speed subspace tended to vary smoothly across x-y space such that opposite ends of the receptive field were sensitive to opposite directions. This picture obtained with full and medium-sized partial field training examples, breaking down only ...
... receptive field. Regions of maximum weights in direction-speed subspace tended to vary smoothly across x-y space such that opposite ends of the receptive field were sensitive to opposite directions. This picture obtained with full and medium-sized partial field training examples, breaking down only ...
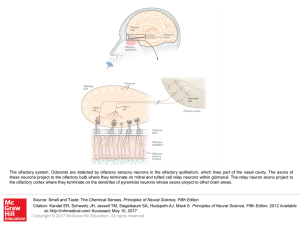
Synapse formation
... Synapse: Zone / junction between two neurons – Comprises: axon terminal of presynaptic neuron, the synaptic gap, and the dendrite of the postsynaptic neuron. During Learning: – axon terminals of the presynaptic neuron release a neurotransmitter called glutamate into the synaptic gap between the pres ...
... Synapse: Zone / junction between two neurons – Comprises: axon terminal of presynaptic neuron, the synaptic gap, and the dendrite of the postsynaptic neuron. During Learning: – axon terminals of the presynaptic neuron release a neurotransmitter called glutamate into the synaptic gap between the pres ...
PPT
... complex features and large receptive fields in higher layers). In this hierarchy, processing of visual input is done in bottom-up direction, and attentional modulation (selective enhancement of processing) works in a topdown fashion. December 1, 2009 ...
... complex features and large receptive fields in higher layers). In this hierarchy, processing of visual input is done in bottom-up direction, and attentional modulation (selective enhancement of processing) works in a topdown fashion. December 1, 2009 ...
reverse engineering of the visual system using networks of spiking
... ganglion cells in the retina, relay cells in the thalamus, cortical areas V1, V2, V4, and the posterior inferotemporal cortex. Calculations suggest that each of these stages only has about 10 ms to do the necessary computation. Ten milliseconds may seem plenty of time given the speed of today's elec ...
... ganglion cells in the retina, relay cells in the thalamus, cortical areas V1, V2, V4, and the posterior inferotemporal cortex. Calculations suggest that each of these stages only has about 10 ms to do the necessary computation. Ten milliseconds may seem plenty of time given the speed of today's elec ...
UNIVERSIDAD SAN FRANCISCO DE QUITO USFQ Detección y
... therefore the system does not require to be individually trained by the user to begin recognizing events. The objective, is to leave a set of weights and bias W that can be used as parameters on the neural network to produce acceptable recognition for any person. Opposed to the Personal Mode, the sa ...
... therefore the system does not require to be individually trained by the user to begin recognizing events. The objective, is to leave a set of weights and bias W that can be used as parameters on the neural network to produce acceptable recognition for any person. Opposed to the Personal Mode, the sa ...
Lecture 16
... Leaky integrate and fire neurons Encode each individual spike Time is represented exactly Each spike has an associated time The timing of recent incoming spikes determines whether a neuron will fire • Computationally expensive • Can we do almost as well without encoding every single spike? ...
... Leaky integrate and fire neurons Encode each individual spike Time is represented exactly Each spike has an associated time The timing of recent incoming spikes determines whether a neuron will fire • Computationally expensive • Can we do almost as well without encoding every single spike? ...
Associative memory with spatiotemporal chaos control
... systems @1,2#, and chaos seems to be essential in such systems. Even in high life forms, such as in the operations of the neurons in the human brain, it is recognized that there exists a certain chaotic dynamics in the networks. The question naturally arises whether such chaotic dynamics plays a fun ...
... systems @1,2#, and chaos seems to be essential in such systems. Even in high life forms, such as in the operations of the neurons in the human brain, it is recognized that there exists a certain chaotic dynamics in the networks. The question naturally arises whether such chaotic dynamics plays a fun ...
Modeling the Evolution of Decision Rules in the Human Brain
... Cohen-Grossberg equations for a competitive neural network: Each xi excites itself, inhibits the others. As time increases, the system always goes to a steady state (point attractor) because there is a system energy function or Lyapunov function, called V, that decreases along ...
... Cohen-Grossberg equations for a competitive neural network: Each xi excites itself, inhibits the others. As time increases, the system always goes to a steady state (point attractor) because there is a system energy function or Lyapunov function, called V, that decreases along ...
Medical Image Segmentation Using Artificial Neural Networks
... 3. Compute the centroid and the covariance matrix for class l as described in (Amartur et al., 1992). 4. Solve equation (8) using Euler’s approximation. 5. If there is a significant change in the input of each neuron, repeat from step 2), else, terminate. If the number of clusters is large, the netw ...
... 3. Compute the centroid and the covariance matrix for class l as described in (Amartur et al., 1992). 4. Solve equation (8) using Euler’s approximation. 5. If there is a significant change in the input of each neuron, repeat from step 2), else, terminate. If the number of clusters is large, the netw ...
ICANN2006web
... Patterns in {N_i,p & N_i,n} are backbones of the Hopfield model. They form the backbone structure of the model. ...
... Patterns in {N_i,p & N_i,n} are backbones of the Hopfield model. They form the backbone structure of the model. ...