1. What different types of attention exist? Name and describe at least
... Exogenous or bottom-up attention: type of attention associated with sensory stimuli “popping out” of the background withouth cognitive input, e.g., a flash of light in the darkness, a loud sound in quietness, a warm spot in a cold environment etc. Endogenous / selective / top-down attention: attenti ...
... Exogenous or bottom-up attention: type of attention associated with sensory stimuli “popping out” of the background withouth cognitive input, e.g., a flash of light in the darkness, a loud sound in quietness, a warm spot in a cold environment etc. Endogenous / selective / top-down attention: attenti ...
Learning ap
... Operant Conditioning-behavior is influenced by its consequences. Examplestudying gets you good grades. ...
... Operant Conditioning-behavior is influenced by its consequences. Examplestudying gets you good grades. ...
Set 3
... Human emotions are largely learned and include: affection, pride, guilt, pity, envy, and resentment Emotions are represented in the prefrontal cortex and the limbic system namely the amygdala Lesion of the left prefrontal area produces depression Lesion of right prefrontal produces laughter ...
... Human emotions are largely learned and include: affection, pride, guilt, pity, envy, and resentment Emotions are represented in the prefrontal cortex and the limbic system namely the amygdala Lesion of the left prefrontal area produces depression Lesion of right prefrontal produces laughter ...
The Biology of Mind take
... the cortex. The medulla secretes hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) during stressful and emotional situations, while the adrenal cortex regulates salt and carbohydrate metabolism. ...
... the cortex. The medulla secretes hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) during stressful and emotional situations, while the adrenal cortex regulates salt and carbohydrate metabolism. ...
The Biology of Mind take 2
... the cortex. The medulla secretes hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) during stressful and emotional situations, while the adrenal cortex regulates salt and carbohydrate metabolism. ...
... the cortex. The medulla secretes hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) during stressful and emotional situations, while the adrenal cortex regulates salt and carbohydrate metabolism. ...
Overview of the Brain
... thalamus, hypothalamus, amygdala, and the cerebellum. • Each of these regions are divided into twin halves—the left and right hemispheres of the brain with the exception of the cerebellum which is attached to the brain stem. • These structures are responsible for low level tasks including processing ...
... thalamus, hypothalamus, amygdala, and the cerebellum. • Each of these regions are divided into twin halves—the left and right hemispheres of the brain with the exception of the cerebellum which is attached to the brain stem. • These structures are responsible for low level tasks including processing ...
Learning/Behaviorism
... – Associations are learned when they are naturally adaptive – Training that override biological tendencies is short-lived • Example: Performing pig ...
... – Associations are learned when they are naturally adaptive – Training that override biological tendencies is short-lived • Example: Performing pig ...
PowerPoint for 9/29
... Supporting player: the slowercommunicating endocrine system (hormones) Star of the show: the brain and its structures ...
... Supporting player: the slowercommunicating endocrine system (hormones) Star of the show: the brain and its structures ...
PsychScich03
... been learned through the study of the effects of drugs and toxins on emotion, thought, and behavior • Drugs and toxins can alter neurotransmitter action: – Agonists:enhance the actions of neurotransmitters – Antagonists:inhibit the actions of neurotransmitters • Researchers often inject agonists or ...
... been learned through the study of the effects of drugs and toxins on emotion, thought, and behavior • Drugs and toxins can alter neurotransmitter action: – Agonists:enhance the actions of neurotransmitters – Antagonists:inhibit the actions of neurotransmitters • Researchers often inject agonists or ...
Major lobes - Ohio University
... Consciousness => states existing for a noticeable period of time, integrating reportable sensory information about different modalities, with an influence on other processes in the brain. Each system, which has internal states and is complex enough to comment on them, will claim that it's consciou ...
... Consciousness => states existing for a noticeable period of time, integrating reportable sensory information about different modalities, with an influence on other processes in the brain. Each system, which has internal states and is complex enough to comment on them, will claim that it's consciou ...
The Nervous System
... 1. Control center for all body activities 2. Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
... 1. Control center for all body activities 2. Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
Exercise and the Bra..
... down into a form easily burned by neurons. This substance is released into the space between the cells and the neurons swallow it, maintaining their energy levels. But while scientists knew that the brain had and could access these energy stores, they had been unable to study when the brain’s stored ...
... down into a form easily burned by neurons. This substance is released into the space between the cells and the neurons swallow it, maintaining their energy levels. But while scientists knew that the brain had and could access these energy stores, they had been unable to study when the brain’s stored ...
Behavioral Neuroscience
... More intelligent animals have increased “uncommitted” or association areas of the cortex. ...
... More intelligent animals have increased “uncommitted” or association areas of the cortex. ...
Robotic/Human Loops - Computer Science & Engineering
... – Understand scientific basis for superiority of human intelligence over current machine learning and AI – Create neurally-based cognitively intelligent systems – Develop neuromorphic robots which interact with humans – Complement Neuroscience wet lab and cognitive research ...
... – Understand scientific basis for superiority of human intelligence over current machine learning and AI – Create neurally-based cognitively intelligent systems – Develop neuromorphic robots which interact with humans – Complement Neuroscience wet lab and cognitive research ...
Autobiography for 2016 Kavli Prize in Neuroscience Carla J. Shatz
... binocular vision, which resulted in the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1981, revealed brain circuits of almost crystalline- like perfection. Every day as a student I watched the beauty of visual system organization unfold before my eyes. I thought, “all research must be like this”! Of cou ...
... binocular vision, which resulted in the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1981, revealed brain circuits of almost crystalline- like perfection. Every day as a student I watched the beauty of visual system organization unfold before my eyes. I thought, “all research must be like this”! Of cou ...
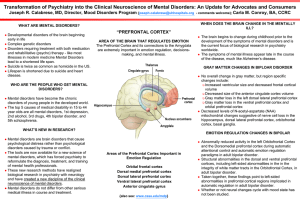
Transformation of Psychiatry into the Clinical Neuroscience of
... 2nd alcohol, 3rd drugs, 4th bipolar disorder, and 5th schizophrenia. ...
... 2nd alcohol, 3rd drugs, 4th bipolar disorder, and 5th schizophrenia. ...
The Brain The brain is responsible for everything we think, feel and
... The somatosensory cortex runs parallel to the primary motor cortex and like it has different parts the body associated with areas of the cortex. Some body parts have a larger area of cortex devoted to them, depending on the sensitivity of the body part. The hands and mouth have a larger area of cort ...
... The somatosensory cortex runs parallel to the primary motor cortex and like it has different parts the body associated with areas of the cortex. Some body parts have a larger area of cortex devoted to them, depending on the sensitivity of the body part. The hands and mouth have a larger area of cort ...
Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves
... • The two cerebral hemispheres share many functions • Each hemisphere also performs unique functions • Functional specialization of each hemisphere is more pronounced in men • Females generally have larger connections between 2 sides ...
... • The two cerebral hemispheres share many functions • Each hemisphere also performs unique functions • Functional specialization of each hemisphere is more pronounced in men • Females generally have larger connections between 2 sides ...
Endocrine glands
... “movie” of changes in the activity of the brain using images from different time periods. ...
... “movie” of changes in the activity of the brain using images from different time periods. ...
Brain Matters - FirstClass Login
... Cells of the nervous system, called neurons, are specialized to carry "messages" through an electrochemical process. The human brain has about 100 billion neurons. ...
... Cells of the nervous system, called neurons, are specialized to carry "messages" through an electrochemical process. The human brain has about 100 billion neurons. ...
Introductory activity and article
... record how people relate to one another and to their environments. They also study the formation of groups; the causes of various forms of social behavior; and the role of churches, schools, and other institutions within a society. Sociology is a social science and is closely related to anthropology ...
... record how people relate to one another and to their environments. They also study the formation of groups; the causes of various forms of social behavior; and the role of churches, schools, and other institutions within a society. Sociology is a social science and is closely related to anthropology ...