Nerve activates contraction
... digestion and elimination of feces and urine and with conserving body energy Heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rates are at low normal levels; pupils are constricted; skin is warm; digestive tract is actively digesting ...
... digestion and elimination of feces and urine and with conserving body energy Heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rates are at low normal levels; pupils are constricted; skin is warm; digestive tract is actively digesting ...
File
... • Secreted by the _________________ ______________ • Circulates in ventricles, central canal of spinal cord, and the subarachnoid space • Completely surrounds the brain and spinal cord • Excess or wasted CSF is absorbed by the ___________________ ___________ • _____________ _____________ similar to ...
... • Secreted by the _________________ ______________ • Circulates in ventricles, central canal of spinal cord, and the subarachnoid space • Completely surrounds the brain and spinal cord • Excess or wasted CSF is absorbed by the ___________________ ___________ • _____________ _____________ similar to ...
Chapter 48 Nervous Systems
... Glia actively take up the neurotransmitter at some synapses and metabolize it as fuel. The neurotransmitter acetylcholine is degraded by acetylcholinesterase, an enzyme in the synaptic cleft. Postsynaptic potentials are graded; their magnitude varies with a number of factors, including the amoun ...
... Glia actively take up the neurotransmitter at some synapses and metabolize it as fuel. The neurotransmitter acetylcholine is degraded by acetylcholinesterase, an enzyme in the synaptic cleft. Postsynaptic potentials are graded; their magnitude varies with a number of factors, including the amoun ...
Nerve Muscle Physiology
... • Secreted by many tissue in body e.g., muscles/ neurons/ astrocytes • Functions: – Facilitate initial growth and development of nerve cells in CNS & PNS ...
... • Secreted by many tissue in body e.g., muscles/ neurons/ astrocytes • Functions: – Facilitate initial growth and development of nerve cells in CNS & PNS ...
Nerve Muscle Physiology
... • Secreted by many tissue in body e.g., muscles/ neurons/ astrocytes • Functions: – Facilitate initial growth and development of nerve cells in CNS & PNS ...
... • Secreted by many tissue in body e.g., muscles/ neurons/ astrocytes • Functions: – Facilitate initial growth and development of nerve cells in CNS & PNS ...
FREE Sample Here
... The spinal cord segments are named according to vertebral bones surrounding the spinal cord. The incoming afferent sensory nerves and outgoing efferent motor nerves exit the vertebral column between each vertebral bone resulting in 31 discrete nerve segments. The area that is innervated by each of t ...
... The spinal cord segments are named according to vertebral bones surrounding the spinal cord. The incoming afferent sensory nerves and outgoing efferent motor nerves exit the vertebral column between each vertebral bone resulting in 31 discrete nerve segments. The area that is innervated by each of t ...
File - CYPA Psychology
... the involuntary functioning of blood vessels, body organs, and glands? A) central nervous system B) autonomic nervous system C) somatic nervous system D) sympathetic nervous system ...
... the involuntary functioning of blood vessels, body organs, and glands? A) central nervous system B) autonomic nervous system C) somatic nervous system D) sympathetic nervous system ...
Protocadherin mediates collective axon extension of neurons
... showed similar directional movements to neuronal growth cones. Thus, the results showed that Pcdh17 promotes cell migration by localizing at interaxonal adhesion sites and recruiting the WAVE complex and further downstream factors, which enhance the efficiency of axon elongation. “The functions of c ...
... showed similar directional movements to neuronal growth cones. Thus, the results showed that Pcdh17 promotes cell migration by localizing at interaxonal adhesion sites and recruiting the WAVE complex and further downstream factors, which enhance the efficiency of axon elongation. “The functions of c ...
The Function & Anatomy of Neurons What is a Neuron?
... Satellite Cells- Surround cell body and aid in controlling chemical environment. ...
... Satellite Cells- Surround cell body and aid in controlling chemical environment. ...
Document
... • Spontaneous activity allows for bidirectional signaling • S-curve is common • Different cells have different ranges and different dynamics • Population code ...
... • Spontaneous activity allows for bidirectional signaling • S-curve is common • Different cells have different ranges and different dynamics • Population code ...
THE NeurobiologyOF “We”
... Right hemisphere signals (are those) the mirror neuron system uses to simulate the other within ourselves and to construct a neural map of our interdependent sense of a ‘self.’ It’s how we can be both an ‘I’ and part of an ‘us.’ ”20 So how can we re-shape our brain to become more open and receptive ...
... Right hemisphere signals (are those) the mirror neuron system uses to simulate the other within ourselves and to construct a neural map of our interdependent sense of a ‘self.’ It’s how we can be both an ‘I’ and part of an ‘us.’ ”20 So how can we re-shape our brain to become more open and receptive ...
Modeling and interpretation of extracellular potentials
... • Source of extracellular potential: Transmembrane currents ...
... • Source of extracellular potential: Transmembrane currents ...
Glutamate
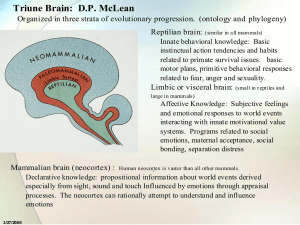
... related to primate survival issues. basic motor plans, primitive behavioral responses related to fear, anger and sexuality. ...
... related to primate survival issues. basic motor plans, primitive behavioral responses related to fear, anger and sexuality. ...
3 The Third-Person View of the Mind
... in. Its function is to receive information about the environment from the senses, decide how to move the body to achieve survival and reproduction, and control the muscles to carry out the planned action. Figure 3-1 illustrates this role of the brain as the link between the senses and muscles. Incre ...
... in. Its function is to receive information about the environment from the senses, decide how to move the body to achieve survival and reproduction, and control the muscles to carry out the planned action. Figure 3-1 illustrates this role of the brain as the link between the senses and muscles. Incre ...
Chapter 13 - Martini
... Components of a reflex arc 1. Stimulus activates a receptor. 2. Impulse travels along a sensory pathway. 3. Integration occurs in an integration center (most often in the CNS) 4. Impulse then travels by a motor pathway. 5. An effector responds. ...
... Components of a reflex arc 1. Stimulus activates a receptor. 2. Impulse travels along a sensory pathway. 3. Integration occurs in an integration center (most often in the CNS) 4. Impulse then travels by a motor pathway. 5. An effector responds. ...
LESSON PLAN
... - the spinal cord is located inside the v………. c…….. and it is protected by the spinal meninges, a structure made up of 3 layers of tissue: dura mater (which comes into direct contact with bones/bone tissue), the arachnoid and pia mater (which come into direct contact with the nervous system); betwee ...
... - the spinal cord is located inside the v………. c…….. and it is protected by the spinal meninges, a structure made up of 3 layers of tissue: dura mater (which comes into direct contact with bones/bone tissue), the arachnoid and pia mater (which come into direct contact with the nervous system); betwee ...
lecture #6
... • each cell surrounds multiple unmyelinated PNS axons with a single layer of its plasma membrane • produces part of the myelin sheath surrounding an axon in the PNS • also contributes to regeneration of PNS axons ...
... • each cell surrounds multiple unmyelinated PNS axons with a single layer of its plasma membrane • produces part of the myelin sheath surrounding an axon in the PNS • also contributes to regeneration of PNS axons ...
Purinergic signaling in acupuncture
... ATP, “purinergic signaling” (since ATP is a purine nucleotide), and formulated the purinergic signaling hypothesis (2). In 2009, Burnstock proposed that purinergic signaling could be involved in the physiological mechanisms mediating acupuncture effects. This hypothesis suggested that mechanical def ...
... ATP, “purinergic signaling” (since ATP is a purine nucleotide), and formulated the purinergic signaling hypothesis (2). In 2009, Burnstock proposed that purinergic signaling could be involved in the physiological mechanisms mediating acupuncture effects. This hypothesis suggested that mechanical def ...
D. What Causes Multiple Sclerosis?
... fiber that transmits the nerve impulse is like the wire, and the myelin sheath is like the insulation around the wire. Myelin is present in both the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), but it is only the destruction of CNS myelin that produces the symptoms of MS. ...
... fiber that transmits the nerve impulse is like the wire, and the myelin sheath is like the insulation around the wire. Myelin is present in both the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), but it is only the destruction of CNS myelin that produces the symptoms of MS. ...
Dynamic Range Analysis of HH Model for Excitable Neurons
... this number may vary widely across neuron types [1]. Neurons communicate with each other by means of electrical signal passing through long protoplasmic fibers known as axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potential to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipie ...
... this number may vary widely across neuron types [1]. Neurons communicate with each other by means of electrical signal passing through long protoplasmic fibers known as axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potential to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipie ...
The Nervous System - Florida International University
... Sensory information crosses to the opposite side in the spinal cord The sensory information ascends to the ...
... Sensory information crosses to the opposite side in the spinal cord The sensory information ascends to the ...
axon
... Multiple Sclerosis MS is thought to be an autoimmune disease in which the myelin is lost in multiple areas, leaving scar tissue called sclerosis. These damaged areas are also known as plaques or lesions. Sometimes the nerve fiber itself is damaged or broken. ...
... Multiple Sclerosis MS is thought to be an autoimmune disease in which the myelin is lost in multiple areas, leaving scar tissue called sclerosis. These damaged areas are also known as plaques or lesions. Sometimes the nerve fiber itself is damaged or broken. ...
Biol 203 Lab Week 10 Nervous System Histology
... Multiple Sclerosis MS is thought to be an autoimmune disease in which the myelin is lost in multiple areas, leaving scar tissue called sclerosis. These damaged areas are also known as plaques or lesions. Sometimes the nerve fiber itself is damaged or broken. Myelin not only protects nerve fibers, bu ...
... Multiple Sclerosis MS is thought to be an autoimmune disease in which the myelin is lost in multiple areas, leaving scar tissue called sclerosis. These damaged areas are also known as plaques or lesions. Sometimes the nerve fiber itself is damaged or broken. Myelin not only protects nerve fibers, bu ...
Chapter 3 The Nervous System and the Brain
... the heart, lungs, bladder, liver, kidneys, and other bodily related functions and its preganglionic neurons/fibers are rather long and its postganglionic neurons/fibers are short. The Enteric Nervous System is the third division of the autonomic nervous system. It is a collective mass of nerve fiber ...
... the heart, lungs, bladder, liver, kidneys, and other bodily related functions and its preganglionic neurons/fibers are rather long and its postganglionic neurons/fibers are short. The Enteric Nervous System is the third division of the autonomic nervous system. It is a collective mass of nerve fiber ...