SNPs: the great importance of small differences
... to affect the relative risk of contracting a disease, in extreme cases a single SNP may actually cause a disease. In sickle cell anemia, for instance, substitution of a single nucleotide in the gene for hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying red blood pigment, results in synthesis of an altered protein whi ...
... to affect the relative risk of contracting a disease, in extreme cases a single SNP may actually cause a disease. In sickle cell anemia, for instance, substitution of a single nucleotide in the gene for hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying red blood pigment, results in synthesis of an altered protein whi ...
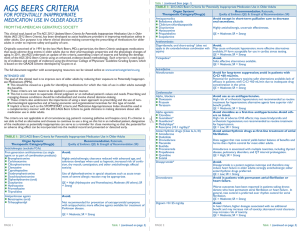
Antifungal management in the haematology patient
... levels – yes use 7mg/Kg BD (200mg BD orally) and consider combination therapy with an echinocandin and measure levels ...
... levels – yes use 7mg/Kg BD (200mg BD orally) and consider combination therapy with an echinocandin and measure levels ...
PROTECTIVE EFFECT OF NIGELLA SATIVA AGAINST ASPIRIN INDUCED GASTRIC DAMAGE IN RATS Original Article
... results also revealed that the damages were less in ethanolic extract followed by aqueous extract groups in a dose dependent manner [Fig 1D, Fig 1E, Fig 1F]. Aspirin is non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) which inhibits cycloxygenase (COX) enzyme irreversibly. COX enzyme converts arachidoni ...
... results also revealed that the damages were less in ethanolic extract followed by aqueous extract groups in a dose dependent manner [Fig 1D, Fig 1E, Fig 1F]. Aspirin is non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) which inhibits cycloxygenase (COX) enzyme irreversibly. COX enzyme converts arachidoni ...
NC Division of Medical Assistance Medicaid and Health Choice
... Related Clinical Coverage Policies Refer to http://dma.ncdhhs.gov/ for the related coverage policies listed below: 9A, Over the Counter Products 9B, Hemophilia Specialty Pharmacy Program ...
... Related Clinical Coverage Policies Refer to http://dma.ncdhhs.gov/ for the related coverage policies listed below: 9A, Over the Counter Products 9B, Hemophilia Specialty Pharmacy Program ...
this PDF file - The Southwest Respiratory and Critical
... cases of angioedema which present to the emergency department; 11% of these patients require ICU admission. We report two patients who required emergency surgical airways secondary to angioedema related to ACE-inhibitors. Clinicians need to remember that these situations can be extremely dangerous a ...
... cases of angioedema which present to the emergency department; 11% of these patients require ICU admission. We report two patients who required emergency surgical airways secondary to angioedema related to ACE-inhibitors. Clinicians need to remember that these situations can be extremely dangerous a ...
Ken`s PowerPoint Slides
... diuretic, calcium channel blocker, ACE inhibitor or ARB (Moderate) • Difference: JNC 7 recommended thiazides as first line treatment; beta blockers removed from first group of medications ...
... diuretic, calcium channel blocker, ACE inhibitor or ARB (Moderate) • Difference: JNC 7 recommended thiazides as first line treatment; beta blockers removed from first group of medications ...
Antibiotic distribution into the CNS
... The smaller the better for CNS penetration Lipophilicity: The more lipophilic usually the better- although very lipophilic molecules are often highly protein bound or bind to lipid membranes. Diffusion can also be pH dependent ...
... The smaller the better for CNS penetration Lipophilicity: The more lipophilic usually the better- although very lipophilic molecules are often highly protein bound or bind to lipid membranes. Diffusion can also be pH dependent ...
CIELAP – There is No "AWAY" - Canadian Institute for
... sludge spread on farm fields. In humans, between 50 - 90% of the active ingredients in drugs are not absorbed and are excreted. The figures are similar in other animals, and for antibiotics, widely used in animal feed, some 25 - 75% of the drugs pass into the environment. Consequently, major points ...
... sludge spread on farm fields. In humans, between 50 - 90% of the active ingredients in drugs are not absorbed and are excreted. The figures are similar in other animals, and for antibiotics, widely used in animal feed, some 25 - 75% of the drugs pass into the environment. Consequently, major points ...
STIM Antihypertensives
... This site is regulated by aldosterone Actions depend on the renal prostaglandin production and therefore inhibited by NSAIDs Amiloride and Triamterene interfere with Na entry through the epithelial sodium ion channels in the apical membrane of the collecting tubule Spironolactone and eplerenone bind ...
... This site is regulated by aldosterone Actions depend on the renal prostaglandin production and therefore inhibited by NSAIDs Amiloride and Triamterene interfere with Na entry through the epithelial sodium ion channels in the apical membrane of the collecting tubule Spironolactone and eplerenone bind ...
Organogels: Properties and Applications in drug delivery
... solubility limit of the organogelators. This results in the precipitation of the organogelators as fiber-like structures which undergoes physical interaction so as to form a gelled structure. These solid fiber-like structures align themselves into bundles. On the other hand, fluid-fiber matrix is fo ...
... solubility limit of the organogelators. This results in the precipitation of the organogelators as fiber-like structures which undergoes physical interaction so as to form a gelled structure. These solid fiber-like structures align themselves into bundles. On the other hand, fluid-fiber matrix is fo ...
Update on Oral anticoagulation therapy
... compliance may potentially have a higher risk of not achieving a therapeutic effect of the NOACs because of their relatively short half-life.6 NOACs have been in use only for a few years and the emergence of further serious adverse effects is still a possibility.26 Renal Function: All NOACs are excr ...
... compliance may potentially have a higher risk of not achieving a therapeutic effect of the NOACs because of their relatively short half-life.6 NOACs have been in use only for a few years and the emergence of further serious adverse effects is still a possibility.26 Renal Function: All NOACs are excr ...
Tetracyclines
... Acinetobacter sp; anaerobes, both gram-positive and gramnegative; atypical agents, rickettsiae, chlamydia, and legionella; and rapidly growing mycobacteria all are susceptible. Proteus and P aeruginosa, however, are intrinsically resistant. ...
... Acinetobacter sp; anaerobes, both gram-positive and gramnegative; atypical agents, rickettsiae, chlamydia, and legionella; and rapidly growing mycobacteria all are susceptible. Proteus and P aeruginosa, however, are intrinsically resistant. ...
Nasalox Insert
... Contraindicated in patients with hypersensivity to Oxymetazoline Hydrochloride. Side Effects When this medicine is used for short period of time at low doses, side effects are usually rare. However stinging, burning, sneezing, increased nasal discharge, drying of the nostrils, and altered taste may ...
... Contraindicated in patients with hypersensivity to Oxymetazoline Hydrochloride. Side Effects When this medicine is used for short period of time at low doses, side effects are usually rare. However stinging, burning, sneezing, increased nasal discharge, drying of the nostrils, and altered taste may ...
Arnebia Euchroma in Diabetic Rats Abdollah Ghasemi Pirbalouti
... Burn and wound healing is a process by which damaged tissue is restored as closely as possible to its normal state and wound contraction is the process of shrinkage of the area of the wound. It is mainly dependent upon the type and extent of damage, the general state of health and the ability of the ...
... Burn and wound healing is a process by which damaged tissue is restored as closely as possible to its normal state and wound contraction is the process of shrinkage of the area of the wound. It is mainly dependent upon the type and extent of damage, the general state of health and the ability of the ...
PHL 424 5th S
... lincomycin, an antibiotic produced by Streptomyces lincolnensis Lincomycin, although structurally distinct, resembles erythromycin in activity, but it is toxic and no longer used ...
... lincomycin, an antibiotic produced by Streptomyces lincolnensis Lincomycin, although structurally distinct, resembles erythromycin in activity, but it is toxic and no longer used ...
Enabling Pharmacists To Respond To The Health Needs Of
... In spite of these changes, however, the practice Act and its penumbra of Acts and rules still approach pharmacy practice from the viewpoint of pharmacists as dispensers of medicines who may also provide ...
... In spite of these changes, however, the practice Act and its penumbra of Acts and rules still approach pharmacy practice from the viewpoint of pharmacists as dispensers of medicines who may also provide ...
Foods and Meds to Avoid with MAOIs
... Why are there dietary restrictions to follow with Ayahuasca? Ayahuasca (Banisteriopsis caapi vine) is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI). MAOIs block an enzyme called monoamine oxidase, which breaks down excess tyramine in the body. Tyramine is an amino acid that helps regulate blood pressure. But ...
... Why are there dietary restrictions to follow with Ayahuasca? Ayahuasca (Banisteriopsis caapi vine) is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI). MAOIs block an enzyme called monoamine oxidase, which breaks down excess tyramine in the body. Tyramine is an amino acid that helps regulate blood pressure. But ...
F ull L ength O riginal R esearch P aper
... known as fast dissolving tablets [4]. United States ...
... known as fast dissolving tablets [4]. United States ...
Nanomedicine Taxonomy
... systems; and MEMS devices which contain miniature moving parts for heart pacemakers and surgical devices. As previously mentioned micro device applications will be described in this nanomedicine taxonomy even though they are not nano. ...
... systems; and MEMS devices which contain miniature moving parts for heart pacemakers and surgical devices. As previously mentioned micro device applications will be described in this nanomedicine taxonomy even though they are not nano. ...
Hey Dude! How Did I Get Here?
... 3 Friends taken to same hospital after trying a new marijuana for the first time ...
... 3 Friends taken to same hospital after trying a new marijuana for the first time ...
Evidence for the roles of ... mediators in exercise-induced asthma: the ...
... flurbiprofen had a major inhibitory action in 5 of 8 subjects. Flurbiprofen alone also inhibited the response in the majority of subjects, but had a lesser effect on the maximum post-exercise fall in FEY1 than that achieved with terfenadine alone. The drug combination proved to have an inhibitory ef ...
... flurbiprofen had a major inhibitory action in 5 of 8 subjects. Flurbiprofen alone also inhibited the response in the majority of subjects, but had a lesser effect on the maximum post-exercise fall in FEY1 than that achieved with terfenadine alone. The drug combination proved to have an inhibitory ef ...
Drug interaction

A drug interaction is a situation in which a substance (usually another drug) affects the activity of a drug when both are administered together. This action can be synergistic (when the drug's effect is increased) or antagonistic (when the drug's effect is decreased) or a new effect can be produced that neither produces on its own. Typically, interactions between drugs come to mind (drug-drug interaction). However, interactions may also exist between drugs and foods (drug-food interactions), as well as drugs and medicinal plants or herbs (drug-plant interactions). People taking antidepressant drugs such as monoamine oxidase inhibitors should not take food containing tyramine as hypertensive crisis may occur (an example of a drug-food interaction). These interactions may occur out of accidental misuse or due to lack of knowledge about the active ingredients involved in the relevant substances.It is therefore easy to see the importance of these pharmacological interactions in the practice of medicine. If a patient is taking two drugs and one of them increases the effect of the other it is possible that an overdose may occur. The interaction of the two drugs may also increase the risk that side effects will occur. On the other hand, if the action of a drug is reduced it may cease to have any therapeutic use because of under dosage. Notwithstanding the above, on occasion these interactions may be sought in order to obtain an improved therapeutic effect. Examples of this include the use of codeine with paracetamol to increase its analgesic effect. Or the combination of clavulanic acid with amoxicillin in order to overcome bacterial resistance to the antibiotic. It should also be remembered that there are interactions that, from a theoretical standpoint, may occur but in clinical practice have no important repercussions.The pharmaceutical interactions that are of special interest to the practice of medicine are primarily those that have negative effects for an organism. The risk that a pharmacological interaction will appear increases as a function of the number of drugs administered to a patient at the same time.It is possible that an interaction will occur between a drug and another substance present in the organism (i.e. foods or alcohol). Or in certain specific situations a drug may even react with itself, such as occurs with dehydration. In other situations, the interaction does not involve any effect on the drug. In certain cases, the presence of a drug in an individual's blood may affect certain types of laboratory analysis (analytical interference).It is also possible for interactions to occur outside an organism before administration of the drugs has taken place. This can occur when two drugs are mixed, for example, in a saline solution prior to intravenous injection. Some classic examples of this type of interaction include that Thiopentone and Suxamethonium should not be placed in the same syringe and same is true for Benzylpenicillin and Heparin. These situations will all be discussed under the same heading due to their conceptual similarity.Drug interactions may be the result of various processes. These processes may include alterations in the pharmacokinetics of the drug, such as alterations in the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of a drug. Alternatively, drug interactions may be the result of the pharmacodynamic properties of the drug, e.g. the co-administration of a receptor antagonist and an agonist for the same receptor.