lecture1423813661
... electric and magnetic field vectors where as circuit theory deals with the voltages and currents. Voltages and currents are integrated effects of electric and magnetic fields respectively. Electromagnetic field problems involve three space variables along with the time variable and hence the solutio ...
... electric and magnetic field vectors where as circuit theory deals with the voltages and currents. Voltages and currents are integrated effects of electric and magnetic fields respectively. Electromagnetic field problems involve three space variables along with the time variable and hence the solutio ...
Module 8 Electromagnetism
... Everybody is familiar with a toy magnet, that mysterious little U-shaped device that picks up needles or pins and holds them indefinitely in what seems to be like magic. As a child you probably played with small magnets. But magnet is far from being a mere toy. It is an essential part of machines, t ...
... Everybody is familiar with a toy magnet, that mysterious little U-shaped device that picks up needles or pins and holds them indefinitely in what seems to be like magic. As a child you probably played with small magnets. But magnet is far from being a mere toy. It is an essential part of machines, t ...
Pdf - Text of NPTEL IIT Video Lectures
... Since, we do not have any conducting medium inside this wave guide, this wave guide is completely hollow, it means it is filled by pure dielectric, there is no possibility of conduction current enclosed by this magnetic field lines. The conduction current is 0 inside the rectangular wave guide, so o ...
... Since, we do not have any conducting medium inside this wave guide, this wave guide is completely hollow, it means it is filled by pure dielectric, there is no possibility of conduction current enclosed by this magnetic field lines. The conduction current is 0 inside the rectangular wave guide, so o ...
EM Induction 2
... An emf is induced when there is relative motion between a conductor and a magnet. Either can move. Flux cutting always induces an emf, but a current is only induced in a complete circuit. Flux Linking is when an emf is induced by changing the magnitude or direction of the flux itself, eg. By AC cur ...
... An emf is induced when there is relative motion between a conductor and a magnet. Either can move. Flux cutting always induces an emf, but a current is only induced in a complete circuit. Flux Linking is when an emf is induced by changing the magnitude or direction of the flux itself, eg. By AC cur ...
Poster_2
... that gives for our electrons IAe ≈ 5 kA and for fast ions (deuterons) IAd ≈ 600 kA. Both currents are less compared with the discharge current (Ic ≥ 2 MA). Then upon the electrons’ magnetization the beam of fast ions comes into play. In the Fig. 7 two components of the deuteron beam can be distingui ...
... that gives for our electrons IAe ≈ 5 kA and for fast ions (deuterons) IAd ≈ 600 kA. Both currents are less compared with the discharge current (Ic ≥ 2 MA). Then upon the electrons’ magnetization the beam of fast ions comes into play. In the Fig. 7 two components of the deuteron beam can be distingui ...
lecture19
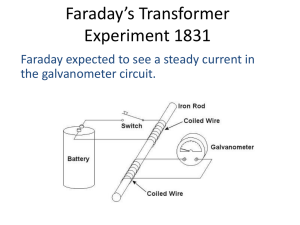
... You can use Faraday’s Law (as written above) to calculate the magnitude of the emf (or whatever the problem wants). Then use Lenz’s Law to figure out the direction of the induced current (or the direction of whatever the problem wants). The direction of the induced emf is in the direction of the cur ...
... You can use Faraday’s Law (as written above) to calculate the magnitude of the emf (or whatever the problem wants). Then use Lenz’s Law to figure out the direction of the induced current (or the direction of whatever the problem wants). The direction of the induced emf is in the direction of the cur ...
induced current
... about by a changing magnetic field. Since a source emf is always needed to produce a current, the coil behaves as if it were a source of emf. This emf is known as the induced emf. ...
... about by a changing magnetic field. Since a source emf is always needed to produce a current, the coil behaves as if it were a source of emf. This emf is known as the induced emf. ...
Experiment: Testing A Variety of Objects for Magnetic Attraction
... History of Magnetism The Chinese discovered the magnetic compass as early as 200 BC. At first tellers used it. Later people realised that it was a way to find the direction and South. The ancient Greeks knew that the lodestone or magnetite attracted iron It is known that the Vikings used a lodestone ...
... History of Magnetism The Chinese discovered the magnetic compass as early as 200 BC. At first tellers used it. Later people realised that it was a way to find the direction and South. The ancient Greeks knew that the lodestone or magnetite attracted iron It is known that the Vikings used a lodestone ...
MAGNETIC FIELD
... We can change the type of particle and its speed. We can also determine the direction of the field vector B, perpendicular to the screen, and its modulus. The scaling factor allows us to zoom in and out. The fire/stop button alternates between the particles in movement and at rest. A1: Click on ...
... We can change the type of particle and its speed. We can also determine the direction of the field vector B, perpendicular to the screen, and its modulus. The scaling factor allows us to zoom in and out. The fire/stop button alternates between the particles in movement and at rest. A1: Click on ...
Aurora

An aurora is a natural light display in the sky, predominantly seen in the high latitude (Arctic and Antarctic) regions. Auroras are produced when the magnetosphere is sufficiently disturbed by the solar wind that the trajectories of charged particles in both solar wind and magnetospheric plasma, mainly in the form of electrons and protons, precipitate them into the upper atmosphere (thermosphere/exosphere), where their energy is lost. The resulting ionization and excitation of atmospheric constituents emits light of varying colour and complexity. The form of the aurora, occurring within bands around both polar regions, is also dependent on the amount of acceleration imparted to the precipitating particles. Precipitating protons generally produce optical emissions as incident hydrogen atoms after gaining electrons from the atmosphere. Proton auroras are usually observed at lower latitudes. Different aspects of an aurora are elaborated in various sections below.