Magnetic cloud field intensities and solar wind velocities
... velocitiesis pres•mablythe causeof the lackof intense speedof • 400 km/s. Although the positive correlation })el,weenfast (',MEs stormsduringlow speede.jecta. There is alsoan indication that, this type of behavior is peculiar for mag- and magnetic storms have been stressedand is reasonnetic clouds, ...
... velocitiesis pres•mablythe causeof the lackof intense speedof • 400 km/s. Although the positive correlation })el,weenfast (',MEs stormsduringlow speede.jecta. There is alsoan indication that, this type of behavior is peculiar for mag- and magnetic storms have been stressedand is reasonnetic clouds, ...
Electricity and Magnetism Summary Notes
... field extends into space. A compass, it a weak magnet, which can move freely and so lines up with the Earth’s magnetic field. It does not point to true North but to magnetic North. ...
... field extends into space. A compass, it a weak magnet, which can move freely and so lines up with the Earth’s magnetic field. It does not point to true North but to magnetic North. ...
7 - web page for staff
... ‘Curl´ operator perform a derivative of vector and returns a vector quantity. For Cartesian coordinates, can be written as H ax H x Hx ...
... ‘Curl´ operator perform a derivative of vector and returns a vector quantity. For Cartesian coordinates, can be written as H ax H x Hx ...
magnetic field - DiMaggio
... Magnetism Notes Magnet: any material that attracts iron or materials containing iron, nickel, cobalt All magnets have a north and a south pole. The word attract is used when 2 magnets pull together. o Unlike or opposites poles attract The word repel is used when 2 magnets push apart. o Like ...
... Magnetism Notes Magnet: any material that attracts iron or materials containing iron, nickel, cobalt All magnets have a north and a south pole. The word attract is used when 2 magnets pull together. o Unlike or opposites poles attract The word repel is used when 2 magnets push apart. o Like ...
Experiment 3.3 Thomson Experiment Aim To use a computer
... Record the radius of the beam ............................... The magnetic force on the beam is providing a centripetal force for the circular path. Therefore we can equate the magnetic force with the centripetal force on the beam. Equate the equation for magnetic force with the equation for centrip ...
... Record the radius of the beam ............................... The magnetic force on the beam is providing a centripetal force for the circular path. Therefore we can equate the magnetic force with the centripetal force on the beam. Equate the equation for magnetic force with the equation for centrip ...
magnetic field
... Mars also has a very weak magnetic field. (About 5,000 times weaker than Earth’s) The interior of Mars appears to have cooled so much that it is no longer liquid. • The volcanoes in Mars are no longer active • There is no Earthquake activity on Mars ...
... Mars also has a very weak magnetic field. (About 5,000 times weaker than Earth’s) The interior of Mars appears to have cooled so much that it is no longer liquid. • The volcanoes in Mars are no longer active • There is no Earthquake activity on Mars ...
Magnetic Fields
... compass needles pointed. Their lives depended on knowing where they were, so I guess it is appropriate that we acknowledge their precedence. Thus, by convention, the thing we call Earth’s North Magnetic Pole is actually the south magnetic pole of Earth’s magnetic field. ...
... compass needles pointed. Their lives depended on knowing where they were, so I guess it is appropriate that we acknowledge their precedence. Thus, by convention, the thing we call Earth’s North Magnetic Pole is actually the south magnetic pole of Earth’s magnetic field. ...
Other Solar System Bodies
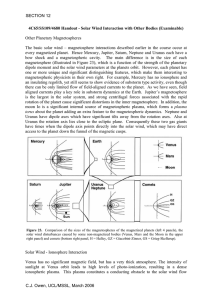
... (Figure 8.5 from K&R, reproduced overleaf). The solar wind and IMF are frozen out of the cavity occupied by the ionospheric plasma. Thus there is a bow shock upstream of Venus that acts to slow and deflect the solar wind and a magnetosheath between the topside of the ionosphere and bow shock, where ...
... (Figure 8.5 from K&R, reproduced overleaf). The solar wind and IMF are frozen out of the cavity occupied by the ionospheric plasma. Thus there is a bow shock upstream of Venus that acts to slow and deflect the solar wind and a magnetosheath between the topside of the ionosphere and bow shock, where ...
What is Magnetism?
... I own a jewelry store and recently I have made a lot of money using magnets to make earrings, necklaces, and even bracelets. Unfortunately, I only have one big magnet left, but I need to make 3 different pieces of magnetic jewelry. Since I only make money if my jewelry is magnetic, I was wondering i ...
... I own a jewelry store and recently I have made a lot of money using magnets to make earrings, necklaces, and even bracelets. Unfortunately, I only have one big magnet left, but I need to make 3 different pieces of magnetic jewelry. Since I only make money if my jewelry is magnetic, I was wondering i ...
File
... The strength of an electromagnet is affected by the number of ______ in the wire. The strength of an electromagnet is affected by the amount of electrical ___________ in the wire. The strength of an electromagnet is affected by the material (core) the wire is wrapped around. This core is most ...
... The strength of an electromagnet is affected by the number of ______ in the wire. The strength of an electromagnet is affected by the amount of electrical ___________ in the wire. The strength of an electromagnet is affected by the material (core) the wire is wrapped around. This core is most ...
Plate Tectonics - Helena High School
... • Coal was found in Antarctica, therefore Antarctica must have been closer to the equator at one time. ...
... • Coal was found in Antarctica, therefore Antarctica must have been closer to the equator at one time. ...
Magnetism and its uses
... individuals navigate. Magnets always point north. What makes some materials magnets, other materials attracted to magnets and many materials that are neither? ...
... individuals navigate. Magnets always point north. What makes some materials magnets, other materials attracted to magnets and many materials that are neither? ...
THE EARTH`S REVERSIBLE MAGNETIC FIELD. By William Reville
... mantle and crust. This movement creates a natural dynamo and therefore a magnetic field similar in shape to the field of a bar magnet. There have been several reports over the centuries, from various parts of the world, of compass needles behaving strangely when placed over certain rocks. It was rep ...
... mantle and crust. This movement creates a natural dynamo and therefore a magnetic field similar in shape to the field of a bar magnet. There have been several reports over the centuries, from various parts of the world, of compass needles behaving strangely when placed over certain rocks. It was rep ...
Snow Day 5 - Russell County Schools
... are drawn to you, just like how some metal objects may be drawn to magnets. Magnetism is the force that electric currents2 exert on other electric currents. This force can be created by the motion of electrons in the atoms of certain materials, which are called magnets. The force may also be produce ...
... are drawn to you, just like how some metal objects may be drawn to magnets. Magnetism is the force that electric currents2 exert on other electric currents. This force can be created by the motion of electrons in the atoms of certain materials, which are called magnets. The force may also be produce ...
Electricity and Magnetism Study Guide - Mr. L`s Room
... magnetic force. Lines closely spaced indicate strong magnetic force. Lines farther apart indicate weaker magnetic force. Magnetic field lines are closest at the poles. ...
... magnetic force. Lines closely spaced indicate strong magnetic force. Lines farther apart indicate weaker magnetic force. Magnetic field lines are closest at the poles. ...
Aurora

An aurora is a natural light display in the sky, predominantly seen in the high latitude (Arctic and Antarctic) regions. Auroras are produced when the magnetosphere is sufficiently disturbed by the solar wind that the trajectories of charged particles in both solar wind and magnetospheric plasma, mainly in the form of electrons and protons, precipitate them into the upper atmosphere (thermosphere/exosphere), where their energy is lost. The resulting ionization and excitation of atmospheric constituents emits light of varying colour and complexity. The form of the aurora, occurring within bands around both polar regions, is also dependent on the amount of acceleration imparted to the precipitating particles. Precipitating protons generally produce optical emissions as incident hydrogen atoms after gaining electrons from the atmosphere. Proton auroras are usually observed at lower latitudes. Different aspects of an aurora are elaborated in various sections below.