the magnetic field of the hot spectroscopic binary hd 5550
... 2002). HD 5550 was previously reported to be an Ap SrCrEu star (Renson et al. 1991). Carrier et al. (2002) also reported that the secondary has chemical peculiarities, but they could not distinguish more precisely the peculiar type of this component. We observed HD 5550 in the frame of the BinaMIcS ...
... 2002). HD 5550 was previously reported to be an Ap SrCrEu star (Renson et al. 1991). Carrier et al. (2002) also reported that the secondary has chemical peculiarities, but they could not distinguish more precisely the peculiar type of this component. We observed HD 5550 in the frame of the BinaMIcS ...
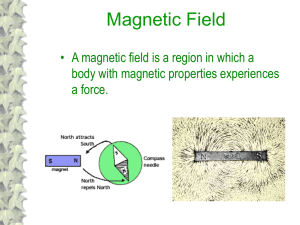
Electromagnetic Induction
... • The closer the lines are together the stronger the field • Magnetic domains are microscopic magnetic field lines caused from the movement of electrons • Domains line up when external magnetic field is present • Magnetic field lines per area is called magnetic flux ...
... • The closer the lines are together the stronger the field • Magnetic domains are microscopic magnetic field lines caused from the movement of electrons • Domains line up when external magnetic field is present • Magnetic field lines per area is called magnetic flux ...
List of important topics: Electricity • Charge • Coulomb Force
... overall rotating charge that can be considered as a loop. The combined movement of all the electrons in an atom does not always create such a pattern but if it does then the atom possesses ...
... overall rotating charge that can be considered as a loop. The combined movement of all the electrons in an atom does not always create such a pattern but if it does then the atom possesses ...
Electromagnetism - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... -as loop rotates, motion of wire loop changes in the magnetic field induced current produced -end of loop connected to slip ring commutator -connections to external circuit made by stationary brushes in contact with commutator -when loop is 1/2 way through rotation in MF current flows one direct ...
... -as loop rotates, motion of wire loop changes in the magnetic field induced current produced -end of loop connected to slip ring commutator -connections to external circuit made by stationary brushes in contact with commutator -when loop is 1/2 way through rotation in MF current flows one direct ...
Study Notes Lesson 17 Magnetism
... Although the magnet as a whole may be stationary, it is composed of atoms whose electrons are in constant motion about atomic nuclei. This moving charge constitutes a tiny current and produces a magnetic field. More important, electrons spinning about their own axes constitute a charge in motion and ...
... Although the magnet as a whole may be stationary, it is composed of atoms whose electrons are in constant motion about atomic nuclei. This moving charge constitutes a tiny current and produces a magnetic field. More important, electrons spinning about their own axes constitute a charge in motion and ...
Magnetic Fields And Right Hand Rules
... find the magnetic field on a closed loop that surrounds a current. In Gauss’ law we want to choose our Gaussian surface so that the electric field is constant on the surface. In Ampere’s law we want to choose our closed loop so that the magnetic field is constant on the loop. The form of Ampere’s la ...
... find the magnetic field on a closed loop that surrounds a current. In Gauss’ law we want to choose our Gaussian surface so that the electric field is constant on the surface. In Ampere’s law we want to choose our closed loop so that the magnetic field is constant on the loop. The form of Ampere’s la ...
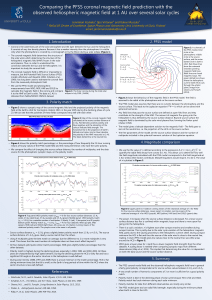
Figure 1 - Research
... • Corona is the outermost part of the solar atmosphere and the layer between the Sun and the heliosphere. It consists of very low density plasma. Because it has a weaker intensity than the photosphere it is visible only when the photosphere is covered by a coronagraph or by the Moon during a solar e ...
... • Corona is the outermost part of the solar atmosphere and the layer between the Sun and the heliosphere. It consists of very low density plasma. Because it has a weaker intensity than the photosphere it is visible only when the photosphere is covered by a coronagraph or by the Moon during a solar e ...
ph507-16-6sun
... A comet's tail always points away from the Sun, no matter in what direction it moves. ...
... A comet's tail always points away from the Sun, no matter in what direction it moves. ...
Magnetic Reversals
... opposite direction from today’s. All sorts of explanations were proposed, but in the end the only one which passed all tests was that in the distant past, indeed, the magnetic polarity of the Earth was ...
... opposite direction from today’s. All sorts of explanations were proposed, but in the end the only one which passed all tests was that in the distant past, indeed, the magnetic polarity of the Earth was ...
Magnetism Vocabulary Terms
... The line of attractive force that runs through the center of the earth. The earth's magnetic axis differs slightly from its rotational axis. ...
... The line of attractive force that runs through the center of the earth. The earth's magnetic axis differs slightly from its rotational axis. ...
Aurora

An aurora is a natural light display in the sky, predominantly seen in the high latitude (Arctic and Antarctic) regions. Auroras are produced when the magnetosphere is sufficiently disturbed by the solar wind that the trajectories of charged particles in both solar wind and magnetospheric plasma, mainly in the form of electrons and protons, precipitate them into the upper atmosphere (thermosphere/exosphere), where their energy is lost. The resulting ionization and excitation of atmospheric constituents emits light of varying colour and complexity. The form of the aurora, occurring within bands around both polar regions, is also dependent on the amount of acceleration imparted to the precipitating particles. Precipitating protons generally produce optical emissions as incident hydrogen atoms after gaining electrons from the atmosphere. Proton auroras are usually observed at lower latitudes. Different aspects of an aurora are elaborated in various sections below.