Plates move apart.
... diagram below. When molten material rises from the asthenosphere, cold ocean water cools the rock until it becomes solid. As the plates move apart, new cracks open in the solid rock. More molten material rises and hardens. The growing ridge stands high above the sea floor. The world’s longest ridge, ...
... diagram below. When molten material rises from the asthenosphere, cold ocean water cools the rock until it becomes solid. As the plates move apart, new cracks open in the solid rock. More molten material rises and hardens. The growing ridge stands high above the sea floor. The world’s longest ridge, ...
Magnetic Effects of Electric current
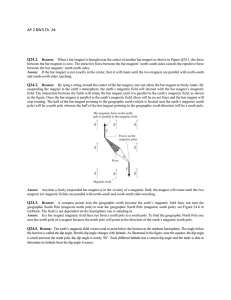
... Question 32: Imagine that you are sitting in a chamber with your back to one wall. An electron beam, moving horizontally from back wall towards the front wall, is deflected by a strong magnetic field to your right side. What is the direction of magnetic field? Answer: The direction of magnetic field ...
... Question 32: Imagine that you are sitting in a chamber with your back to one wall. An electron beam, moving horizontally from back wall towards the front wall, is deflected by a strong magnetic field to your right side. What is the direction of magnetic field? Answer: The direction of magnetic field ...
Figure 3. Field Coil Test Circuit Schematic
... assemblies, which will produce sinusoidal varying magnetic fields in the surrounding space. A small "search" coil nearby will intercept some of the sinusoidal-varying magnetic flux. When moving the search coil in or out of the field coil, the magnetic flux through the large coil changes, creating an ...
... assemblies, which will produce sinusoidal varying magnetic fields in the surrounding space. A small "search" coil nearby will intercept some of the sinusoidal-varying magnetic flux. When moving the search coil in or out of the field coil, the magnetic flux through the large coil changes, creating an ...
Interactive Notes
... The filings line up in the shape of the field, as shown above. The direction of the arrows can be seen by placing a compass in the field. The compass points in the direction of the arrows, away from North and towards South. Note - this means that when a compass points to the Earth's North Pole, ther ...
... The filings line up in the shape of the field, as shown above. The direction of the arrows can be seen by placing a compass in the field. The compass points in the direction of the arrows, away from North and towards South. Note - this means that when a compass points to the Earth's North Pole, ther ...
Lec17 - Purdue Physics
... by an external force. If the current I is decreasing, what is the direction of the magnetic force on the left edge of the loop? a. Toward the right ...
... by an external force. If the current I is decreasing, what is the direction of the magnetic force on the left edge of the loop? a. Toward the right ...
introduction
... giving rise to resultant magnetization equal difference between them. It has a critical temperature below which the magnetic moments on both lattice have an orderly arrangement while above the critical temperature the magnetic moments randomly oriented as in paramagnetic substances. Ferromagnetic or ...
... giving rise to resultant magnetization equal difference between them. It has a critical temperature below which the magnetic moments on both lattice have an orderly arrangement while above the critical temperature the magnetic moments randomly oriented as in paramagnetic substances. Ferromagnetic or ...
What is a Magnetic Monopole?
... Dipole model describes the interactions (not point charges, but oriented dipoles) Dirac string not infinitely thin, rather an observable flux tube Divergence is always zero ...
... Dipole model describes the interactions (not point charges, but oriented dipoles) Dirac string not infinitely thin, rather an observable flux tube Divergence is always zero ...
Evolution of Neutron Star Magnetic Fields
... A neutron star is born hot, and cools with time (unless accretion occurs on the surface). The conductivity of the outer crust therefore increases with time. Cooling rates of neutron stars have been computed under various assumptions, a useful compendium is found in Page (1998). Using a typical “stan ...
... A neutron star is born hot, and cools with time (unless accretion occurs on the surface). The conductivity of the outer crust therefore increases with time. Cooling rates of neutron stars have been computed under various assumptions, a useful compendium is found in Page (1998). Using a typical “stan ...
Time From the Perspective of a Particle Physicist
... • photosphere cooler than convection region dark line absorption spectrum ...
... • photosphere cooler than convection region dark line absorption spectrum ...
File
... iv) Magnetic Axis is a straight line passing through the magnetic poles of the earth. It is inclined to Geographic Axis nearly at an angle of 17°. v) Magnetic Meridian at any place is a vertical plane passing through the magnetic north and south poles of the earth. vi) Magnetic Equator is a great ci ...
... iv) Magnetic Axis is a straight line passing through the magnetic poles of the earth. It is inclined to Geographic Axis nearly at an angle of 17°. v) Magnetic Meridian at any place is a vertical plane passing through the magnetic north and south poles of the earth. vi) Magnetic Equator is a great ci ...
Aurora

An aurora is a natural light display in the sky, predominantly seen in the high latitude (Arctic and Antarctic) regions. Auroras are produced when the magnetosphere is sufficiently disturbed by the solar wind that the trajectories of charged particles in both solar wind and magnetospheric plasma, mainly in the form of electrons and protons, precipitate them into the upper atmosphere (thermosphere/exosphere), where their energy is lost. The resulting ionization and excitation of atmospheric constituents emits light of varying colour and complexity. The form of the aurora, occurring within bands around both polar regions, is also dependent on the amount of acceleration imparted to the precipitating particles. Precipitating protons generally produce optical emissions as incident hydrogen atoms after gaining electrons from the atmosphere. Proton auroras are usually observed at lower latitudes. Different aspects of an aurora are elaborated in various sections below.