What Generators Do and Regulators Ought To
... system to a safe value by controlling the internal voltage of the generator. The voltage regulator, like the cut-out, has a shunt winding (3m) made up of many turns of fine wire wrapped around a soft iron core. Suspended above the regulator core are a pair of contact points (3n), similar to the cut- ...
... system to a safe value by controlling the internal voltage of the generator. The voltage regulator, like the cut-out, has a shunt winding (3m) made up of many turns of fine wire wrapped around a soft iron core. Suspended above the regulator core are a pair of contact points (3n), similar to the cut- ...
Magnetic Field Variations
... In general there are few corrections to apply to magnetic data. The largest non-geological variations in the earth’s magnetic field are those associated with diurnal variations, micropulsations and magnetic storms. The vertical gradient of the vertical component of the earth’s magnetic field at thi ...
... In general there are few corrections to apply to magnetic data. The largest non-geological variations in the earth’s magnetic field are those associated with diurnal variations, micropulsations and magnetic storms. The vertical gradient of the vertical component of the earth’s magnetic field at thi ...
Dynamics of Rotational Motion
... The triceps muscle in the back of the upper arm extends the forearm. This muscle in a professional boxer exerts a force of 2.00 × 103 N with an effective perpendicular lever arm of 3.00 cm, producing an angular acceleration of the forearm of 120 rad/s2. What is the moment of inertia of the boxer’s f ...
... The triceps muscle in the back of the upper arm extends the forearm. This muscle in a professional boxer exerts a force of 2.00 × 103 N with an effective perpendicular lever arm of 3.00 cm, producing an angular acceleration of the forearm of 120 rad/s2. What is the moment of inertia of the boxer’s f ...
Document
... The rectangular loop shown is pushed into the magnetic field which points inward. In what direction is the induced current? ...
... The rectangular loop shown is pushed into the magnetic field which points inward. In what direction is the induced current? ...
chapter 3 flywheel
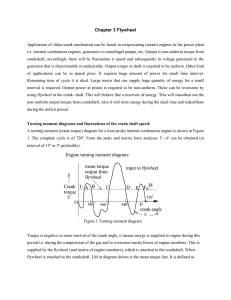
... Our interest is to find maximum and minimum speeds and its positions in Figure 5. Points A, B, C, D, E and F are the points where T − θ diagram cuts the mean torque line. These points are transition points from deficit to extra energy or vice versa. So crank starts accelerate from deceleration from ...
... Our interest is to find maximum and minimum speeds and its positions in Figure 5. Points A, B, C, D, E and F are the points where T − θ diagram cuts the mean torque line. These points are transition points from deficit to extra energy or vice versa. So crank starts accelerate from deceleration from ...
Full Chapter
... 22.1 Declination and “true north” Because Earth’s geographic north pole (true north) and magnetic south pole are not located at the exact same place, a compass will not point directly to the geographic north pole. ...
... 22.1 Declination and “true north” Because Earth’s geographic north pole (true north) and magnetic south pole are not located at the exact same place, a compass will not point directly to the geographic north pole. ...
Standard EPS Shell Presentation
... 22.1 Declination and “true north” Because Earth’s geographic north pole (true north) and magnetic south pole are not located at the exact same place, a compass will not point directly to the geographic north pole. ...
... 22.1 Declination and “true north” Because Earth’s geographic north pole (true north) and magnetic south pole are not located at the exact same place, a compass will not point directly to the geographic north pole. ...
Solenoid Coils for Switching and Proportional Valves
... Solenoids and coils are used to convert electrical energy to the mechanical force used to shift valve components to control flow or pressure. In Sun Hydraulics’ terminology, the coil and solenoid are separate components. The solenoid is the tube that contains the armature and pole piece. The coil fi ...
... Solenoids and coils are used to convert electrical energy to the mechanical force used to shift valve components to control flow or pressure. In Sun Hydraulics’ terminology, the coil and solenoid are separate components. The solenoid is the tube that contains the armature and pole piece. The coil fi ...
r 36 lec
... • 1) tapping the iron to help the domains align • 2) sliding a magnet along the iron to the domains align • Permanent magnets are destroyed by • 1) heating 2) dropping the magnet because it knocks the domains out of alignment ...
... • 1) tapping the iron to help the domains align • 2) sliding a magnet along the iron to the domains align • Permanent magnets are destroyed by • 1) heating 2) dropping the magnet because it knocks the domains out of alignment ...
Today: Finish Ch 23: Electric Current Chapter 24: Magnetism
... as shown; hence it turns. After a half turn, the sides have reversed, so deflection is in the opposite direction – makes coil turns back. • To prevent this, reverse the direction of current every time coil makes a half ...
... as shown; hence it turns. After a half turn, the sides have reversed, so deflection is in the opposite direction – makes coil turns back. • To prevent this, reverse the direction of current every time coil makes a half ...
9.5
... Lorentz Force: A charged particle moving through a magnetic field experiences a force that is at right angles to both the direction in which the particle is moving and the direction of the applied field. This force, known as the Lorentz force, develops due to the interaction of the applied magnetic ...
... Lorentz Force: A charged particle moving through a magnetic field experiences a force that is at right angles to both the direction in which the particle is moving and the direction of the applied field. This force, known as the Lorentz force, develops due to the interaction of the applied magnetic ...
Magnetism
... pushes them to the right (labeled "R") side of the strip. This accumulates negative charge on the R-sid e and leaves the left side (labeled "L") of the strip positively charged. As a result of the accumulated charge, an electric field E is generated as shown in the figure so that the electric force ...
... pushes them to the right (labeled "R") side of the strip. This accumulates negative charge on the R-sid e and leaves the left side (labeled "L") of the strip positively charged. As a result of the accumulated charge, an electric field E is generated as shown in the figure so that the electric force ...
Section 22.1 - CPO Science
... 22.1 Declination and “true north” Because Earth’s geographic north pole (true north) and magnetic south pole are not located at the exact same place, a compass will not point directly to the geographic north pole. ...
... 22.1 Declination and “true north” Because Earth’s geographic north pole (true north) and magnetic south pole are not located at the exact same place, a compass will not point directly to the geographic north pole. ...
Magnetism
... • Magnetism is closely linked with electricity. – Magnetic fields affect moving charges. – Moving charges produce magnetic fields. – Changing magnetic fields can create electric fields. ...
... • Magnetism is closely linked with electricity. – Magnetic fields affect moving charges. – Moving charges produce magnetic fields. – Changing magnetic fields can create electric fields. ...