
615-0185 (20-010) Instructions for Dip Needle
... naturally emit a magnetic field, along with nickel, cobalt, neodymium, and a few others. The magnetic properties of Iron, if enough iron is present, can mask the earth’s magnetic field in localized areas. This property can cause large iron deposits to deflect a dip needle beyond what the earth can. ...
... naturally emit a magnetic field, along with nickel, cobalt, neodymium, and a few others. The magnetic properties of Iron, if enough iron is present, can mask the earth’s magnetic field in localized areas. This property can cause large iron deposits to deflect a dip needle beyond what the earth can. ...
Magnet
... the wire to either side of the battery, the positive and the negative side. Then you put one wire going up one side of the battery and one going up on the other side. So the wires go up on either side of the battery like a circle. Then the light bulb has to be touching the copper parts on the end of ...
... the wire to either side of the battery, the positive and the negative side. Then you put one wire going up one side of the battery and one going up on the other side. So the wires go up on either side of the battery like a circle. Then the light bulb has to be touching the copper parts on the end of ...
Rotational motion
... Rotational motion can be described separate from its translational motion. Describing rotation by itself is simple: it’s the same as one-dimensional motion (no vectors!) By convention: counter-clockwise is always positive (like with the unit circle). An example: consider a centrifuge rotating at ω = ...
... Rotational motion can be described separate from its translational motion. Describing rotation by itself is simple: it’s the same as one-dimensional motion (no vectors!) By convention: counter-clockwise is always positive (like with the unit circle). An example: consider a centrifuge rotating at ω = ...
Magnetism
... can be detected. Magnetic field lines show the direction and strength of a magnetic field. The lines are drawn point away from the north pole and towards the south pole. Magnetic field strength (B) is measured in Teslas. ...
... can be detected. Magnetic field lines show the direction and strength of a magnetic field. The lines are drawn point away from the north pole and towards the south pole. Magnetic field strength (B) is measured in Teslas. ...
Magnetic Effect of Electric Current
... 4. AC can be controlled and energy loss is very small but DC can be controlled by only resistances which involves huge energy loss in form of heat. 5. AC machines are durable and do not need much maintenance. Alternating Current (AC) generator: Function: it converts mechanical energy to electrical e ...
... 4. AC can be controlled and energy loss is very small but DC can be controlled by only resistances which involves huge energy loss in form of heat. 5. AC machines are durable and do not need much maintenance. Alternating Current (AC) generator: Function: it converts mechanical energy to electrical e ...
lecture13
... Example: A bar magnet is held above the floor and dropped. In 1, there is nothing between the magnet and the floor. In 2, the magnet falls through a copper loop. How will the magnet in case 2 fall in comparison to case 1? 1) it will fall slower; 2) it will fall faster; 3) it will fall the same When ...
... Example: A bar magnet is held above the floor and dropped. In 1, there is nothing between the magnet and the floor. In 2, the magnet falls through a copper loop. How will the magnet in case 2 fall in comparison to case 1? 1) it will fall slower; 2) it will fall faster; 3) it will fall the same When ...
Lecture 16 - The Local Group
... i =ε According to Maxwell’s equations: dt • A point charge at rest produces E but not B. • A point charge moving with a constant speed produces E & B. • For a point charge to produce and EM wave, the charge must accelerate. ...
... i =ε According to Maxwell’s equations: dt • A point charge at rest produces E but not B. • A point charge moving with a constant speed produces E & B. • For a point charge to produce and EM wave, the charge must accelerate. ...
mr08T
... He keeps loading bricks until there are 300 kg of bricks in the back, with their centre of mass about 70 cm behind the back axle. b. How much total weight now rests on the front wheels? c. How much rests on the back wheels? He continue loading bricks into the back and notice that the car is getting ...
... He keeps loading bricks until there are 300 kg of bricks in the back, with their centre of mass about 70 cm behind the back axle. b. How much total weight now rests on the front wheels? c. How much rests on the back wheels? He continue loading bricks into the back and notice that the car is getting ...
Magnetism Notes
... Bell Ringer • Where the motors that you made last week operating on alternating or direct current? • What would happen with your motor from yesterday if you took off all the insulation off of each end? ...
... Bell Ringer • Where the motors that you made last week operating on alternating or direct current? • What would happen with your motor from yesterday if you took off all the insulation off of each end? ...
Magnetism 17.1 Properties of Magnets 17.2 Electromagnets 17.3
... 17.1 Declination and “true north” Because Earth’s geographic north pole (true north) and magnetic south pole are not located at the exact same place, a compass will not point directly to the geographic north pole. ...
... 17.1 Declination and “true north” Because Earth’s geographic north pole (true north) and magnetic south pole are not located at the exact same place, a compass will not point directly to the geographic north pole. ...
magnetic dipole
... magnetic field lines will be perpendicular to the plane of motion. Electrons behave as if they rotate on an axis clockwise or counterclockwise. This rotation creates a property called electron spin. The electron spin creates a magnetic field, which is neutralized in electron pairs. Therefore, atoms ...
... magnetic field lines will be perpendicular to the plane of motion. Electrons behave as if they rotate on an axis clockwise or counterclockwise. This rotation creates a property called electron spin. The electron spin creates a magnetic field, which is neutralized in electron pairs. Therefore, atoms ...
ch-6 [Magnetism]
... - turn on the key in a DC circuit - Move a magnet up or down inside a stationary coil and vice versa ...
... - turn on the key in a DC circuit - Move a magnet up or down inside a stationary coil and vice versa ...
Magnetism - Cabrillo College
... forces. However, in most materials, the electrons in different atoms all “spin” in different directions, so the magnetic forces all balance out and the material is non-magnetic. In iron, however, the electrons in the atoms can be aligned so they “spin” in the same direction; this results in what we ...
... forces. However, in most materials, the electrons in different atoms all “spin” in different directions, so the magnetic forces all balance out and the material is non-magnetic. In iron, however, the electrons in the atoms can be aligned so they “spin” in the same direction; this results in what we ...














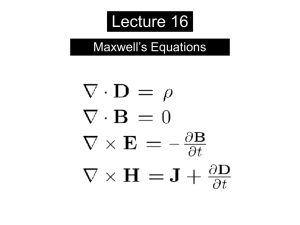





![ch-6 [Magnetism]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004366853_1-cbc1ce7a74752c20e1a6e456bd1e46ed-300x300.png)
