Magnetism Section 1 Magnetism A. —the properties and interactions
... forms a circular pattern about the _______________. b. The _________________ of the field depends on the direction of the __________________. c. The strength of the magnetic _____________ depends on the amount of ___________________ flowing in the wire. B. __________________________—a temporary magn ...
... forms a circular pattern about the _______________. b. The _________________ of the field depends on the direction of the __________________. c. The strength of the magnetic _____________ depends on the amount of ___________________ flowing in the wire. B. __________________________—a temporary magn ...
Practice Sheet #24
... c. a magnet’s south pole. d. a magnet’s north pole. _____ 8. A device that increases the voltage of an alternating current is called a(n) a. electric motor. c. step-up transformer b. galvanometer. d. step-down transformer _____ 9. The magnetic field of a solenoid can be increased by a. adding more l ...
... c. a magnet’s south pole. d. a magnet’s north pole. _____ 8. A device that increases the voltage of an alternating current is called a(n) a. electric motor. c. step-up transformer b. galvanometer. d. step-down transformer _____ 9. The magnetic field of a solenoid can be increased by a. adding more l ...
8J Summary Sheet
... • a stationary object stays stationary; • a moving object continues to move at the same speed. ...
... • a stationary object stays stationary; • a moving object continues to move at the same speed. ...
PPT
... In (a) the magnetic field and flux are increasing. The current moves in the direction to oppose that – to decrease the magnetic field. In (b) the magnetic field and flux are decreasing. Again, the current moves in the direction to oppose that. In (c) there is no change in flux, so there is no ...
... In (a) the magnetic field and flux are increasing. The current moves in the direction to oppose that – to decrease the magnetic field. In (b) the magnetic field and flux are decreasing. Again, the current moves in the direction to oppose that. In (c) there is no change in flux, so there is no ...
Concept Questions
... A hollow cylinder of outer radius R and mass m with moment of inertia I cm about the center of mass starts from rest and moves down an incline tilted at an angle from the horizontal. The center of mass of the cylinder has dropped a vertical distance h when it reaches the bottom of the incline. Let ...
... A hollow cylinder of outer radius R and mass m with moment of inertia I cm about the center of mass starts from rest and moves down an incline tilted at an angle from the horizontal. The center of mass of the cylinder has dropped a vertical distance h when it reaches the bottom of the incline. Let ...
m 0 N 2 A / l
... • Consider a solenoid of length l with N windings and radius r (Area A=p r2). • A current I produces a magnetic field in the solenoid of B = m0 N I / l • This produces a total flux through each winding of = A B = (m0 N A / l ) I – Define the Inductance L = (m0 N2 A / l ) (not a length!!) • If the ...
... • Consider a solenoid of length l with N windings and radius r (Area A=p r2). • A current I produces a magnetic field in the solenoid of B = m0 N I / l • This produces a total flux through each winding of = A B = (m0 N A / l ) I – Define the Inductance L = (m0 N2 A / l ) (not a length!!) • If the ...
TCAP Review 2013 – Page 9 – Electromagnetism
... What kind of poles does a magnet have? (p. 425) ...
... What kind of poles does a magnet have? (p. 425) ...
Faraday`s Law - barransclass
... Rotation Powers a Generator Motion through the field induces a potential which generates a current that charges the battery ...
... Rotation Powers a Generator Motion through the field induces a potential which generates a current that charges the battery ...
A rotating coil - Collins.co.uk.
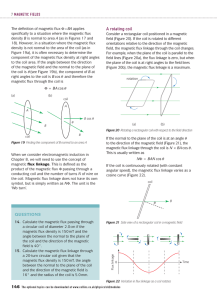
... The definition of magnetic flux Φ = BA applies specifically to a situation where the magnetic flux density B is normal to area A (as in Figures 17 and 18). However, in a situation where the magnetic flux density is not normal to the area of the coil (as in Figure 19a), it is often necessary to deter ...
... The definition of magnetic flux Φ = BA applies specifically to a situation where the magnetic flux density B is normal to area A (as in Figures 17 and 18). However, in a situation where the magnetic flux density is not normal to the area of the coil (as in Figure 19a), it is often necessary to deter ...
Chaper 21 flashcards
... 17) Regions having large numbers of atoms with aligned magnetic fields are called (nails, poles, magnetic domains). 18) The type of generator that large power plants use in the US is (AC, DC, PC) generators 19) Voltage can be induced in a conductor by changing a magnetic field is known as (Ohm’s Far ...
... 17) Regions having large numbers of atoms with aligned magnetic fields are called (nails, poles, magnetic domains). 18) The type of generator that large power plants use in the US is (AC, DC, PC) generators 19) Voltage can be induced in a conductor by changing a magnetic field is known as (Ohm’s Far ...
Number 1 - HomeworkNOW.com
... Magnet – any material that contains iron, nickel, or cobalt and it attracted to materials containing iron, nickel, or cobalt ...
... Magnet – any material that contains iron, nickel, or cobalt and it attracted to materials containing iron, nickel, or cobalt ...