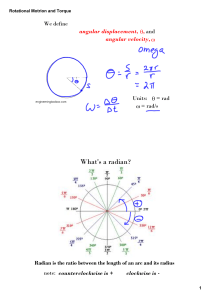
PHYS 196 Class Problem 1
... battery. (a) What is the steady current? (b) How much energy is stored in the inductor when the steadystate current is established? 10. A 200-turn solenoid has a cross-sectional area equal to 4.0cm2 and a length equal to 30 cm. The solenoid carries a current of 4.0A. (a) Calculate the magnetic energ ...
... battery. (a) What is the steady current? (b) How much energy is stored in the inductor when the steadystate current is established? 10. A 200-turn solenoid has a cross-sectional area equal to 4.0cm2 and a length equal to 30 cm. The solenoid carries a current of 4.0A. (a) Calculate the magnetic energ ...
Scott Foresman Science
... put a moving magnet inside a wire coil. This created an electric current. Faraday invented a device called a dynamo. A dynamo has a magnet inside a coil of wire. When the magnet moves back and forth, the dynamo produces electricity. When the magnet stops moving, the electric current stops. This show ...
... put a moving magnet inside a wire coil. This created an electric current. Faraday invented a device called a dynamo. A dynamo has a magnet inside a coil of wire. When the magnet moves back and forth, the dynamo produces electricity. When the magnet stops moving, the electric current stops. This show ...
It is sometimes difficult to find the polarity of an
... armature 44 times for each revolution of the tire. The tire has a radius of 0.33 m. The armature has 75 turns, each with an area of 2.6 x 10-3 m2, and rotates in a 0.10-T magnetic field. When the peak emf being generated is 6.0 V, what is the linear speed of the bike? ...
... armature 44 times for each revolution of the tire. The tire has a radius of 0.33 m. The armature has 75 turns, each with an area of 2.6 x 10-3 m2, and rotates in a 0.10-T magnetic field. When the peak emf being generated is 6.0 V, what is the linear speed of the bike? ...
B Bc θ
... 10. Record the angle (θ1 ) and determine its uncertainty (δθ1 ) from the precision of the compass. 11. Determine the fractional uncertainty (δθ1 /θ1 ) for this measurement and record this in your data table. 12. Record the current I1 and determine δI1 from the precision of the ammeter. 13. Determine ...
... 10. Record the angle (θ1 ) and determine its uncertainty (δθ1 ) from the precision of the compass. 11. Determine the fractional uncertainty (δθ1 /θ1 ) for this measurement and record this in your data table. 12. Record the current I1 and determine δI1 from the precision of the ammeter. 13. Determine ...
Chapter 7 - Cloudfront.net
... same angular motion. Every point on the rotating object does not have the same linear motion. ...
... same angular motion. Every point on the rotating object does not have the same linear motion. ...
electric current
... 1. A galvanometer uses the magnetic force from a current through a loop of wire in a circuit to measure? 2. A commutator is a device that reverses the current through a(n) 3. What is a coil of wire with a current called? ...
... 1. A galvanometer uses the magnetic force from a current through a loop of wire in a circuit to measure? 2. A commutator is a device that reverses the current through a(n) 3. What is a coil of wire with a current called? ...
B - college physics
... Click to see each of the following: Effective current of electrons Magnetic force on electron Charge separation in rod Orientation of electric field Electric force on electrons ...
... Click to see each of the following: Effective current of electrons Magnetic force on electron Charge separation in rod Orientation of electric field Electric force on electrons ...
WRL0001.tmp - MOCKSTER.NET!
... 2)If you increase the time two colliding object are in contact, the force on the objects… a)increase b)decrease c)remains the same 3) Another way of saying "change of momentum over time"… a)force b)acceleration c)impulse d)speed e)none of these 4) In a frictionless setting, a resting mass "2m" is hi ...
... 2)If you increase the time two colliding object are in contact, the force on the objects… a)increase b)decrease c)remains the same 3) Another way of saying "change of momentum over time"… a)force b)acceleration c)impulse d)speed e)none of these 4) In a frictionless setting, a resting mass "2m" is hi ...
Torque - Chain & Drives
... • Self-locking worm gear ratios (40:1 & higher) are susceptible to a phenomenon called “stairstepping” when backdriving or overhauling. If the worm speed is less than the lockup speed of the gearset and the inertia of the worm is not comparable to the inertia of the overhauling load an erratic rotat ...
... • Self-locking worm gear ratios (40:1 & higher) are susceptible to a phenomenon called “stairstepping” when backdriving or overhauling. If the worm speed is less than the lockup speed of the gearset and the inertia of the worm is not comparable to the inertia of the overhauling load an erratic rotat ...
Emagnetism - WordPress.com
... charges at rest (Static Electricity) Magnetostatics: charges in steady motion Electromagnetic waves: waves excited by charges in time-varying motion. ...
... charges at rest (Static Electricity) Magnetostatics: charges in steady motion Electromagnetic waves: waves excited by charges in time-varying motion. ...
Induction AP/IB
... to produce electricity • When we change the direction of the magnetic field we also change the direction of the current • So it is either positive (decreasing magnetic field) or negative (increasing magnetic field) ...
... to produce electricity • When we change the direction of the magnetic field we also change the direction of the current • So it is either positive (decreasing magnetic field) or negative (increasing magnetic field) ...
TAP410-0: Preparation for electromagnetic topic
... latter will need a mains supply that can produce a current of a few amperes and/or a signal generator. Some form of electron beam tube (‘Teltron tube’) is helpful in Episode 413 but an old black and white TV or oscilloscope plus a magnet can show the deflection of charged particles. One or more sets ...
... latter will need a mains supply that can produce a current of a few amperes and/or a signal generator. Some form of electron beam tube (‘Teltron tube’) is helpful in Episode 413 but an old black and white TV or oscilloscope plus a magnet can show the deflection of charged particles. One or more sets ...
Electromagnetic induction
... • What must happen to a conductor (or to the magnetic field in which it’s placed) for electricity to be generated? • What factors would cause the induced emf to be greater? • What is Lenz’s law and what are the applications of this law? ...
... • What must happen to a conductor (or to the magnetic field in which it’s placed) for electricity to be generated? • What factors would cause the induced emf to be greater? • What is Lenz’s law and what are the applications of this law? ...