23sun4s
... surface Nuclear fusion and magnetic fields play key roles in the energetics and structure of the Sun ...
... surface Nuclear fusion and magnetic fields play key roles in the energetics and structure of the Sun ...
Laura Worden ELED 3221 October 24, 2013 INDIRECT
... _____________________________________________________________________________ Big Idea: Magnets have an invisible force called a magnetic field. The magnetic field force comes from the poles of the magnet, which allows it to attract some metals, but not all of them. This force also gives magnets the ...
... _____________________________________________________________________________ Big Idea: Magnets have an invisible force called a magnetic field. The magnetic field force comes from the poles of the magnet, which allows it to attract some metals, but not all of them. This force also gives magnets the ...
selescu 347
... MHD is the extension of fluid dynamics to ionized gases, including the effects of electric and magnetic fields. So, the general method presented in the part one can be extended to some special (but usual) cases in magneto-plasma dynamics, considering an adiabatic but non-isentropic flow (taking into ...
... MHD is the extension of fluid dynamics to ionized gases, including the effects of electric and magnetic fields. So, the general method presented in the part one can be extended to some special (but usual) cases in magneto-plasma dynamics, considering an adiabatic but non-isentropic flow (taking into ...
can electric charge exist in the absence of a charged particle?
... the strength of the magnetic field to the change in the electric field and the strength of the electric field to the change in the magnetic field. Taken together these interact two form a system which oscillates. Maxwell was able to show that the velocity of propagation of such an oscillation is rel ...
... the strength of the magnetic field to the change in the electric field and the strength of the electric field to the change in the magnetic field. Taken together these interact two form a system which oscillates. Maxwell was able to show that the velocity of propagation of such an oscillation is rel ...
The Transport of Cosmic Rays
... 1 TeV, as the effects of the heliosphere at 1 TeV are smaller (but still significant). • The gyro-radius of a 1 TeV proton in the interstellar magnetic field is ~ 74 AU, which is signifiantly smaller than the heliosphere. • The interstellar field is distorted in the flow around the heliosphere out t ...
... 1 TeV, as the effects of the heliosphere at 1 TeV are smaller (but still significant). • The gyro-radius of a 1 TeV proton in the interstellar magnetic field is ~ 74 AU, which is signifiantly smaller than the heliosphere. • The interstellar field is distorted in the flow around the heliosphere out t ...
Magnetic properties of materials- I
... • These dipoles might align when an external electric field is applied. • An electron circulating about the nucleus can be considered as a current loop of radius r and speed v. ...
... • These dipoles might align when an external electric field is applied. • An electron circulating about the nucleus can be considered as a current loop of radius r and speed v. ...
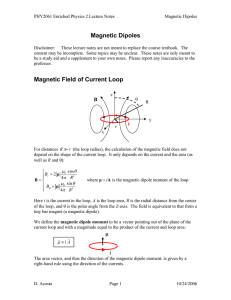
Examples of magnetic field calculations and applications 1 Example
... In the above we have written I as the current per unit width on the sheet. The direction of the magnetic field is given by the right-hand-rule. Note that the field is independent of the distance from the sheet. Thus the fields when superimposed from the two sheets, add between the sheets and cancel ...
... In the above we have written I as the current per unit width on the sheet. The direction of the magnetic field is given by the right-hand-rule. Note that the field is independent of the distance from the sheet. Thus the fields when superimposed from the two sheets, add between the sheets and cancel ...
Magnetism
... Magnetism • Magnetism is one of the most important fields in physics in terms of applications. • Magnetism is closely linked with electricity. – Magnetic fields affect moving charges. – Moving charges produce magnetic fields. – Changing magnetic fields can create electric fields. ...
... Magnetism • Magnetism is one of the most important fields in physics in terms of applications. • Magnetism is closely linked with electricity. – Magnetic fields affect moving charges. – Moving charges produce magnetic fields. – Changing magnetic fields can create electric fields. ...
Component Parts of a Dynamo
... divided on a horizontal diameter, the two halves being held by bolts B. Each pole P carries an exciting coil, and is fitted with an extension S called the pole shoe. In the figure the dotted lines indicate the paths of the magnetic fluxes, and it will be seen that the flux from each pole divides int ...
... divided on a horizontal diameter, the two halves being held by bolts B. Each pole P carries an exciting coil, and is fitted with an extension S called the pole shoe. In the figure the dotted lines indicate the paths of the magnetic fluxes, and it will be seen that the flux from each pole divides int ...
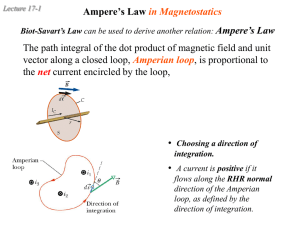
Biot-Savart Law
... In most substances, the magnetic moment of one electron is canceled by that of another electron orbiting in the opposite direction The net result is that the magnetic effect produced by the orbital motion of the electrons is either zero or very small ...
... In most substances, the magnetic moment of one electron is canceled by that of another electron orbiting in the opposite direction The net result is that the magnetic effect produced by the orbital motion of the electrons is either zero or very small ...
Electricity and Magnetism Study Guide - Mr. L`s Room
... Magnets always have 2 poles. Magnetic effect is always strongest at the poles— North and South. Like poles repel. Opposite poles attract. This interaction is called magnetic force. Any material that exerts a magnetic force is considered a magnet. The spacing of magnetic field lines indicates the str ...
... Magnets always have 2 poles. Magnetic effect is always strongest at the poles— North and South. Like poles repel. Opposite poles attract. This interaction is called magnetic force. Any material that exerts a magnetic force is considered a magnet. The spacing of magnetic field lines indicates the str ...
1 PHYS:1200 LECTURE 27 — ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM (5
... wrapped around it and a battery to drive current in the wires. When current is applied to the coil surrounding the nail, the nail becomes magnetized and a stronger magnetic field is produced than the field of the coil alone. The magnetization of the nail is not permanent and will diminish quickl ...
... wrapped around it and a battery to drive current in the wires. When current is applied to the coil surrounding the nail, the nail becomes magnetized and a stronger magnetic field is produced than the field of the coil alone. The magnetization of the nail is not permanent and will diminish quickl ...
Induced EMF - Purdue Physics
... Induced EMF has a direction such that it opposes the change in magnetic flux that produced it. ...
... Induced EMF has a direction such that it opposes the change in magnetic flux that produced it. ...
What is a Magnet?
... sense that once they have been magnetized, they retain a certain degree of magnetism. Permanent magnets are generally made of ferromagnetic material. Such material consists of atoms and molecules that each have a magnetic field and are positioned to reinforce each other. They do not lose their prope ...
... sense that once they have been magnetized, they retain a certain degree of magnetism. Permanent magnets are generally made of ferromagnetic material. Such material consists of atoms and molecules that each have a magnetic field and are positioned to reinforce each other. They do not lose their prope ...
IGCSE-61-Magnetism & Electromagnetism Presentation
... State what happens when different types of magnetic poles are placed near to each other. (see page 180) (a) What is the difference between magnetically soft and hard materials? (b) Give examples and uses of each type. (see page 180) (a) Draw the magnetic field patterns between and around magnets sho ...
... State what happens when different types of magnetic poles are placed near to each other. (see page 180) (a) What is the difference between magnetically soft and hard materials? (b) Give examples and uses of each type. (see page 180) (a) Draw the magnetic field patterns between and around magnets sho ...
Ferrofluid

A ferrofluid (portmanteau of ferromagnetic and fluid) is a liquid that becomes strongly magnetized in the presence of a magnetic field.Ferrofluid was invented in 1963 by NASA's Steve Papell as a liquid rocket fuel that could be drawn toward a pump inlet in a weightless environment by applying a magnetic field.Ferrofluids are colloidal liquids made of nanoscale ferromagnetic, or ferrimagnetic, particles suspended in a carrier fluid (usually an organic solvent or water). Each tiny particle is thoroughly coated with a surfactant to inhibit clumping. Large ferromagnetic particles can be ripped out of the homogeneous colloidal mixture, forming a separate clump of magnetic dust when exposed to strong magnetic fields. The magnetic attraction of nanoparticles is weak enough that the surfactant's Van der Waals force is sufficient to prevent magnetic clumping or agglomeration. Ferrofluids usually do not retain magnetization in the absence of an externally applied field and thus are often classified as ""superparamagnets"" rather than ferromagnets.The difference between ferrofluids and magnetorheological fluids (MR fluids) is the size of the particles. The particles in a ferrofluid primarily consist of nanoparticles which are suspended by Brownian motion and generally will not settle under normal conditions. MR fluid particles primarily consist of micrometre-scale particles which are too heavy for Brownian motion to keep them suspended, and thus will settle over time because of the inherent density difference between the particle and its carrier fluid. These two fluids have very different applications as a result.