The strongest magnetic fields in the universe: how strong
... do most probably not reach any of the above quantum electrodynamic limits. Presumably one does not need to call for additional chromodynamic limitations. This assertion may be based on the role electrons play in current generation, which is at the base of any large scale magnetic field production. E ...
... do most probably not reach any of the above quantum electrodynamic limits. Presumably one does not need to call for additional chromodynamic limitations. This assertion may be based on the role electrons play in current generation, which is at the base of any large scale magnetic field production. E ...
Module 6 - Magnetic Resonance Imaging
... So, to recap, the number of spins in the lower energy level is slightly greater than the number in the higher energy level at room temperature. The entire nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) signal is generated by this tiny energy difference between the spins in the lower energy state and the spins in ...
... So, to recap, the number of spins in the lower energy level is slightly greater than the number in the higher energy level at room temperature. The entire nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) signal is generated by this tiny energy difference between the spins in the lower energy state and the spins in ...
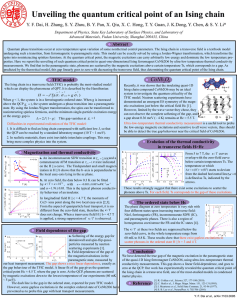
Unveiling the quantum critical point of an Ising chain
... undergoing such a transition, from ferromagnetic to paramagnetic state. This model can be exactly solved by using a Jordan-Wigner transformation, which transforms the spins into noninteracting spinless fermions. At the quantum critical point, the magnetic excitations can carry arbitrarily low energy ...
... undergoing such a transition, from ferromagnetic to paramagnetic state. This model can be exactly solved by using a Jordan-Wigner transformation, which transforms the spins into noninteracting spinless fermions. At the quantum critical point, the magnetic excitations can carry arbitrarily low energy ...
23sun3s
... Nuclear fusion and magnetic fields play key roles in the energetics and structure of the Sun ...
... Nuclear fusion and magnetic fields play key roles in the energetics and structure of the Sun ...
Booklet #6 - Science 9 Homework Page
... Some motors run on direct current (DC). It is 'direct', because the electricity flows in only one direction. Alternating current (AC) flows back and forth 60 times per second. ...
... Some motors run on direct current (DC). It is 'direct', because the electricity flows in only one direction. Alternating current (AC) flows back and forth 60 times per second. ...
XI. MICROWAVE COMPONENTS R. Fontana J.
... modes have been observed experimentally to be excited with any of the couplings designed to date (1). In order to improve this system, it is desired to excite mainly the perturbed TEM mode. Therefore, an investigation was started to determine the field distribution of each of these two modes (2). ...
... modes have been observed experimentally to be excited with any of the couplings designed to date (1). In order to improve this system, it is desired to excite mainly the perturbed TEM mode. Therefore, an investigation was started to determine the field distribution of each of these two modes (2). ...
PowerPoint slides - Physics 420 UBC Physics Demonstrations
... ELECTRIC MOTORS & GENERATORS Andrew Holliday ...
... ELECTRIC MOTORS & GENERATORS Andrew Holliday ...
Biot-Savart Law
... The Biot-Savart Law is used to calculate the magnetic field at a given position. ...
... The Biot-Savart Law is used to calculate the magnetic field at a given position. ...
Magnetism - HSphysics
... N-pole shown as an arrowhead. It can be used to find the direction of a magnetic field. Remember the N-pole of the compass points to the Earth’s N-pole. The Earth’s magnetic field is produced by electric currents at its core. It is similar to the field that would be due to an imaginary large bar mag ...
... N-pole shown as an arrowhead. It can be used to find the direction of a magnetic field. Remember the N-pole of the compass points to the Earth’s N-pole. The Earth’s magnetic field is produced by electric currents at its core. It is similar to the field that would be due to an imaginary large bar mag ...
Producing Electric Current
... When the coil is fixed and the magnet rotates, the current is the same as if the coil rotates and the magnet is fixed. Construction of a generator in a power plant Electromagnets contain coils of wire wrapped around ...
... When the coil is fixed and the magnet rotates, the current is the same as if the coil rotates and the magnet is fixed. Construction of a generator in a power plant Electromagnets contain coils of wire wrapped around ...
a plane-symmetric magnetized inhomogeneous cosmological model
... permeability in order to account for variations in magnetic flux density in the steady state, and if we look at the solenoidal magnetic field pattern around a bar magnet, this is not very difficult to visualize. The magnetic field lines are clearly more concentrated at the poles of the magnet than e ...
... permeability in order to account for variations in magnetic flux density in the steady state, and if we look at the solenoidal magnetic field pattern around a bar magnet, this is not very difficult to visualize. The magnetic field lines are clearly more concentrated at the poles of the magnet than e ...
Electron Spin Resonance
... the theory section on Larmor precession). Since the precession frequency is proportional to the applied field, one may want to change the voltage from the power supply to observe this effect. Spin resonance From quantum theory, a photon of frequency (i.e., energy) matching the energy difference of a ...
... the theory section on Larmor precession). Since the precession frequency is proportional to the applied field, one may want to change the voltage from the power supply to observe this effect. Spin resonance From quantum theory, a photon of frequency (i.e., energy) matching the energy difference of a ...
Ferrofluid

A ferrofluid (portmanteau of ferromagnetic and fluid) is a liquid that becomes strongly magnetized in the presence of a magnetic field.Ferrofluid was invented in 1963 by NASA's Steve Papell as a liquid rocket fuel that could be drawn toward a pump inlet in a weightless environment by applying a magnetic field.Ferrofluids are colloidal liquids made of nanoscale ferromagnetic, or ferrimagnetic, particles suspended in a carrier fluid (usually an organic solvent or water). Each tiny particle is thoroughly coated with a surfactant to inhibit clumping. Large ferromagnetic particles can be ripped out of the homogeneous colloidal mixture, forming a separate clump of magnetic dust when exposed to strong magnetic fields. The magnetic attraction of nanoparticles is weak enough that the surfactant's Van der Waals force is sufficient to prevent magnetic clumping or agglomeration. Ferrofluids usually do not retain magnetization in the absence of an externally applied field and thus are often classified as ""superparamagnets"" rather than ferromagnets.The difference between ferrofluids and magnetorheological fluids (MR fluids) is the size of the particles. The particles in a ferrofluid primarily consist of nanoparticles which are suspended by Brownian motion and generally will not settle under normal conditions. MR fluid particles primarily consist of micrometre-scale particles which are too heavy for Brownian motion to keep them suspended, and thus will settle over time because of the inherent density difference between the particle and its carrier fluid. These two fluids have very different applications as a result.