24-1 Magnets: permanent & temporary
... Touch a magnet to a piece of metal (iron nail) and try to pick up paper clips along the nail Nail has become polarized (temporarily) Either end of a magnet will attach to a metal ...
... Touch a magnet to a piece of metal (iron nail) and try to pick up paper clips along the nail Nail has become polarized (temporarily) Either end of a magnet will attach to a metal ...
Chapter 4 Review
... ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ...
... ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ...
Chapter 6 Lesson 3
... voice coil sits in a permanent magnetic field. • Current changes in the coil and alters it’s magnetic field. This causes the forces to the permanent magnet to move it back and forth. • The coil’s vibrations make the cone move back and forth, creating sound waves in the air. ...
... voice coil sits in a permanent magnetic field. • Current changes in the coil and alters it’s magnetic field. This causes the forces to the permanent magnet to move it back and forth. • The coil’s vibrations make the cone move back and forth, creating sound waves in the air. ...
File - Lanier Bureau of Investigation
... Electrical conduction – a method of charging an object when electrons move from one object to another by touch Electrical induction – a method of charging an object that occurs when charges in an uncharged object are rearranged without direct contact from a charged object. ...
... Electrical conduction – a method of charging an object when electrons move from one object to another by touch Electrical induction – a method of charging an object that occurs when charges in an uncharged object are rearranged without direct contact from a charged object. ...
Study Guide - Chapter 29
... 5. Torque on a Current Loop in a Uniform Magnetic Field Though the net force on a loop of wire in a uniform magnetic field is always zero, a magnetic field can exert torque on a loop of wire. This is given by the equation: t t‚B 7t œ . t is called the magnetic moment. It is defined as follows.: The ...
... 5. Torque on a Current Loop in a Uniform Magnetic Field Though the net force on a loop of wire in a uniform magnetic field is always zero, a magnetic field can exert torque on a loop of wire. This is given by the equation: t t‚B 7t œ . t is called the magnetic moment. It is defined as follows.: The ...
Compass Basics - NSW Public Schools
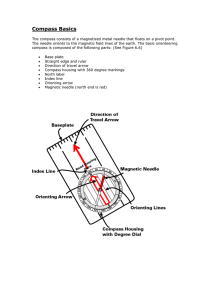
... Compass Basics The compass consists of a magnetized metal needle that floats on a pivot point. The needle orients to the magnetic field lines of the earth. The basic orienteering compass is composed of the following parts: (See Figure 6.6) ...
... Compass Basics The compass consists of a magnetized metal needle that floats on a pivot point. The needle orients to the magnetic field lines of the earth. The basic orienteering compass is composed of the following parts: (See Figure 6.6) ...
Confinement of spherical plasma by means of fields generated by
... field. In stars there is a process of self-generation of such field which provides a minimum of magnetic induction in the central region – in the core of the star due to the magnetic dynamo. Generating of self magnetic field also takes place in ball lightning [1]. Therefore, a particular interest pr ...
... field. In stars there is a process of self-generation of such field which provides a minimum of magnetic induction in the central region – in the core of the star due to the magnetic dynamo. Generating of self magnetic field also takes place in ball lightning [1]. Therefore, a particular interest pr ...
Magnetic Fields and Forces
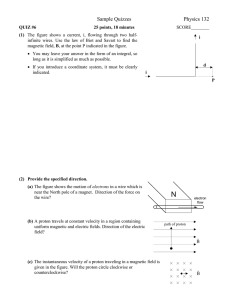
... Particle 1, with a charge q1 = 3.60 μC and a speed of v1 = 382 m/s, travels at right angles to a uniform magnetic field. The magnetic force it experiences is 4.25 x 10-3 N. Particle 2, with a charge of q2 = 5.30 μC and a speed of v2 = 1.30 x 103 m/s, moves at an angle of 55.0º relative to the same m ...
... Particle 1, with a charge q1 = 3.60 μC and a speed of v1 = 382 m/s, travels at right angles to a uniform magnetic field. The magnetic force it experiences is 4.25 x 10-3 N. Particle 2, with a charge of q2 = 5.30 μC and a speed of v2 = 1.30 x 103 m/s, moves at an angle of 55.0º relative to the same m ...
Chapter 15 Lesson 2 How are Electricity and Magnetism Related
... A free swinging magnet will point north with its north seeking pole-that end is marked with an N. Like electrical charges, opposite forces between magnetic poles attract, N-S, positive –negative Like poles repel: south repels south; north repels north Magnets keep their poles even when cut in two. A ...
... A free swinging magnet will point north with its north seeking pole-that end is marked with an N. Like electrical charges, opposite forces between magnetic poles attract, N-S, positive –negative Like poles repel: south repels south; north repels north Magnets keep their poles even when cut in two. A ...
Mag Fields Pres New
... uniform magnetic field of flux density 0.15 mT at 90 degrees. What is the radius of its circular path. ...
... uniform magnetic field of flux density 0.15 mT at 90 degrees. What is the radius of its circular path. ...
Class #28 Slides
... Another Example of Faraday’s Law & Lenz’s Rule: Eddy-Current Braking A magnetic field points into the page as shown. For example, this field could be created by an electromagnet or between the poles of permanent magnets. A metal pendulum swings into the magnetic field. What happens to the motion of ...
... Another Example of Faraday’s Law & Lenz’s Rule: Eddy-Current Braking A magnetic field points into the page as shown. For example, this field could be created by an electromagnet or between the poles of permanent magnets. A metal pendulum swings into the magnetic field. What happens to the motion of ...
Faraday`s Law of Electromagnetic Induction - UTK-EECS
... Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction 1. If the flux linking a loop (or turn) varies as a function of time, a voltage is induced between its terminals. 2. The value of the induced voltage is proportional to the rate of change of flux The “-” sign indicates that the inducted E has a tendency to ...
... Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction 1. If the flux linking a loop (or turn) varies as a function of time, a voltage is induced between its terminals. 2. The value of the induced voltage is proportional to the rate of change of flux The “-” sign indicates that the inducted E has a tendency to ...
Ferrofluid

A ferrofluid (portmanteau of ferromagnetic and fluid) is a liquid that becomes strongly magnetized in the presence of a magnetic field.Ferrofluid was invented in 1963 by NASA's Steve Papell as a liquid rocket fuel that could be drawn toward a pump inlet in a weightless environment by applying a magnetic field.Ferrofluids are colloidal liquids made of nanoscale ferromagnetic, or ferrimagnetic, particles suspended in a carrier fluid (usually an organic solvent or water). Each tiny particle is thoroughly coated with a surfactant to inhibit clumping. Large ferromagnetic particles can be ripped out of the homogeneous colloidal mixture, forming a separate clump of magnetic dust when exposed to strong magnetic fields. The magnetic attraction of nanoparticles is weak enough that the surfactant's Van der Waals force is sufficient to prevent magnetic clumping or agglomeration. Ferrofluids usually do not retain magnetization in the absence of an externally applied field and thus are often classified as ""superparamagnets"" rather than ferromagnets.The difference between ferrofluids and magnetorheological fluids (MR fluids) is the size of the particles. The particles in a ferrofluid primarily consist of nanoparticles which are suspended by Brownian motion and generally will not settle under normal conditions. MR fluid particles primarily consist of micrometre-scale particles which are too heavy for Brownian motion to keep them suspended, and thus will settle over time because of the inherent density difference between the particle and its carrier fluid. These two fluids have very different applications as a result.