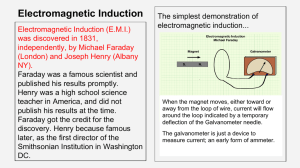
Task 1
... slightly different, at least in its macroscopic manifestation: it is the energy that is available for ____________ from chemical reactions (for example, by burning a fuel). The electrical potential energy of an electrically ____________ object is defined as the work that must be done to move it from ...
... slightly different, at least in its macroscopic manifestation: it is the energy that is available for ____________ from chemical reactions (for example, by burning a fuel). The electrical potential energy of an electrically ____________ object is defined as the work that must be done to move it from ...
Magnetic field around a current
... Conceptual Example 7 An Induction Stove Two pots of water are placed on an induction stove at the same time. The stove itself is cool to the touch. The water in the ferromagnetic metal pot is boiling while that in the glass pot is not. How can such a cool stove boil water, and why isn’t the water in ...
... Conceptual Example 7 An Induction Stove Two pots of water are placed on an induction stove at the same time. The stove itself is cool to the touch. The water in the ferromagnetic metal pot is boiling while that in the glass pot is not. How can such a cool stove boil water, and why isn’t the water in ...
the emf induced in a moving conductor
... the tracks. Because the only force on the rod is its weight, it falls with an acceleration equal to the acceleration of gravity. Connect a resistor connected between the tops of the tracks. (a) Does the rod now fall with the acceleration of gravity? (b) How does the principle of conservation of ener ...
... the tracks. Because the only force on the rod is its weight, it falls with an acceleration equal to the acceleration of gravity. Connect a resistor connected between the tops of the tracks. (a) Does the rod now fall with the acceleration of gravity? (b) How does the principle of conservation of ener ...
Lecture Notes Y F Chapter 29
... Direction of the Induced EMF’s and Currents In the previous problem, we found the direction of the induced current by noting that the force resulting from the induced current had to oppose the applied force. This observation can be generalized into: Lenz’s Law The direction of any magnetic induct ...
... Direction of the Induced EMF’s and Currents In the previous problem, we found the direction of the induced current by noting that the force resulting from the induced current had to oppose the applied force. This observation can be generalized into: Lenz’s Law The direction of any magnetic induct ...
Electromagnetic Induction Key Concept is Magnetic Flux
... Note that a changing B will induce an E and a changing E will induce a B. This B can in turn induce an E, which will induce a B, and so on… It can be shown that these equations predict the existence of a self-sustaining “wave” that propagates with a velocity of: ...
... Note that a changing B will induce an E and a changing E will induce a B. This B can in turn induce an E, which will induce a B, and so on… It can be shown that these equations predict the existence of a self-sustaining “wave” that propagates with a velocity of: ...
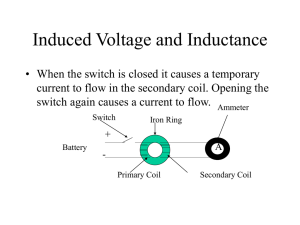
Induced Voltage and Inductance
... Motors and back emf • A motor is basically a generator in reverse. That is a current is supplied to a loop by an emf source and the magnetic torque on the loop causes it to rotate. • As the loop rotates changing magnetic flux induces an emf which reduces the current in the loop, (lenz’s law). Back ...
... Motors and back emf • A motor is basically a generator in reverse. That is a current is supplied to a loop by an emf source and the magnetic torque on the loop causes it to rotate. • As the loop rotates changing magnetic flux induces an emf which reduces the current in the loop, (lenz’s law). Back ...
Transformers and Generators - juan
... magnetic field, and a loop of wire which rotates in the magnetic field. As the wire rotates in the magnetic field, the changing strength of the magnetic field through the wire produces a force which drives the electric charges around the wire. AS the loop spins, the direction of the force changes, s ...
... magnetic field, and a loop of wire which rotates in the magnetic field. As the wire rotates in the magnetic field, the changing strength of the magnetic field through the wire produces a force which drives the electric charges around the wire. AS the loop spins, the direction of the force changes, s ...