Exam #: Printed Name: Signature: PHYSICS DEPARTMENT
... purposes, be sure to submit this page together with your answers when the exam is ...
... purposes, be sure to submit this page together with your answers when the exam is ...
Lecture19
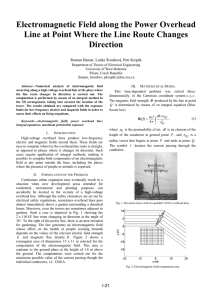
... the total flux passing through the winding: d φ (t ) v(t ) = − ('sign' is given by Lenz's law.) dt Ampere's Law (integral form) relates magnetomotive force, M (t), induced in magnetic core to the total current passing through interior of path: FMM (t ) = ...
... the total flux passing through the winding: d φ (t ) v(t ) = − ('sign' is given by Lenz's law.) dt Ampere's Law (integral form) relates magnetomotive force, M (t), induced in magnetic core to the total current passing through interior of path: FMM (t ) = ...
B - Purdue Physics
... the plane of this page as shown. The value of the Ampere’s Law line integral of B∙ dl counterclockwise around the circular path is -μo2I1 What is the magnitude of the currents in I2 and I3? ...
... the plane of this page as shown. The value of the Ampere’s Law line integral of B∙ dl counterclockwise around the circular path is -μo2I1 What is the magnitude of the currents in I2 and I3? ...
3-Continental_Drift
... animals live only on certain continents. Many fossil animals and plants exhibit a similarly restricted geographic range. ...
... animals live only on certain continents. Many fossil animals and plants exhibit a similarly restricted geographic range. ...
This starts from Easy derivation of Maxwell’s and Wave Equation.
... Summary of handling fields at interface of two materials. 1. Draw interface. 2. On each side draw components of each field so set obeys right hand rule, with amplitude of each B = n (matching) E. 3. Apply boundary conditions using angle propagation make with perpendicular to surface to specify tang ...
... Summary of handling fields at interface of two materials. 1. Draw interface. 2. On each side draw components of each field so set obeys right hand rule, with amplitude of each B = n (matching) E. 3. Apply boundary conditions using angle propagation make with perpendicular to surface to specify tang ...
Magnets - Science with Ms. C
... Know that magnetism is the force of attraction or repulsion of magnetic materials. Surrounding a magnet is a magnetic field that applies a force, a push or pull, without actually touching an object. Evidence of a magnetic field can be found in how the field af fects magnetic materials (includi ...
... Know that magnetism is the force of attraction or repulsion of magnetic materials. Surrounding a magnet is a magnetic field that applies a force, a push or pull, without actually touching an object. Evidence of a magnetic field can be found in how the field af fects magnetic materials (includi ...
21.5-6
... ex. a) Find the velocity of the wire 3 sec after a current of 3A starts flowing through it, assuming the wire starts from rest and there is no friction. b) If the coefficient of static friction between the wire and the rails is µ s=0.4, what is the minimum current to start the wire moving? ...
... ex. a) Find the velocity of the wire 3 sec after a current of 3A starts flowing through it, assuming the wire starts from rest and there is no friction. b) If the coefficient of static friction between the wire and the rails is µ s=0.4, what is the minimum current to start the wire moving? ...
lecture17
... directly out of the page, and all have the same amplitude E. (b) A second way of representing unpolarized light – the light is the superposition of two polarized waves whose planes of oscillation are perpendicular to each other. ...
... directly out of the page, and all have the same amplitude E. (b) A second way of representing unpolarized light – the light is the superposition of two polarized waves whose planes of oscillation are perpendicular to each other. ...
Physics 431: Electricity and Magnetism
... The course is designed for senior level physics majors; however other engineering and science majors with the correct preparation are very welcome. Nb: this is a course that is mandatory for all Physics Majors. Therefore, this is a course whose audience is composed by students who intend to pursue g ...
... The course is designed for senior level physics majors; however other engineering and science majors with the correct preparation are very welcome. Nb: this is a course that is mandatory for all Physics Majors. Therefore, this is a course whose audience is composed by students who intend to pursue g ...
Magnetochemistry

Magnetochemistry is concerned with the magnetic properties of chemical compounds. Magnetic properties arise from the spin and orbital angular momentum of the electrons contained in a compound. Compounds are diamagnetic when they contain no unpaired electrons. Molecular compounds that contain one or more unpaired electrons are paramagnetic. The magnitude of the paramagnetism is expressed as an effective magnetic moment, μeff. For first-row transition metals the magnitude of μeff is, to a first approximation, a simple function of the number of unpaired electrons, the spin-only formula. In general, spin-orbit coupling causes μeff to deviate from the spin-only formula. For the heavier transition metals, lanthanides and actinides, spin-orbit coupling cannot be ignored. Exchange interaction can occur in clusters and infinite lattices, resulting in ferromagnetism, antiferromagnetism or ferrimagnetism depending on the relative orientations of the individual spins.