Reciprocating Saw Dissection: Motor Description
... • Driven by electromagnetics • Like magnetic poles repel, opposite magnetic poles attract • Current passed through a coil of wire produces a magnetic field • Changing the direction of current in a coil reverses the magnetic field • The amount of current in a coil will determine the strength of the p ...
... • Driven by electromagnetics • Like magnetic poles repel, opposite magnetic poles attract • Current passed through a coil of wire produces a magnetic field • Changing the direction of current in a coil reverses the magnetic field • The amount of current in a coil will determine the strength of the p ...
Document
... have the same resistance. Given that brightness is proportional to power dissipated, the brightness of bulbs B and C together, compared with the brightness of bulb A, is 1. twice as much. 2. the same. 3. half as much. ...
... have the same resistance. Given that brightness is proportional to power dissipated, the brightness of bulbs B and C together, compared with the brightness of bulb A, is 1. twice as much. 2. the same. 3. half as much. ...
Teacher`s Notes - Electricity and Magnetism, Part 2 Electricity and
... magnet has a north and a south pole. No matter how small the magnet is, it will have both poles. Students may be familiar with the idea of a compass which uses magnetism to tell directions. This is because our Earth is really a very large magnet. The students can use a magnet with the iron filing di ...
... magnet has a north and a south pole. No matter how small the magnet is, it will have both poles. Students may be familiar with the idea of a compass which uses magnetism to tell directions. This is because our Earth is really a very large magnet. The students can use a magnet with the iron filing di ...
Neutron Stars - Chandra X
... we could crush the electron cloud down to the size of the nucleus? Suppose we could generate a force strong enough to crush all the emptiness out of a rock roughly the size of a football stadium. The rock would be squeezed down to the size of a grain of sand and would still weigh 4 million tons! Suc ...
... we could crush the electron cloud down to the size of the nucleus? Suppose we could generate a force strong enough to crush all the emptiness out of a rock roughly the size of a football stadium. The rock would be squeezed down to the size of a grain of sand and would still weigh 4 million tons! Suc ...
EECS 215: Introduction to Circuits
... • In today’s temperature sensor designs, an artificial cold junction is used instead. The artificial junction is an electric circuit that generates a voltage equal to that expected from a reference junction at temperature T1. ...
... • In today’s temperature sensor designs, an artificial cold junction is used instead. The artificial junction is an electric circuit that generates a voltage equal to that expected from a reference junction at temperature T1. ...
WBL6_Lecture_Ch19
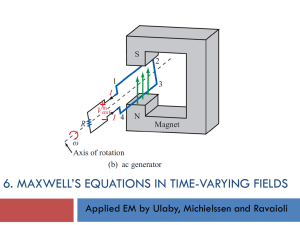
... A solenoid is a wire coiled into a long cylinder. The magnetic field inside is given by: ...
... A solenoid is a wire coiled into a long cylinder. The magnetic field inside is given by: ...
Magnetochemistry

Magnetochemistry is concerned with the magnetic properties of chemical compounds. Magnetic properties arise from the spin and orbital angular momentum of the electrons contained in a compound. Compounds are diamagnetic when they contain no unpaired electrons. Molecular compounds that contain one or more unpaired electrons are paramagnetic. The magnitude of the paramagnetism is expressed as an effective magnetic moment, μeff. For first-row transition metals the magnitude of μeff is, to a first approximation, a simple function of the number of unpaired electrons, the spin-only formula. In general, spin-orbit coupling causes μeff to deviate from the spin-only formula. For the heavier transition metals, lanthanides and actinides, spin-orbit coupling cannot be ignored. Exchange interaction can occur in clusters and infinite lattices, resulting in ferromagnetism, antiferromagnetism or ferrimagnetism depending on the relative orientations of the individual spins.