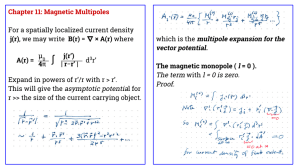
Ferromagnetic Materials : Curie
... The magnetisation of a material, M, is defined as the magnetic moment per unit volume or per unit mass of a material and is dependent on the individual magnetic dipole moments of the atoms in the material and on the interactions of these dipoles with each other. ...
... The magnetisation of a material, M, is defined as the magnetic moment per unit volume or per unit mass of a material and is dependent on the individual magnetic dipole moments of the atoms in the material and on the interactions of these dipoles with each other. ...
Lecture 19: Magnetic properties and the Nephelauxetic effect
... increases with increasing atomic weight, so that for heavier d-block elements, and for f-block elements, the orbital contribution is considerable. For 2nd and 3rd row dblock elements, λ is an order of magnitude larger than for the first-row analogues. Most 2nd and 3rd row d-block elements are low-sp ...
... increases with increasing atomic weight, so that for heavier d-block elements, and for f-block elements, the orbital contribution is considerable. For 2nd and 3rd row dblock elements, λ is an order of magnitude larger than for the first-row analogues. Most 2nd and 3rd row d-block elements are low-sp ...
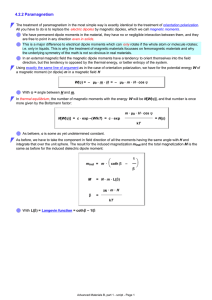
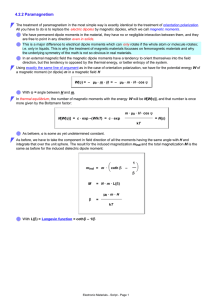
4.2.2 Paramagnetism
... The treatment of paramagnetism in the most simple way is exactly identical to the treatment of orientation polarization. All you have to do is to replace the electric dipoles by magnetic dipoles, which we call magnetic moments. We have permanent dipole moments in the material, they have no or neglig ...
... The treatment of paramagnetism in the most simple way is exactly identical to the treatment of orientation polarization. All you have to do is to replace the electric dipoles by magnetic dipoles, which we call magnetic moments. We have permanent dipole moments in the material, they have no or neglig ...
∫ θ
... An electron orbits a nucleus in a circle with a radius of 0.1 nm at an angular frequency of 1015 rad s-1. It is in a B field of strength 1 Tesla. (a) Evaluate the change in potential energy of the atom when the magnetic moment of the electron changes from being exactly parallel to the B field to bei ...
... An electron orbits a nucleus in a circle with a radius of 0.1 nm at an angular frequency of 1015 rad s-1. It is in a B field of strength 1 Tesla. (a) Evaluate the change in potential energy of the atom when the magnetic moment of the electron changes from being exactly parallel to the B field to bei ...
Worksheet_18 - Iowa State University
... 1. An electron is traveling to the right with a speed of 8.5 x 106 m/s when a magnetic field is turned on. The strength of the magnetic field is 0.050 T, and it is directed into the paper. (a) Describe the path of the electron after the field has been turned on (assuming only magnetic effects). (b) ...
... 1. An electron is traveling to the right with a speed of 8.5 x 106 m/s when a magnetic field is turned on. The strength of the magnetic field is 0.050 T, and it is directed into the paper. (a) Describe the path of the electron after the field has been turned on (assuming only magnetic effects). (b) ...
Magnetochemistry

Magnetochemistry is concerned with the magnetic properties of chemical compounds. Magnetic properties arise from the spin and orbital angular momentum of the electrons contained in a compound. Compounds are diamagnetic when they contain no unpaired electrons. Molecular compounds that contain one or more unpaired electrons are paramagnetic. The magnitude of the paramagnetism is expressed as an effective magnetic moment, μeff. For first-row transition metals the magnitude of μeff is, to a first approximation, a simple function of the number of unpaired electrons, the spin-only formula. In general, spin-orbit coupling causes μeff to deviate from the spin-only formula. For the heavier transition metals, lanthanides and actinides, spin-orbit coupling cannot be ignored. Exchange interaction can occur in clusters and infinite lattices, resulting in ferromagnetism, antiferromagnetism or ferrimagnetism depending on the relative orientations of the individual spins.