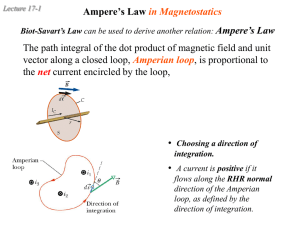
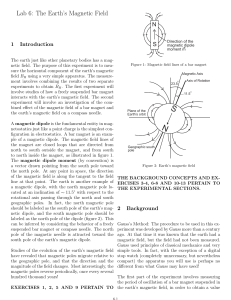
PY2T10 Electricity and Magnetism Dr. Charles Patterson
... • Magnetic fields at the earth’ surface 3 to 6 x 10-5 T (0.3 to 0.6 Gauss, G) 1 G = 10-4 T • Magnetic fields in laboratory routinely ~ 1T • MRI scanner in Lloyd building is 3T ...
... • Magnetic fields at the earth’ surface 3 to 6 x 10-5 T (0.3 to 0.6 Gauss, G) 1 G = 10-4 T • Magnetic fields in laboratory routinely ~ 1T • MRI scanner in Lloyd building is 3T ...
Magnetic forces on moving charges – More than just a
... are sent by the electronic circuits in the TV set. These currents produce a changing magnetic field which directs the electrons onto different parts of the screen. A more spectacular display of these forces is actually crucial to life on Earth. High energy charged particles from the Sun would bombar ...
... are sent by the electronic circuits in the TV set. These currents produce a changing magnetic field which directs the electrons onto different parts of the screen. A more spectacular display of these forces is actually crucial to life on Earth. High energy charged particles from the Sun would bombar ...
Chapter 29 Faraday’s Law
... Michael Faraday formulated his law of induction. • It had been known for some time that a current could be produced in a wire by a changing magnetic field. • Faraday showed that the induced electromotive force is directly related to the rate at which the magnetic field lines cut across the path. ...
... Michael Faraday formulated his law of induction. • It had been known for some time that a current could be produced in a wire by a changing magnetic field. • Faraday showed that the induced electromotive force is directly related to the rate at which the magnetic field lines cut across the path. ...
ppt - Physics
... Michael Faraday formulated his law of induction. • It had been known for some time that a current could be produced in a wire by a changing magnetic field. • Faraday showed that the induced electromotive force is directly related to the rate at which the magnetic field lines cut across the path. ...
... Michael Faraday formulated his law of induction. • It had been known for some time that a current could be produced in a wire by a changing magnetic field. • Faraday showed that the induced electromotive force is directly related to the rate at which the magnetic field lines cut across the path. ...
modelling of magnetic fields generated by cone
... with/without magnetic yokes. The coils are mounted over the welding electrode with vertically oriented axes of symmetry. This model has been solved by FEM [5] for a 2-D field satisfying the Poison equation of the magnetic potential with Dirichlet boundary conditions at the barrier zone around the ma ...
... with/without magnetic yokes. The coils are mounted over the welding electrode with vertically oriented axes of symmetry. This model has been solved by FEM [5] for a 2-D field satisfying the Poison equation of the magnetic potential with Dirichlet boundary conditions at the barrier zone around the ma ...
PHYS219 Fall semester 2014 - Purdue Physics
... The Lorentz Force • The Lorentz Force - the force on a charged particle moving in a magnetic field ...
... The Lorentz Force • The Lorentz Force - the force on a charged particle moving in a magnetic field ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... earth: the so-called cosmic rays. They can cause much damage to terrestrial life if they fall right to the ground and impinge on us. This does not happen because the earth, being a gigantic magnet, serves as a protective field by deflecting the charged cosmic-ray bullets towards the polar regions. T ...
... earth: the so-called cosmic rays. They can cause much damage to terrestrial life if they fall right to the ground and impinge on us. This does not happen because the earth, being a gigantic magnet, serves as a protective field by deflecting the charged cosmic-ray bullets towards the polar regions. T ...
Chapter 29 Magnetic Fields Due to Currents
... newton per meter of wire length. Rail Gun In this device, a magnetic force accelerates a projectile to a high speed in a short time. the currents in the rails produce magnetic fields that are directed downward between the rails. The net magnetic field exerts a force on the gas due to the current thr ...
... newton per meter of wire length. Rail Gun In this device, a magnetic force accelerates a projectile to a high speed in a short time. the currents in the rails produce magnetic fields that are directed downward between the rails. The net magnetic field exerts a force on the gas due to the current thr ...
The Earth`s B-Field
... convecting, and electrically conducting fluid acts to maintain a magnetic field. In the case of the Earth, the magnetic field is induced and constantly maintained by the convection of liquid iron in the outer core. A requirement for the induction of field is a rotating fluid Magnetic fields extend i ...
... convecting, and electrically conducting fluid acts to maintain a magnetic field. In the case of the Earth, the magnetic field is induced and constantly maintained by the convection of liquid iron in the outer core. A requirement for the induction of field is a rotating fluid Magnetic fields extend i ...
Magnetism
Magnetism is a class of physical phenomena that are mediated by magnetic fields. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Every material is influenced to some extent by a magnetic field. The most familiar effect is on permanent magnets, which have persistent magnetic moments caused by ferromagnetism. Most materials do not have permanent moments. Some are attracted to a magnetic field (paramagnetism); others are repulsed by a magnetic field (diamagnetism); others have a more complex relationship with an applied magnetic field (spin glass behavior and antiferromagnetism). Substances that are negligibly affected by magnetic fields are known as non-magnetic substances. These include copper, aluminium, gases, and plastic. Pure oxygen exhibits magnetic properties when cooled to a liquid state.The magnetic state (or magnetic phase) of a material depends on temperature and other variables such as pressure and the applied magnetic field. A material may exhibit more than one form of magnetism as these variables change.